Your Stoma in plants images are available. Stoma in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Stoma in plants files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for stoma in plants images information linked to the stoma in plants interest, you have visit the right site. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Stoma In Plants. Plural stomata) is a tiny opening or pore that is used for gas exchange. Plural stomata) is a tiny opening or pore that is used for gas exchange. A single pore is called stoma, which is found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, controlling the rate of gas exchange. The minimum light level for opening of stomates in most plants is 1/1000 to 1/30 of full sunlight, just enough to cause some net photosynthesis.
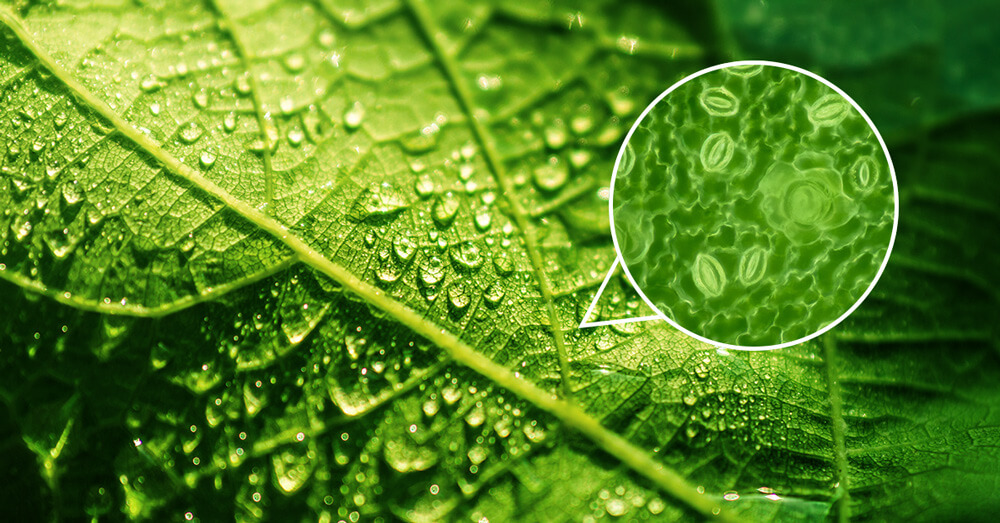
 Air Quality Management Zombie Gardens From zombiegardens.com
Air Quality Management Zombie Gardens From zombiegardens.com
These include the sporangia of some hornworts and mosses, as well as in fossils of the earliest known vascular plants, such as cooksonia and zosterophyllum from around 400 myr ago ( edwards, 1993 ). Functions of stomata in plants. Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. Stomate, also called stoma, plural stomata or stomas, any of the microscopic openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems. The stomata can open and. The stomata control gas exchange in the leaf.
In botany, a stoma (also stomate;
Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. In botany, a stoma (also stomate; Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. The carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis. The stoma is accompanied by a single subsidiary cell, which is placed parallel to the long axis of the pore and this cell may be long or short in length in contrast to the guard cells. Stoma is the pore in the underside of the leaves and stems of plants.
 Source: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Source: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Carbon dioxide is an essential part of photosynthesis. A single pore is called stoma, which is found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, controlling the rate of gas exchange. Stomata are the collection of pores on the underside of the plant leaves. Stomata help in the process of transpiration and photosynthesis which are the most essential. The densities of stomata vary among plant species and are regulated developmentally and in response to environmental changes (64, 116).
