Your Thermotropism in plants images are ready in this website. Thermotropism in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Thermotropism in plants files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for thermotropism in plants pictures information related to the thermotropism in plants topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our website always gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
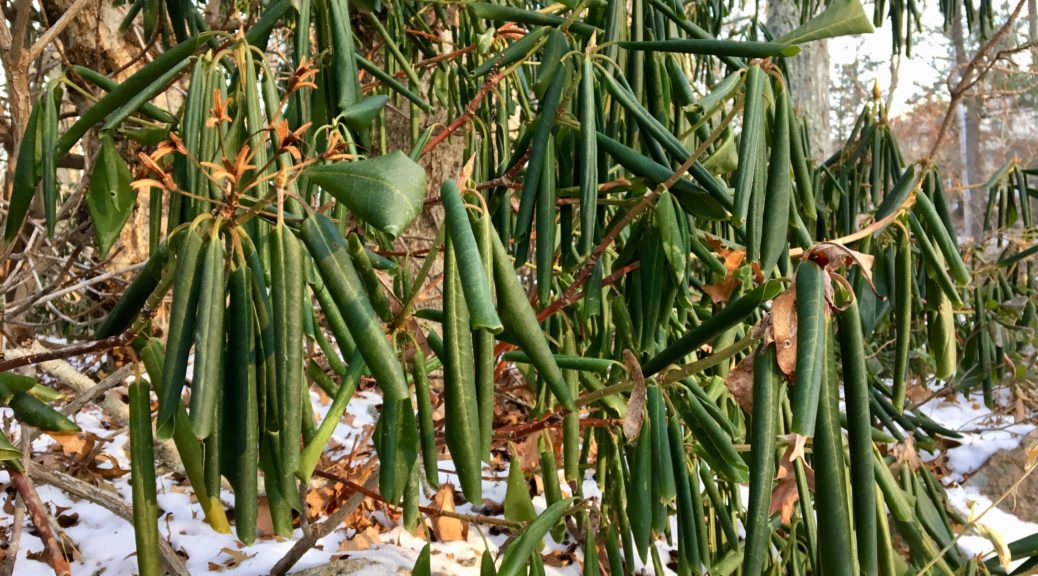
Thermotropism In Plants. Thermotropism in plants, the bending of growing parts, such as the stems or root tips, in response to a heat stimulus. The stem toward the light to optimize the surface for sunlight. For example, rhododendrons often display physical changes in response to a dip in temperature, and then resort back to their normal state once the weather gets warmer again. Despite thermotropism being a classic botanical concept, the underlying ecological function and molecular and biophysical mechanisms remain poorly understood to this day.
 Tropism by Ben Simmons From haikudeck.com
Tropism by Ben Simmons From haikudeck.com
Thermotropism is a form of tropism (movement) whereby the plant displays a growth response or movement according to changes in temperature. Parts of the plants can also respond to the fluctuating temperature of their surrounding. Thermotropism synonyms, thermotropism pronunciation, thermotropism translation, english dictionary definition of thermotropism. A chemical gradient can influence the growth of the organism in a positive or negative way. Positive growth is characterized by growing towards a stimulus and negative growth is growing away from the. Thermotropism in primary roots of zea mays l.
This plant movement happens as a response to the change of temperature in the environment, as heat or cold.
This basically means that a plant alters its normal pattern or direction of growth or movement as the result of an external touch stimulus. In plants, the bending of growing parts, such as the stems or root tips, in response to a heat stimulus. This movement effectively explains the growth of roots in plants. According to botanists, plants also move in the following main ways: Thermotropism this plant movement happens as a response to the change of temperature in the environment, as heat or cold. When atmospheric variation in temperature acts as a stimulus and causes the plant to move towards a specific direction (positive or negative) is called thermotropism.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
For example, rhododendrons often display physical changes in response to a dip in temperature, and then resort back to their normal state once the weather gets warmer again. These include low molecular weight substances such as ions, free oxygen, amino acids, organic acids, sugars, phenols and other secondary metabolites, as well as high molecular weight exudates such as mucilages. What is thigmotropism explain with example?growth movement of plants in response to touch stimulus is called thigmotropism, e.g.,tendrils of sweet pea coiling around a support.what is the meaning of thermotropism?thermotropism is one of the many forms of tropisms. It has been observed in bacteria, plants and fungi. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism);
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Two other types of plant tropisms include thermotropism and chemotropism. Plants show positive thermotropism when they grow towards the source of heat. Two important terms to be familiar with when exploring the literature on temperature effects in plants are thermotropism, which is the plant�s response to temperature,. In biology, a tropism is an involuntary response to a stimulus. When a plant�s leaves curl in response to a chilly window, it�s an example of thermotropism, which is an organism�s tendency to move toward warmth and away from cold.
