Your Secondary growth in plants images are available in this site. Secondary growth in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Secondary growth in plants files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for secondary growth in plants images information linked to the secondary growth in plants interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Secondary Growth In Plants. The herbaceous plants do not undergo secondary growth. Plants) refers to elongation of its shoot & root. A meristem is a site of growth for a plant. During every growing season the stem of a plant increases in width.
 Secondary Growth in Woody Plants From www231.pair.com
Secondary Growth in Woody Plants From www231.pair.com
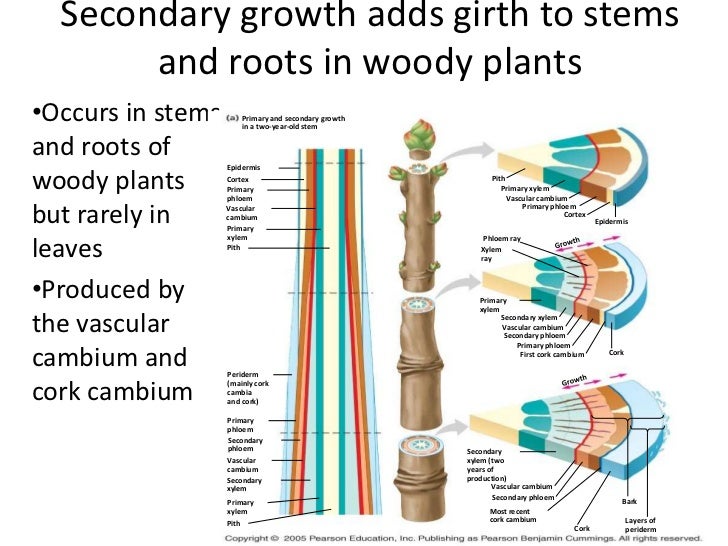
While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots, the details are somewhat different. Plants’ secondary growth is controlled by the lateral meristem tissues. The increase in thickness or girth due to the activity of cambium and cork cambium is known secondary growth. The secondary growth in a monocotyledonous stem or root is only the result of the enlargement of the primary cells, that is, the cells that have already been formed. Evolution of secondary growth in land plants. Sakshi sharma (m.sc i) botany pau, ludhiana 2.
The increase in stem thickness that results from secondary growth is due to the activity of the lateral meristems, which are lacking in herbaceous plants.
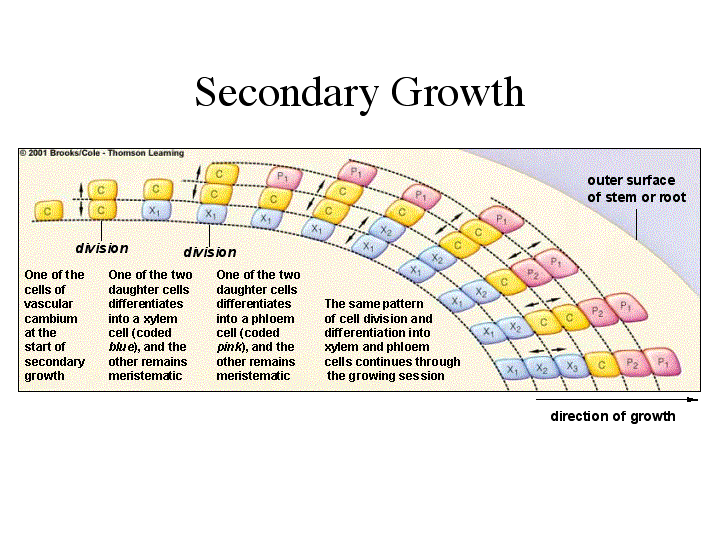
The cells of medullary rays adjoining these intrafascicular. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem. Secondary growth plants • the secondary growth of root and stem in length with the help of apical meristem is called the primary growth. While all plant experiences primary growth, not all experience secondary growth. Secondary growth is the outward growth of the plant, making it thicker and wider. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth, namely, vascular cambium and.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Today, secondary growth occurs only in seeds plants. Secondary growth plants • the secondary growth of root and stem in length with the help of apical meristem is called the primary growth. Secondary growth follows the primary growth. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. Evolution of secondary growth in land plants.