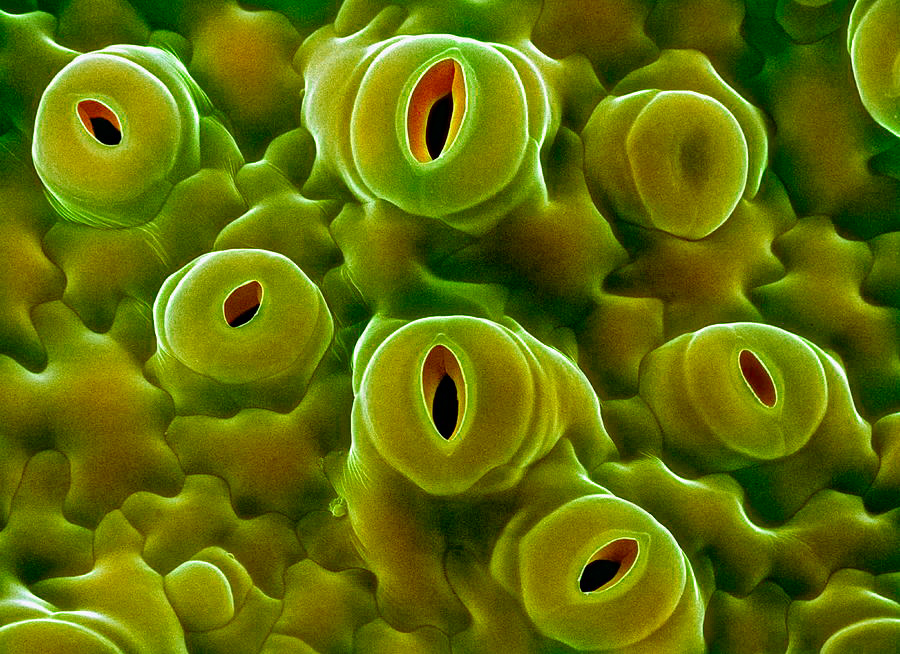
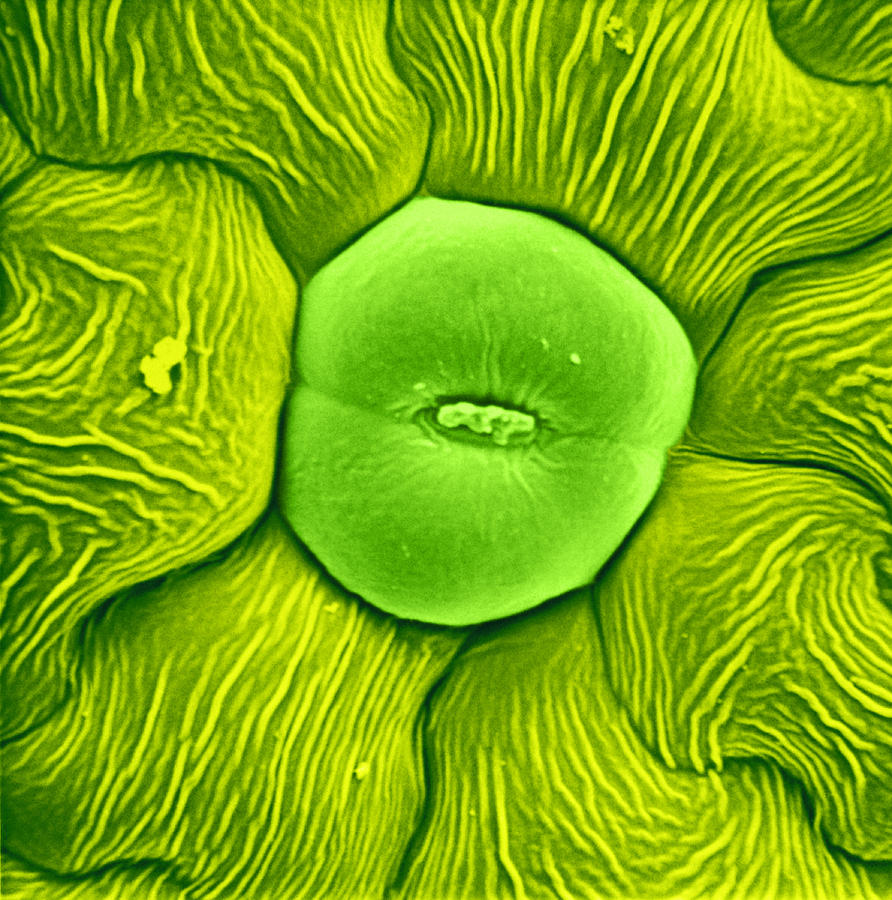 Source: pixels.com
Source: pixels.com
Stoma plant pores also provide a plant’s version of an exhale where they release water molecules. Stomata perform two significant roles in a plant: The carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis. Functions of stomata in plants. In this manner, what is stomata in plants?