 Source: haikudeck.com
For example, rhododendrons often display physical changes in response to a dip in temperature, and then resort back to their normal state once the weather gets warmer again. Chemotropism is defined as the growth of organisms navigated by chemical stimulus from outside of the organism. What is thigmotropism explain with example?growth movement of plants in response to touch stimulus is called thigmotropism, e.g.,tendrils of sweet pea coiling around a support.what is the meaning of thermotropism?thermotropism is one of the many forms of tropisms. This plant movement happens as a response to the change of temperature in the environment, as heat or cold. Thigmotropism is defined as the directional movement of plants in response to the stimulus of touch.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
A chemical gradient can influence the growth of the organism in a positive or negative way. Thermotropism also may protect leaves during periods of high irradiance by sunlight. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism); Plants like rhododendron curl their leaves when it is very cold, and mimosa pudica collapses its leaves and folds them when there. Thermotropism is growth or movement in response to heat or temperature changes, while chemotropism is growth in response to chemicals.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
The growth of plants occurs in response to the temperature stimulus. Thermotropism is a form of tropism (movement) whereby the plant displays a growth response or movement according to changes in temperature. Study the definition and overview of thigmotropism and the senses and tropisms. Above that temperature they bend toward the cooler vessel (negative thermotropism). Plants show positive thermotropism when they grow towards the source of heat.
 Source: seashoretoforestfloor.com
Source: seashoretoforestfloor.com
This movement effectively explains the growth of roots in plants. Scientists do not fully understand the cause of this foliar response. It has been observed in bacteria, plants and fungi. Two important terms to be familiar with when exploring the literature on temperature effects in plants are thermotropism, which is the plant�s response to temperature,. Thermotropism synonyms, thermotropism pronunciation, thermotropism translation, english dictionary definition of thermotropism.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
It may have something to do with leaf cell hydration. It may have something to do with leaf cell hydration. Parts of the plants can also respond to the fluctuating temperature of their surrounding. A chemical gradient can influence the growth of the organism in a positive or negative way. Oppositely, plants show negative thermotropism when they grow away from the heat source.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Two other types of plant tropisms include thermotropism and chemotropism. However, root responses to temperature gradients have not been extensively studied. It may have something to do with leaf cell hydration. Despite thermotropism being a classic botanical concept, the underlying ecological function and molecular and biophysical mechanisms remain poorly understood to this day. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism);
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Chemotropism is defined as the growth of organisms navigated by chemical stimulus from outside of the organism. Plants like rhododendron curl their leaves when it is very cold, and mimosa pudica collapses its leaves and folds them when there. These parts display the curvature movements in response to this kind of stimulus by taking some advantageous position. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel. Thermotropism is a form of tropism (movement) whereby the plant displays a growth response or movement according to changes in temperature.

The stem toward the light to optimize the surface for sunlight. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism); However, root responses to temperature gradients have not been extensively studied. What is thigmotropism explain with example?growth movement of plants in response to touch stimulus is called thigmotropism, e.g.,tendrils of sweet pea coiling around a support.what is the meaning of thermotropism?thermotropism is one of the many forms of tropisms. These include low molecular weight substances such as ions, free oxygen, amino acids, organic acids, sugars, phenols and other secondary metabolites, as well as high molecular weight exudates such as mucilages.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
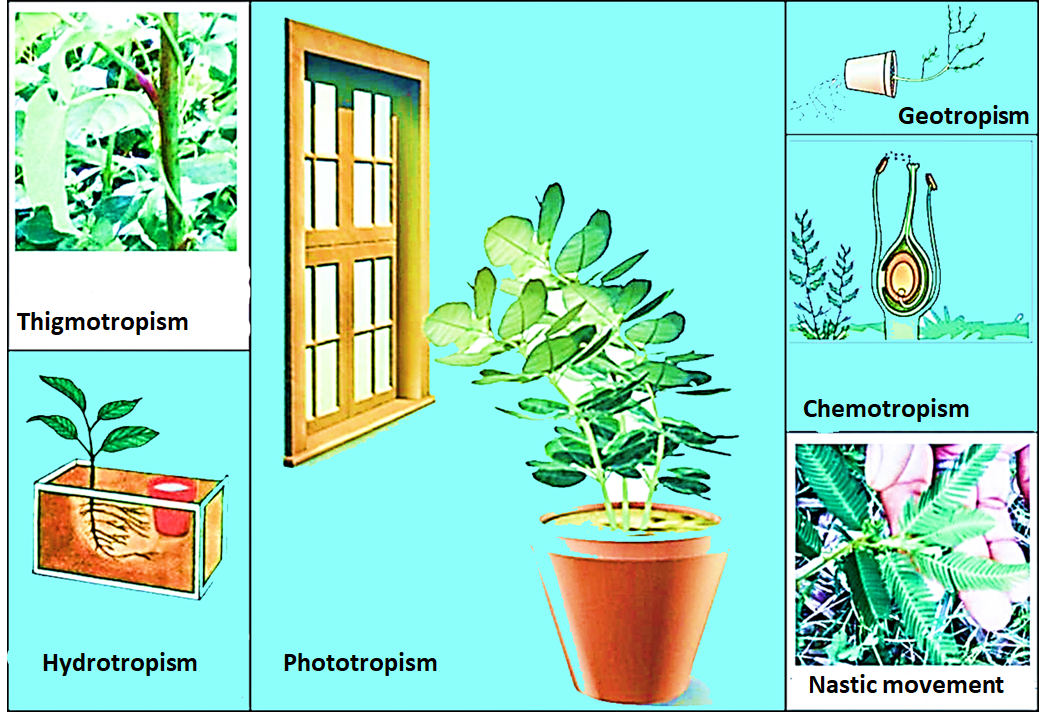
