Your The phloem in a plant images are available. The phloem in a plant are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the The phloem in a plant files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for the phloem in a plant pictures information connected with to the the phloem in a plant topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
The Phloem In A Plant. Phloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve elements , phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells. Phloem is a complex tissue system in plants. But, before this translocation of sugars could proceed, the soluble sugars […] Phloem refers to the living tissue which helps in the transportation of food and organic materials in the plant.
 9.2 transport in the phloem of plants From slideshare.net
9.2 transport in the phloem of plants From slideshare.net
In vivo experiments in potted bananas demonstrated that flu@pga can achieve the downward delivery of flu to banana rhizomes and roots after foliar application, reducing disease severity by 50.4%. Let us learn a bit more about phloem transport. Since the plant is a continuum, phloem will be found in the external part of root cylinders ( figure 1a ), in the stem vascular bundles ( figure 1b) and in the abaxial part of the venations of every single leaf ( figure 1c ). The below mentioned article provides an useful note on the phloem loading and unloading in plants. The food in the form of sucrose is transported by the vascular tissue phloem. Phloem parenchyma is found in both primary and secondary phloem.
Phloem, plant vascular tissue that conducts foods made in the leaves during photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant.
The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; Xylem is the complex tissue of plants that helps in the transportation of water and nutrients in the plant. It is a part of the phloem elements. Phloem, plant vascular tissue that conducts foods made in the leaves during photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots. A complex tissue in the vascular system of higher plants that consists mainly of sieve tubes and elongated parenchyma cells usually with fibers and that functions in translocation and in support and storage — compare xylem example sentences phrases containing phloem learn more about phloem
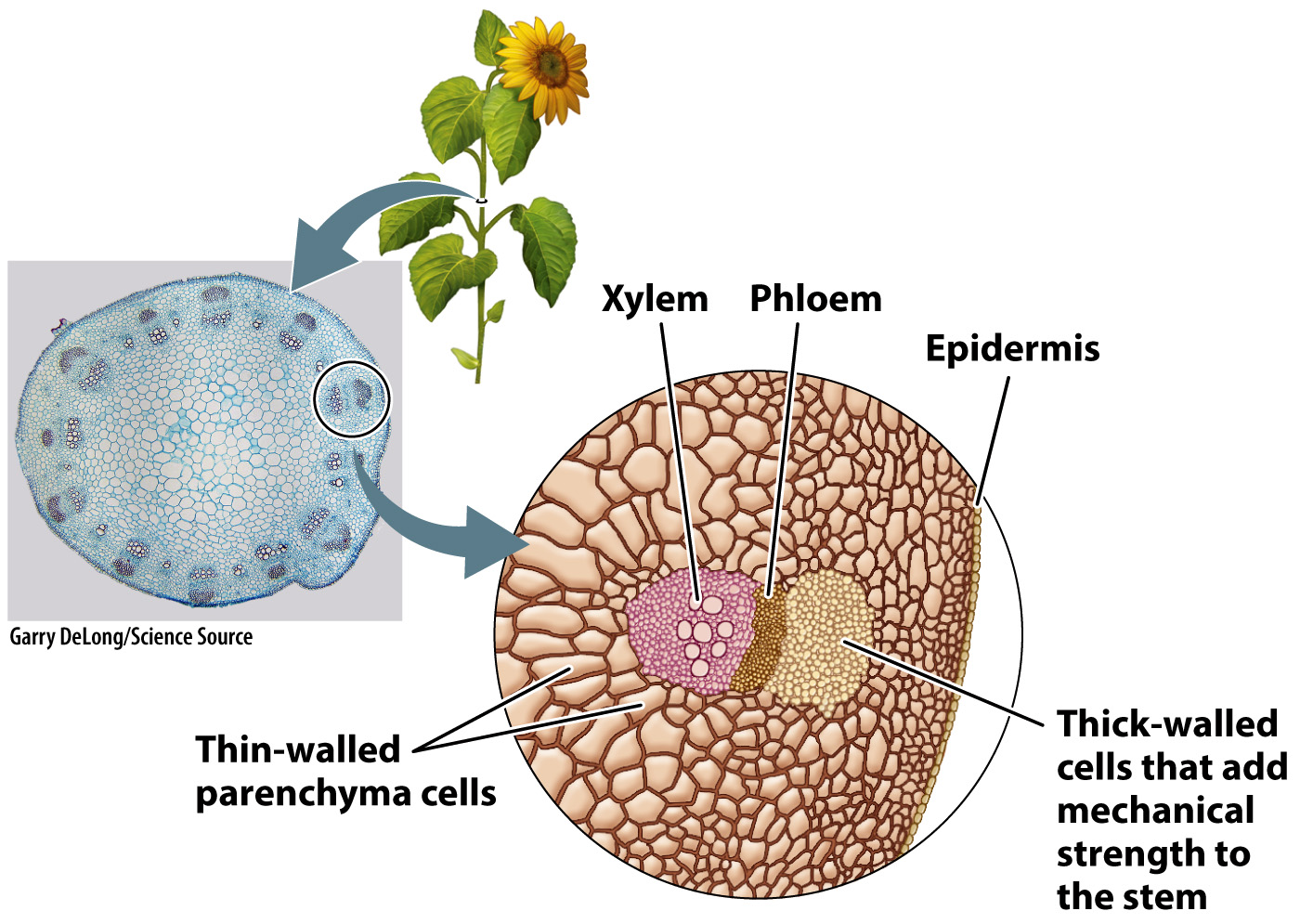 Source: macmillanhighered.com
Source: macmillanhighered.com
In general, this happens between where these substances are. These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants. Vascular bundles are enclosed inside the ground tissue and protected by the epidermis layer. Where is the phloem located? The phloem composed of several types of cells among which some are living cells and some are dead.
 Source: csus.edu