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
The carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis. These include the sporangia of some hornworts and mosses, as well as in fossils of the earliest known vascular plants, such as cooksonia and zosterophyllum from around 400 myr ago ( edwards, 1993 ). Stomate, also called stoma, plural stomata or stomas, any of the microscopic openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems. Specialized cells known as guard cells surround stomata and function to open and close stomatal pores. Likewise, what are stomata in plants?
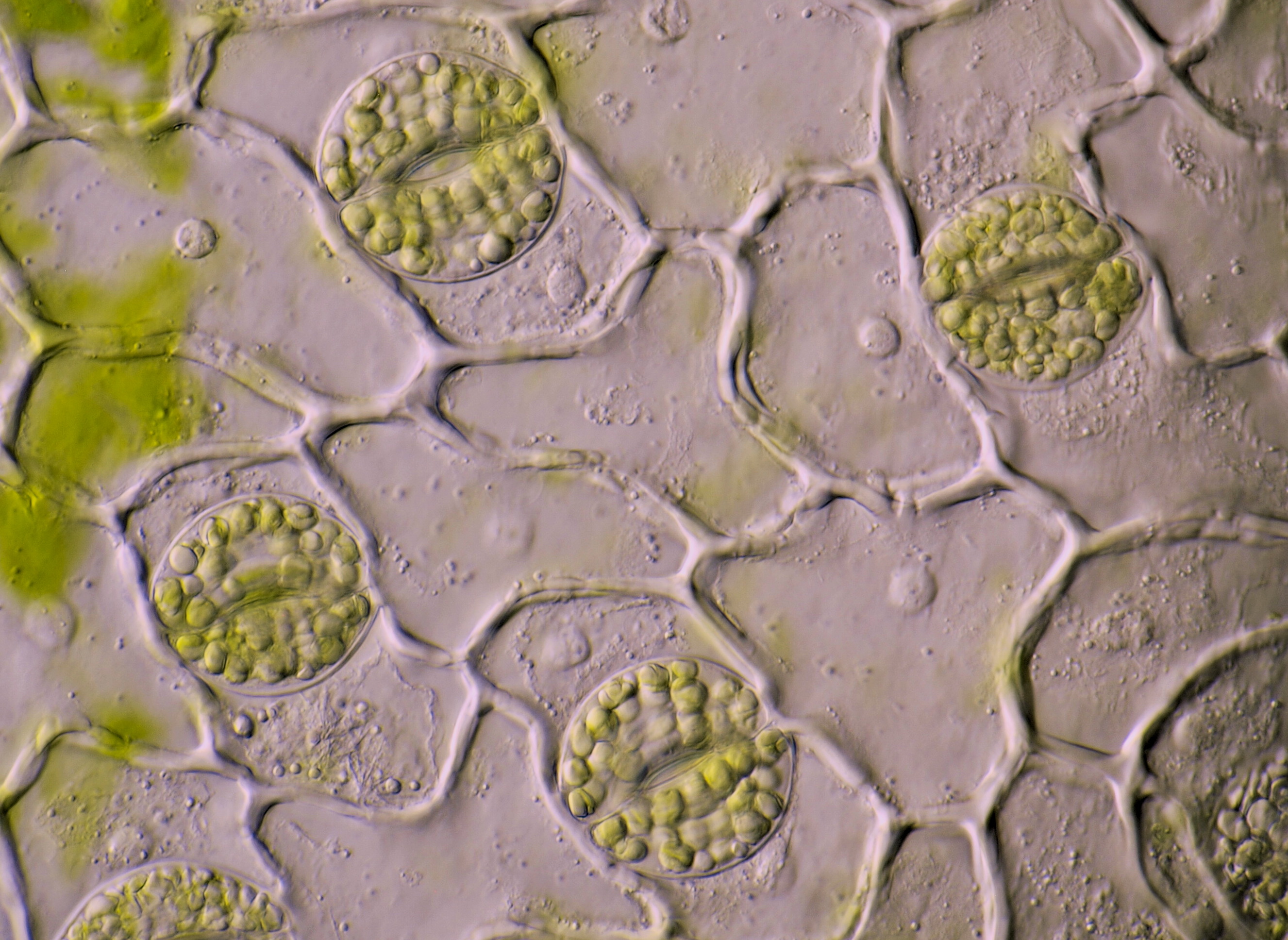 Source: microscopyofnature.com
Source: microscopyofnature.com
Stomates (also termed stomata) are specialized epidermal cells generally found on leaves, but sometimes on stems. Each stoma is guarded by two specialised epidermal cells, called guard cells. Air enters the plant through these openings. Air enters the plant through these openings. They provide for the exchange of gases between the outside air and the branched system of interconnecting air canals within the leaf.