Cell division, cell elongation &. We need to understand that secondary growth occurs in both stems as well as roots. In woody plants, secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the plant. The activity of the lateral meristems, which are lacking in herbs and herbaceous plants, causes secondary growth of plants to increase stem thickness. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth, namely, vascular cambium and.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Dicotyledonous plants and gymnosperms exhibit increase in girth of root and stem. Today, secondary growth occurs only in seeds plants. The increase of the thickness of the shoot and the root of the plant is referred to as the secondary growth. While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots, the details are somewhat different. Plants) refers to elongation of its shoot & root.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
A meristem is a site of growth for a plant. Whereas the growth of root and stem in grith with the help of lateral meristem is called the secondary growth • all plant undergo primary growth but apart primary growth most of the dicotyledonous plant exhibit secondary growth. In woody plants, secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the plant. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth, namely, vascular cambium and. The increase in thickness or girth due to the activity of cambium and cork cambium is known secondary growth.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
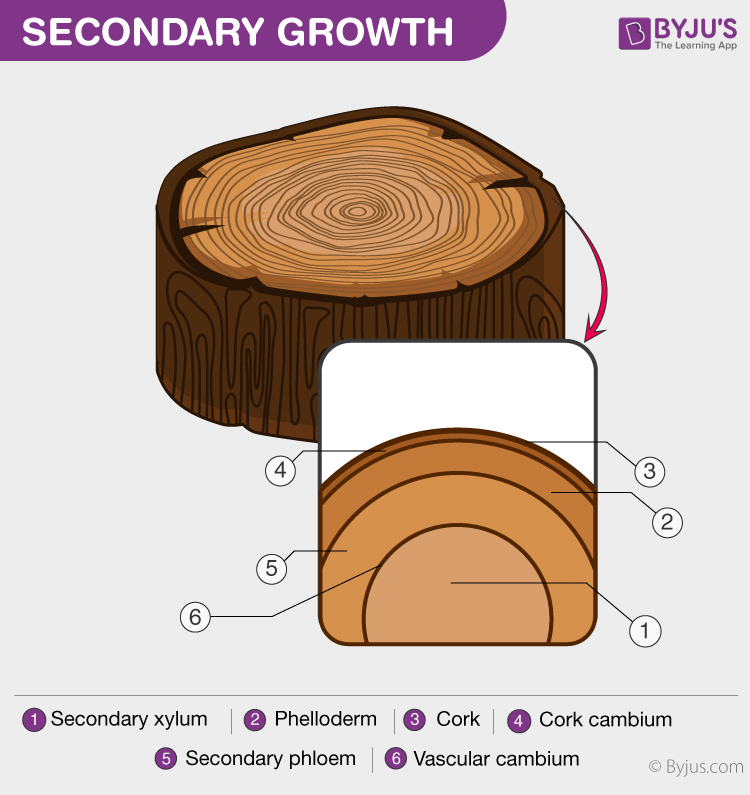
Cells on the inner side of the cork cambium differentiates to form the secondary cortex. Secondary growth in plants 1. It occurs in some dicots, but occurs very rarely in monocots. Secondary growth plants • the secondary growth of root and stem in length with the help of apical meristem is called the primary growth. Secondary growth or “wood” is noticeable in woody plants;
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Secondary growth is seen clearly if you examine the stump of a tree. Secondary growth plants • the secondary growth of root and stem in length with the help of apical meristem is called the primary growth. Secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems i.e., vascular and cork cambium and that causes the stems and roots to thicken i.e., increase in girth. In dicot stem, secondary growth begins with the formation of a continuous cambium ring. The stem, root & trunk of plants.
 Source: mybabysprouts.blogspot.com
Source: mybabysprouts.blogspot.com
Secondary growth is the outward growth of the plant, making it thicker and wider. The lateral meristem is composed of the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. It occurs in some dicots, but occurs very rarely in monocots. The herbaceous plants do not undergo secondary growth. The increase in thickness or girth due to the activity of cambium and cork cambium is known secondary growth.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Cell division, cell elongation &. This is known as secondary thickening. It occurs in some dicots, but occurs very rarely in monocots. Secondary growth helps the plant gain stamina and support for the height. It is a usual feature of dicotyledonous and gymnospermous roots, where it generally starts at a very early stage, so much so that it is difficult to get the roots without secondary growth in.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The secondary growth in root also takes place by the activity of the cambium and cork cambium. Evolution of secondary growth in land plants. In woody plants, primary growth is followed by secondary growth, which allows the plant stem to increase in thickness or girth. Secondary growth helps the plant gain stamina and support for the height. Secondary growth follows the primary growth.