Phloem is defined as the specialized food conducting tissue of the plant cell which assist the conductance of food carbohydrates and amino acids from the photosynthesized part leaf to the. The transportation occurs in the direction of the source to sink. This transport process is called translocation. The food in the form of sucrose is transported by the vascular tissue phloem. Phloem fibres, sieve elements, and phloem parenchyma cells are all types of specialised cells found in phloem tissues.
 Source: blogs.evergreen.edu
Source: blogs.evergreen.edu
The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; Gaud) is a highly versatile herbaceous plant which is widely cropped in southern china. Phloem is the biological tissue of vascular plants that transports photosynthesis, a soluble organic compound produced during photosynthesis, to various regions of the plant. The xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids up and down the plant.
 Source: alevelbiology.co.uk
Source: alevelbiology.co.uk
Phloem is the complex tissue, which acts as a transport system for soluble organic compounds within vascular plants. [in this figure] vascular bundle distribution of a pumpkins’ vine. The phloem is made from cells called sieve tube members. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots. The food in the form of sucrose is transported by the vascular tissue phloem.
 Source: intechopen.com
Source: intechopen.com
The below mentioned article provides an useful note on the phloem loading and unloading in plants. The phloem composed of several types of cells among which some are living cells and some are dead. Gaud) is a highly versatile herbaceous plant which is widely cropped in southern china. The vascular system is comprised of two main types of tissue: Phloem, plant vascular tissue that conducts foods made in the leaves during photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Let us learn a bit more about phloem transport. These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants. A plant is a coordinated network of assimilatory regions (sources) linked to regions of resource utilisation (sinks). It is found only during secondary growth of dicots and gymnosperms with the exception of annuals. The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks.
 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
A plant is a coordinated network of assimilatory regions (sources) linked to regions of resource utilisation (sinks). Where is the phloem located? The xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. In general, this happens between where these substances are. In plants a network of tissues and fibers called the vascular system carries out this task.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
The food in the form of sucrose is transported by the vascular tissue phloem. The phloem vascular system provides a path for assimilate transport from source to sink. But, before this translocation of sugars could proceed, the soluble sugars […] Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. The xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves.