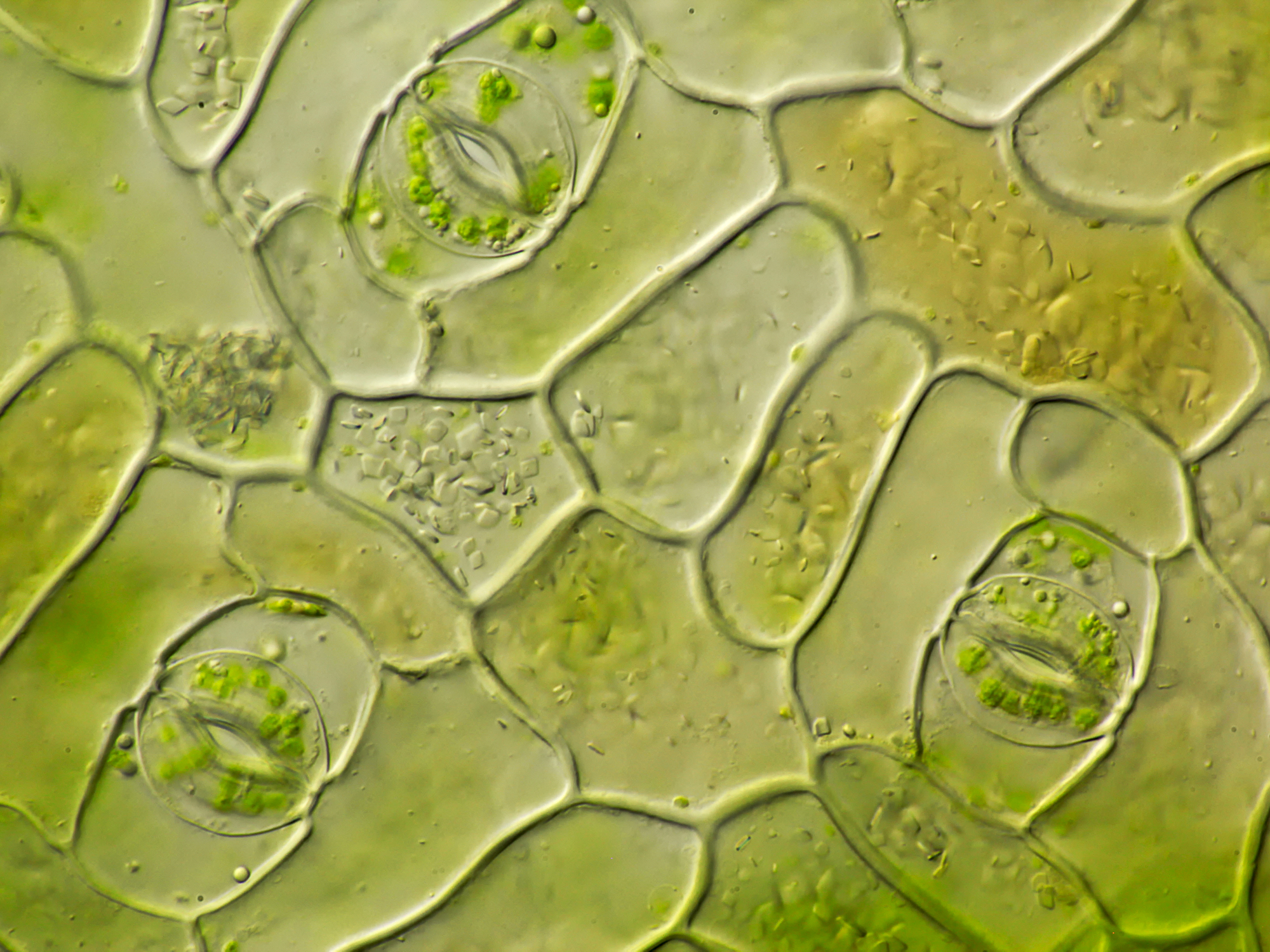 Source: microscopyofnature.com
Source: microscopyofnature.com
The stomatal pore is formed by the two kidney shaped or bean shaped cells called guard cells. Some minute pores which are usually, found in leaf for the exchange of gas and transpiration are known as stomata. Home actinocytic stomata types of stomata in plants. A stoma is said to be parameristic where gmc divides with a wall parallel to the wall that cuts it off from its meristemoid. In most green plants, the stomata are located on the lower side of the.