 Source: cgbioazman.blogspot.com
Source: cgbioazman.blogspot.com
While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots, the details are somewhat different. The vascular cambium and cork are the two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth. The increase in thickness or girth due to the activity of cambium and cork cambium is known secondary growth. In woody plants, primary growth is followed by secondary growth, which allows the plant stem to increase in thickness or girth. In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem.
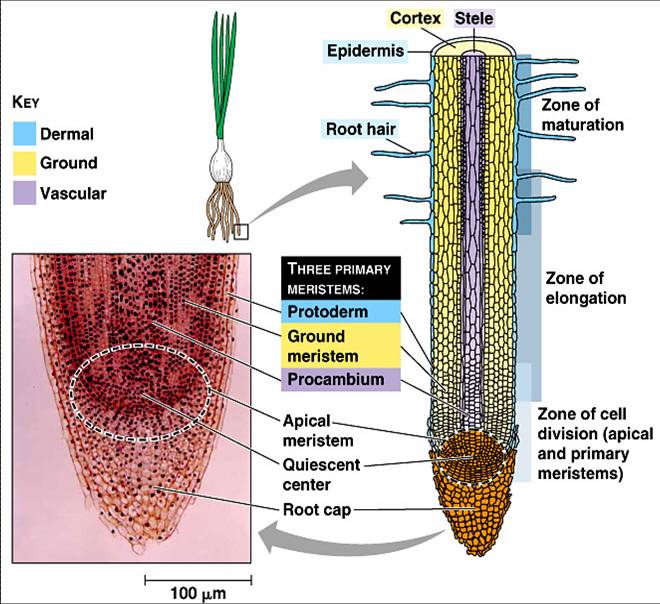 Source: technologysifi.blogspot.com
Source: technologysifi.blogspot.com
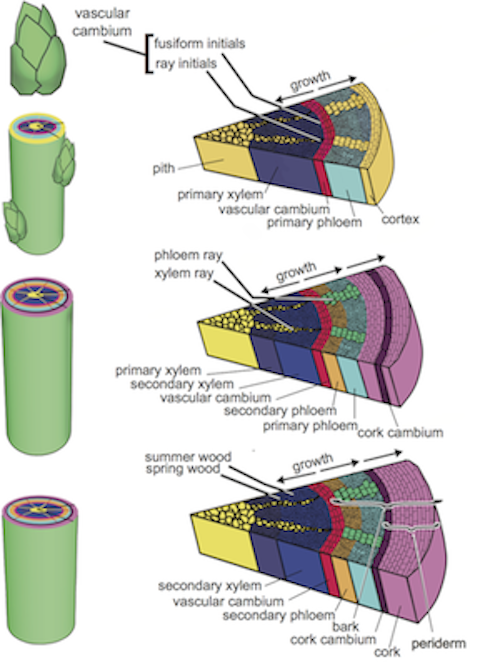
Growth in plants that results from the activity of a cambium producing increase especially in diameter, is mainly responsible for the bulk of the plant body, and supplies protective, supporting, and conducting tissue — compare primary growth. It produces cork cells (bark) containing a waxy substance known as suberin that can repel water. Whereas the growth of root and stem in grith with the help of lateral meristem is called the secondary growth • all plant undergo primary growth but apart primary growth most of the dicotyledonous plant exhibit secondary growth. Secondary growth, or wood, is noticeable in woody plants; In woody plants, cork cambium is the outermost lateral meristem.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Plants’ secondary growth is controlled by the lateral meristem tissues. The increase of the thickness of the shoot and the root of the plant is referred to as the secondary growth. The cells of medullary rays adjoining these intrafascicular. Enables a plant to increase in height. The details below are specific to secondary growth in stems.