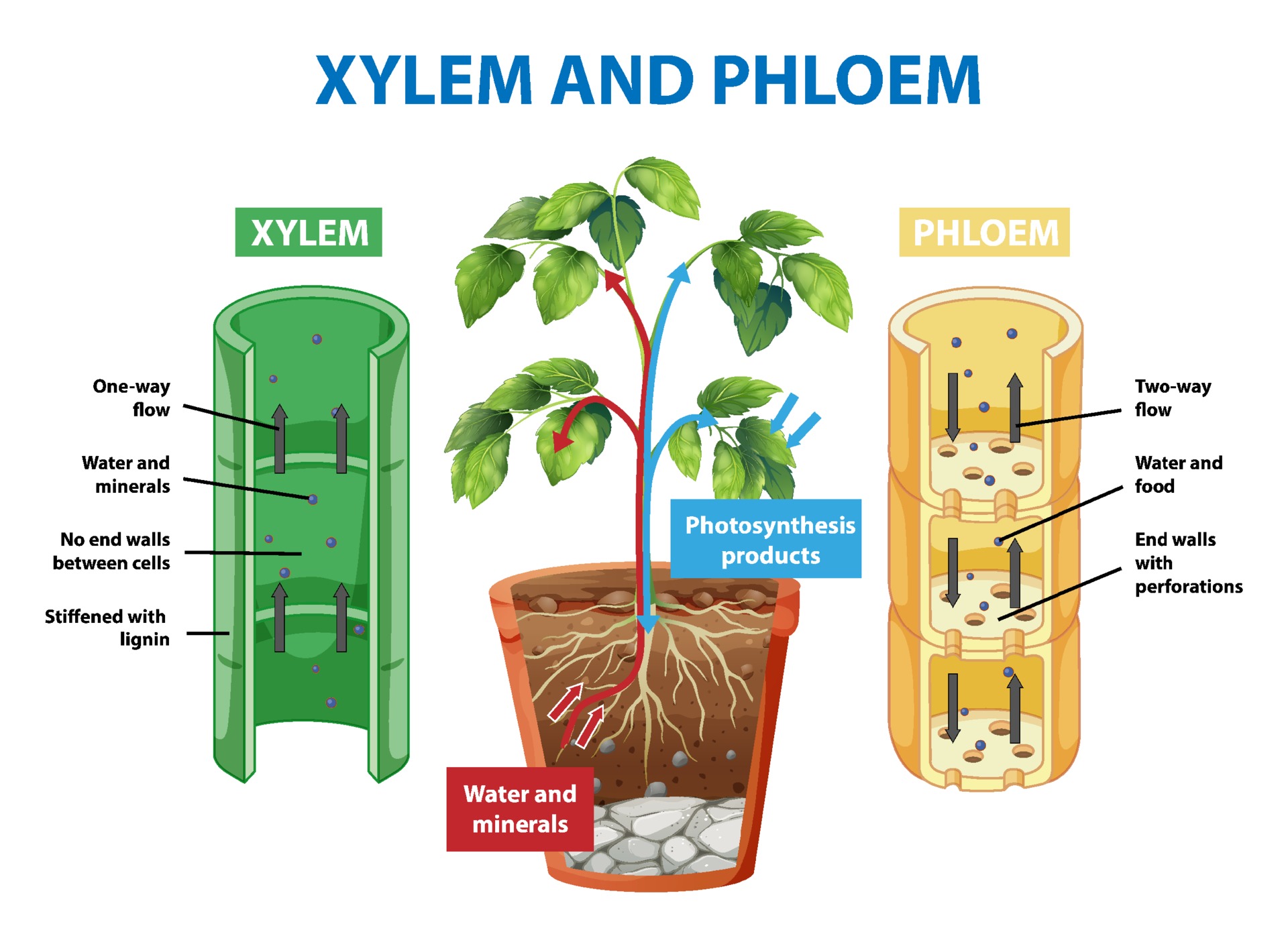 Source: vecteezy.com
Source: vecteezy.com
It is a part of the phloem elements. This transport process is called translocation. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports sucrose and amino acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure. Phloem fibres, sieve elements, and phloem parenchyma cells are all types of specialised cells found in phloem tissues.