 Source: gardeningknowhow.com
Source: gardeningknowhow.com
These hypodermal cells immediately below the guard the stomatal ledges of the guard cells delimit an area. Glinus latioides and trianthema lancastrum etc. The stomatal pore is formed by the two kidney shaped or bean shaped cells called guard cells. Air enters the plant through these openings. The stoma is accompanied by a single subsidiary cell, which is placed parallel to the long axis of the pore and this cell may be long or short in length in contrast to the guard cells.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
In most green plants, the stomata are located on the lower side of the. Most leaves are covered in these tiny pores, which allow the plants to take in carbon dioxide for use in photosynthesis and expel their waste oxygen. A single pore is called stoma, which is found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, controlling the rate of gas exchange. Stomata allow a plant to take in carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis. To maintain the water balance in the plant cells.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
They provide for the exchange of gases between the outside air and the branched system of interconnecting air canals within the leaf. The carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis. Specialized cells known as guard cells surround stomata and function to open and close stomatal pores. Stomata perform two significant roles in a plant: Stomata allow for gas exchange to occur, mainly carbon dioxide to enter the plant to make food molecules such as glucose and for oxygen to be released by the plant.
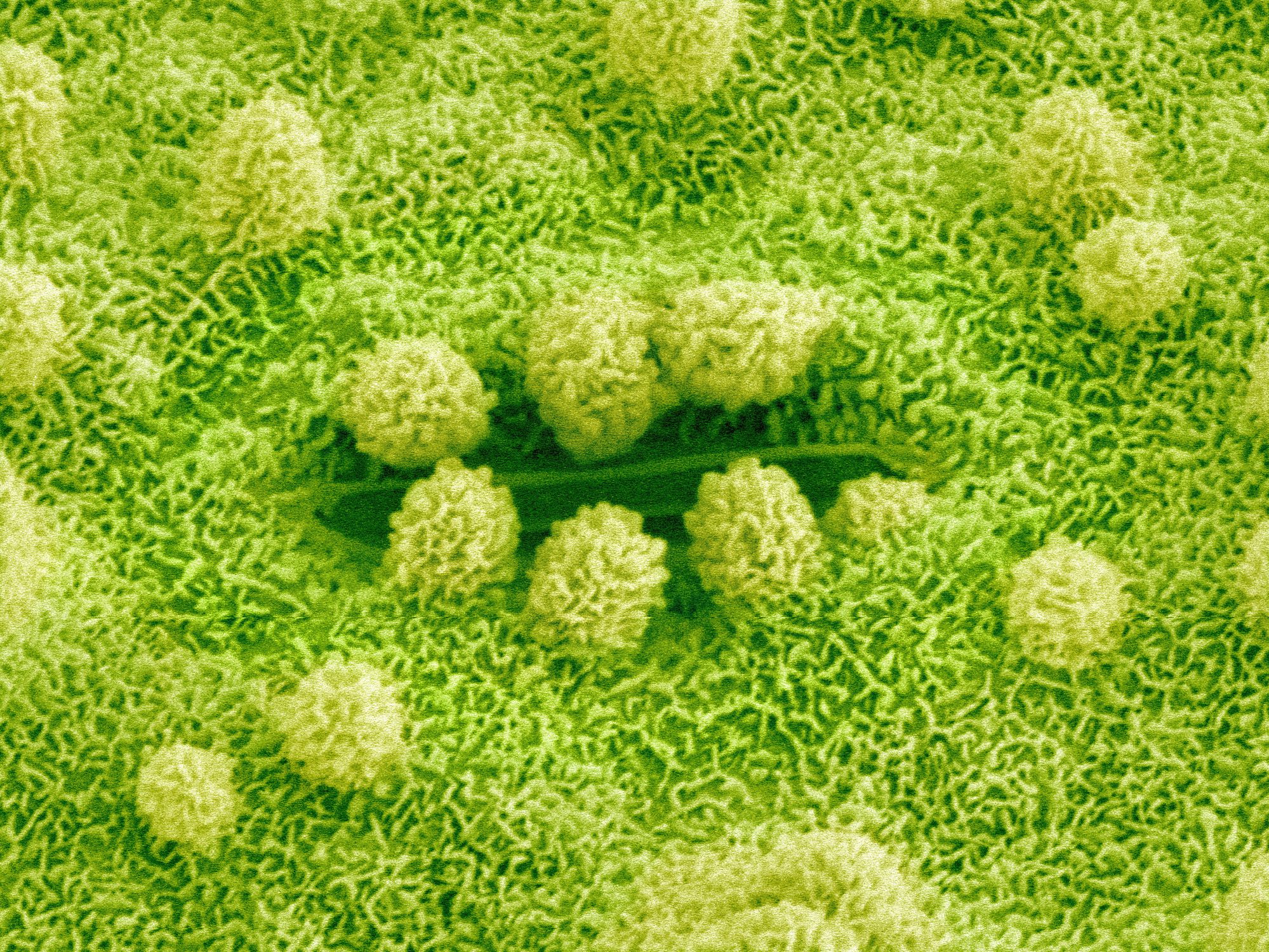 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
In this manner, what is stomata in plants? One of the daughter cells becomes the first lateral subsidiary cell. In plants, a stoma is a tiny pore in the surface of a leaf that is used for gas exchange. Plants need to intake carbon dioxide. Stomata perform two significant roles in a plant:
 Source: wuxal.com
Source: wuxal.com
The stomata control gas exchange in the leaf. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how turgid its guard cells are. Plural stomata) is a tiny opening or pore that is used for gas exchange. The opening and closing of stoma are controlled by. Most leaves are covered in these tiny pores, which allow the plants to take in carbon dioxide for use in photosynthesis and expel their waste oxygen.
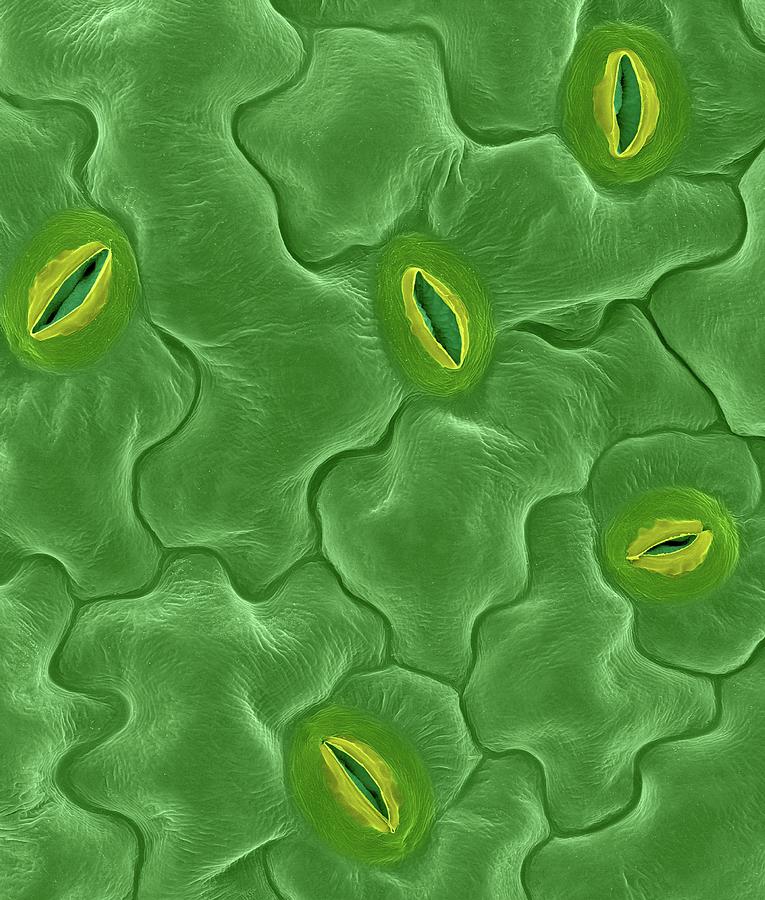 Source: microspedia.blogspot.com
Source: microspedia.blogspot.com
Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. In botany, a stoma (also stomate; In botany, a stoma (also stomate; Stomata open and close to allow the intake of. Plural stomata) is a tiny opening or pore that is used for gas exchange.