The directional growth of a plant in response to the stimulus of heat | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Thermotropism is a form of tropism (movement) whereby the plant displays a growth response or movement according to changes in temperature. Hydrotropism (growth or developmental response to water) thermotropism (response dependent upon temperature) phototropism (movement toward light) gravitropism and geotropism (movement relative to a gravitational field, or toward the center of the earth) Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel. In plants, the bending of growing parts, such as the stems or root tips, in response to a heat stimulus.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Thermotropism also may protect leaves during periods of high irradiance by sunlight. Once you know that, you can probably easily guess that thermotropism is a tendency to respond to (and. Above that temperature they bend toward the cooler vessel (negative thermotropism). It may have something to do with leaf cell hydration. In biology, a tropism is an involuntary response to a stimulus.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Plants show positive thermotropism when they grow towards the source of heat. According to botanists, plants also move in the following main ways: Oppositely, plants show negative thermotropism when they grow away from the heat source. During plant thermotropic responses, organs move towards (engage) or away (avoid) from a directional temperature cue. Parts of the plants can also respond to the fluctuating temperature of their surrounding.

Thigmotropism can be used in ways that increase the chance of a plant catching light for photosynthesis. Thermotropism also may protect leaves during periods of high irradiance by sunlight. Two important terms to be familiar with when exploring the literature on temperature effects in plants are thermotropism, which is the plant�s response to temperature,. These parts display the curvature movements in response to this kind of stimulus by taking some advantageous position. Hydrotropism (growth or developmental response to water) thermotropism (response dependent upon temperature) phototropism (movement toward light) gravitropism and geotropism (movement relative to a gravitational field, or toward the center of the earth)
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Above that temperature they bend toward the cooler vessel (negative thermotropism). These include low molecular weight substances such as ions, free oxygen, amino acids, organic acids, sugars, phenols and other secondary metabolites, as well as high molecular weight exudates such as mucilages. Above that temperature they bend toward the cooler vessel (negative thermotropism). Parts of the plants can also respond to the fluctuating temperature of their surrounding. Two important terms to be familiar with when exploring the literature on temperature effects in plants are thermotropism, which is the plant�s response to temperature,.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism); These include low molecular weight substances such as ions, free oxygen, amino acids, organic acids, sugars, phenols and other secondary metabolites, as well as high molecular weight exudates such as mucilages. Plant roots may exhibit positive thermotropism in one temperature range and negative thermotropism in another temperature. Chemotropism is defined as the growth of organisms navigated by chemical stimulus from outside of the organism. Thigmotropism can be in the form of opening or closing of parts of the plant such as the petals or leaves, the coiling of the plant around the surface, as well as other ways.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Chemotropism is defined as the growth of organisms navigated by chemical stimulus from outside of the organism. Study the definition and overview of thigmotropism and the senses and tropisms. What is thigmotropism explain with example?growth movement of plants in response to touch stimulus is called thigmotropism, e.g.,tendrils of sweet pea coiling around a support.what is the meaning of thermotropism?thermotropism is one of the many forms of tropisms. This basically means that a plant alters its normal pattern or direction of growth or movement as the result of an external touch stimulus. It pertains to the movement or the
 Source: mammothmemory.net
In biology, a tropism is an involuntary response to a stimulus. For example, the rhododendron plan, where leaves are shredded in response to cold weather. Thermotropism this plant movement happens as a response to the change of temperature in the environment, as heat or cold. Parts of the plants can also respond to the fluctuating temperature of their surrounding. Up to a certain temperature the rootlets bend in the direction of the warmer vessel (positive thermotropism);
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title thermotropism in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