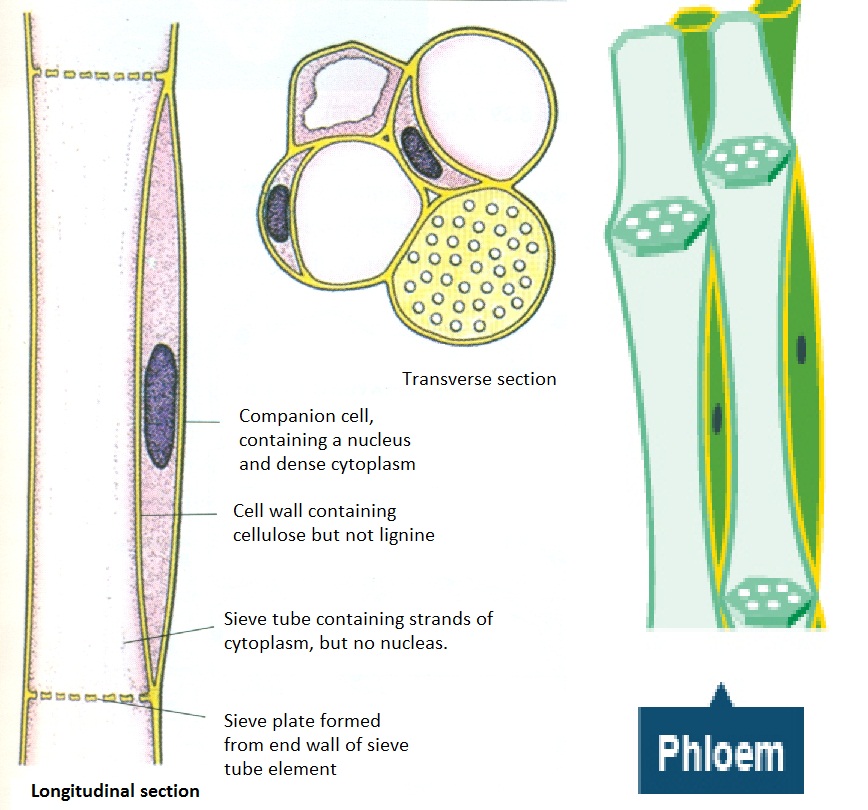 Source: igbiologyy.blogspot.com
Source: igbiologyy.blogspot.com
These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants. The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks. The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; Phloem parenchyma is found in both primary and secondary phloem. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure.
 Source: plantenzo.net
Source: plantenzo.net
Phloem, plant vascular tissue that conducts foods made in the leaves during photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant. Phloem is a complex tissue system in plants. The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks. Phloem parenchyma is found in both primary and secondary phloem. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Phloem translocates water and products of photosynthesis from source tissues to the sink regions where they are utilized or stored. Understanding the profiling of expressed genes in phloem and xylem of ramie is crucial for improving its indus. Translocation is the name of this type of transport. Let us learn a bit more about phloem transport. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Phloem is also important as the xylem tissues for the vascular system of plants. It is the food conducting tissue of vascular plants. The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; Phloem fibres, sieve elements, and phloem parenchyma cells are all types of specialised cells found in phloem tissues. These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Phloem is the biological tissue of vascular plants that transports photosynthesis, a soluble organic compound produced during photosynthesis, to various regions of the plant. Xylem is the complex tissue of plants that helps in the transportation of water and nutrients in the plant. Phloem refers to the living tissue which helps in the transportation of food and organic materials in the plant. The main activity of this tissue is to transport nutrients and food from leaves to other growing parts of plants. The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks.
 Source: blogs.evergreen.edu
Source: blogs.evergreen.edu
Let us learn a bit more about phloem transport. Vascular bundles are enclosed inside the ground tissue and protected by the epidermis layer. But, before this translocation of sugars could proceed, the soluble sugars […] These are found in dicot roots, leaves, and stems but are absent in monocot plants. It is the food conducting tissue of vascular plants.

Understanding the profiling of expressed genes in phloem and xylem of ramie is crucial for improving its indus. Gaud) is a highly versatile herbaceous plant which is widely cropped in southern china. Phloem is also important as the xylem tissues for the vascular system of plants. Together with xylem, they form the vascular tissue system. Since the plant is a continuum, phloem will be found in the external part of root cylinders ( figure 1a ), in the stem vascular bundles ( figure 1b) and in the abaxial part of the venations of every single leaf ( figure 1c ).
 Source: syedgilanis.com
Source: syedgilanis.com
Gaud) is a highly versatile herbaceous plant which is widely cropped in southern china. The phloem carries important sugars, organic compounds, and minerals around a plant. The main activity of this tissue is to transport nutrients and food from leaves to other growing parts of plants. The vascular system is comprised of two main types of tissue: Gaud) is a highly versatile herbaceous plant which is widely cropped in southern china.
 Source: pixels.com
Source: pixels.com
The phloem is made from cells called sieve tube members. [in this figure] vascular bundle distribution of a pumpkins’ vine. Phloem is defined as the specialized food conducting tissue of the plant cell which assist the conductance of food carbohydrates and amino acids from the photosynthesized part leaf to the. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure. A plant is a coordinated network of assimilatory regions (sources) linked to regions of resource utilisation (sinks).
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title the phloem in a plant by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