 Source: cronodon.com
Source: cronodon.com
Stomata are generally more numerous on the underside of leaves. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems. Stomata aid in this process by harvesting the carbon dioxide. The stomata can open and. Stomata are generally more numerous on the underside of leaves.
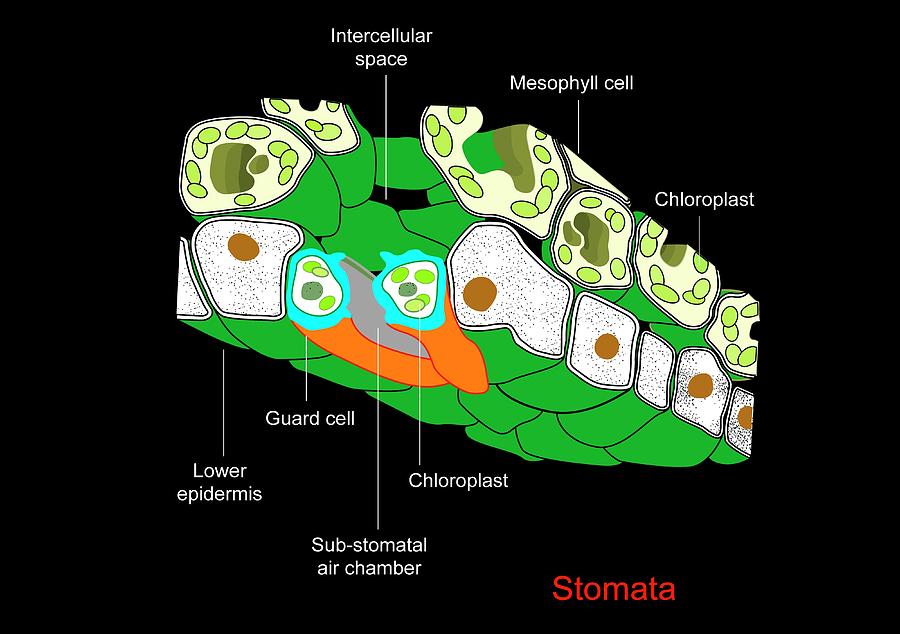 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
The stomatal pores cells are. The loss of excess water in the form of water vapour. He stoma of a plant is a pore, found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, which facilitates the exchange of gases. In floating plant stomata present only on upper surface of leaves. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Plural stomata) is a tiny opening or pore that is used for gas exchange. Functions of stomata in plants. As we need fuel to cook food, plants harness carbon dioxide as fuel to prepare food for themselves. The stomatal pore is formed by the two kidney shaped or bean shaped cells called guard cells. Stomata help in the process of transpiration and photosynthesis which are the most essential.