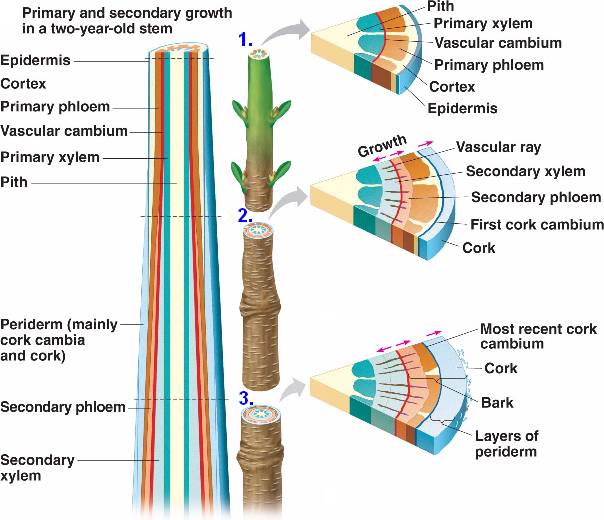 Source: bio1152.nicerweb.com
Source: bio1152.nicerweb.com
The secondary growth in a monocotyledonous stem or root is only the result of the enlargement of the primary cells, that is, the cells that have already been formed. Cork is also known as phelloderm. During every growing season the stem of a plant increases in width. In woody plants, secondary tissues constitute the bulk of the plant. Secondary growth follows the primary growth.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Primary growth occurs at an apical meristem, which are found at the tips of shoots and roots.secondary growth occurs at the. The vascular cambium and cork are the two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth. Secondary growth or “wood” is noticeable in woody plants; Tissues involved the apical meristem (shoot. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth, namely, vascular cambium and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Secondary growth or “wood” is noticeable in woody plants; The details below are specific to secondary growth in stems. The process of secondary growth is controlled by the lateral meristems and is similar in both stems and roots. The vascular cambium and cork are the two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth. Moreover, secondary growth has been documented in extinct taxa of lycophytes and.
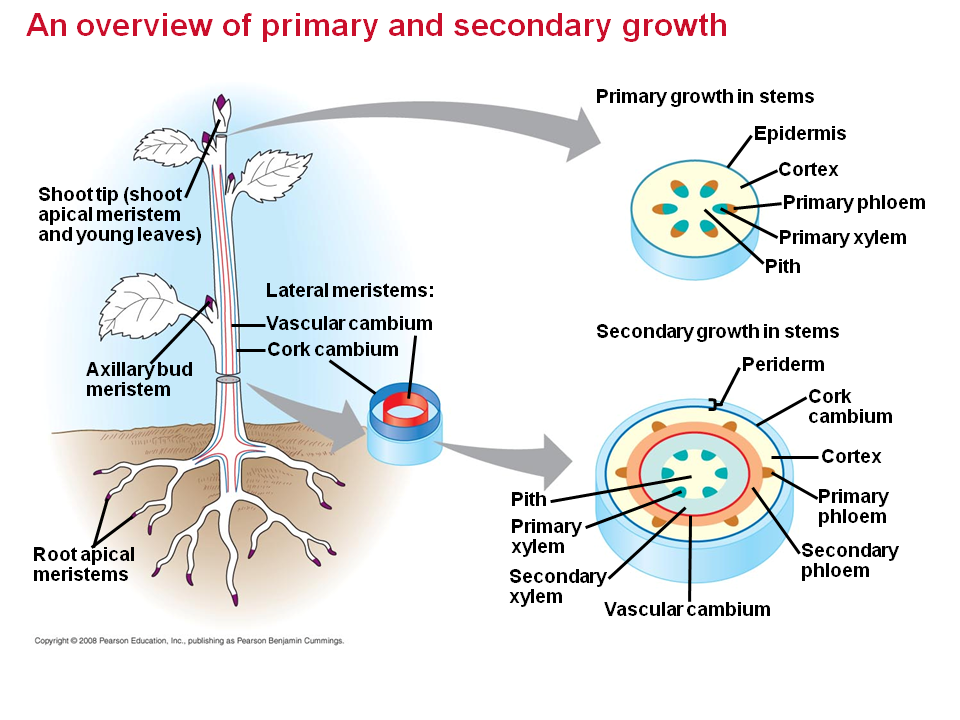
A meristem is a site of growth for a plant. Primary growth occurs at an apical meristem, which are found at the tips of shoots and roots.secondary growth occurs at the. There are two types of lateral tissues involved in secondary growth, namely, vascular cambium and. Plants’ secondary growth is controlled by the lateral meristem tissues. The herbaceous plants do not undergo secondary growth.