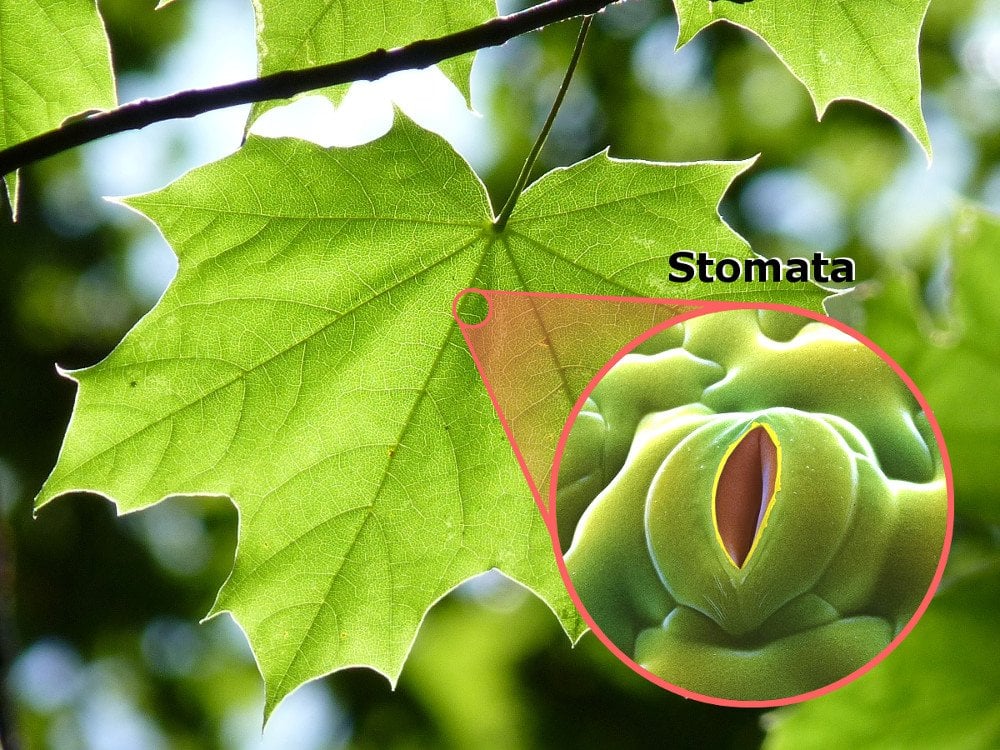 Source: scienceabc.com
Source: scienceabc.com
As we need fuel to cook food, plants harness carbon dioxide as fuel to prepare food for themselves. The stomata can open and. The stoma is accompanied by a single subsidiary cell, which is placed parallel to the long axis of the pore and this cell may be long or short in length in contrast to the guard cells. Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. Air enters the plant through these openings.
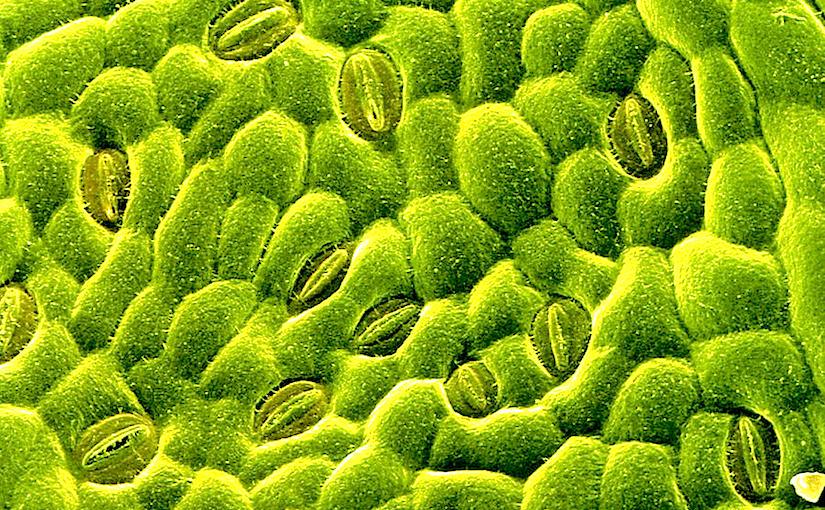 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Air enters the plant through these openings. The stoma is accompanied by a single subsidiary cell, which is placed parallel to the long axis of the pore and this cell may be long or short in length in contrast to the guard cells. The carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis. These hypodermal cells immediately below the guard the stomatal ledges of the guard cells delimit an area. 12.17b) and mesoperigenous stoma of liriodendron.
 Source: zombiegardens.com
Source: zombiegardens.com
Plants need to intake carbon dioxide. In grasses the stomatal guard cells are dumbbell shaped. The stomatal pores cells are. Likewise, what are stomata in plants? 12.17b) and mesoperigenous stoma of liriodendron.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
In submerged plant /leaves stomata absent. Stomata refer to the pores that are present, usually on the underside of leaves of a plant, which allow for the exchange of the gases oxygen and carbon dioxide. An influx of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis in plants. Air enters the plant through these openings. In this manner, what is stomata in plants?
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title stoma in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