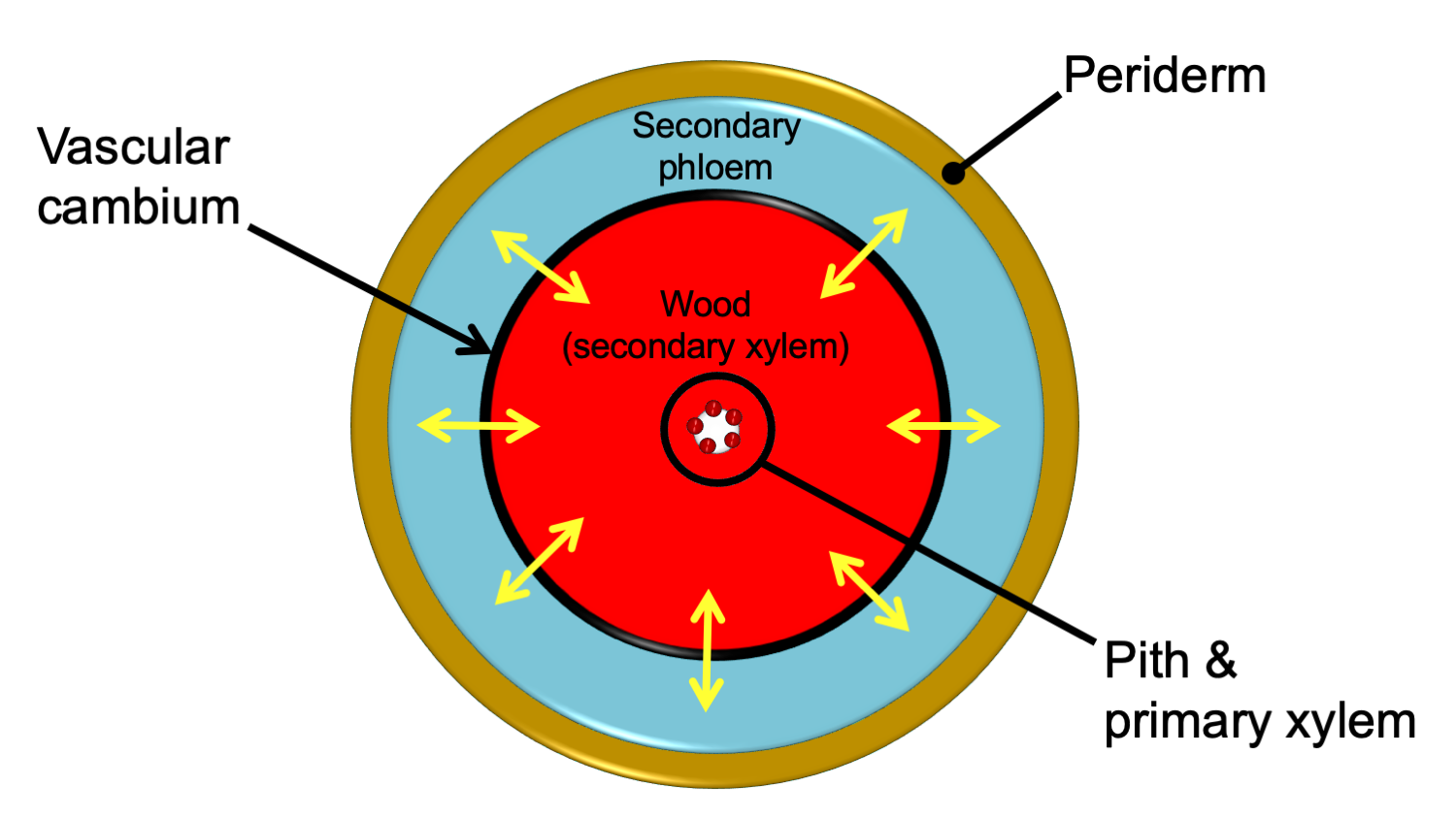 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Moreover, secondary growth has been documented in extinct taxa of lycophytes and. The secondary growth of plants increase in stem thickness and it is due to the activity of the lateral meristems, which are absent in herbs or herbaceous plants. Secondary growth helps the plant gain stamina and support for the height. Secondary growth in plants 1. The cambium present between the primary xylem and primary phloem of a vascular bundle is called intrafascicular cambium.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Cell division, cell elongation &. Secondary growth, or wood, is noticeable in woody plants; The secondary growth of plants increase in stem thickness and it is due to the activity of the lateral meristems, which are absent in herbs or herbaceous plants. It increases the diameter of the stem. The cells of medullary rays adjoining these intrafascicular.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title secondary growth in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






