Your Transpiration in plants definition images are available. Transpiration in plants definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Transpiration in plants definition files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for transpiration in plants definition pictures information connected with to the transpiration in plants definition topic, you have come to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Transpiration In Plants Definition. Plants’ stomata undergo transpiration in order to lose water vapor. Excessive loss of water from the plants through transpiration may lead to the death of plants. It is a type of translocation and part of the water cycle. Hence, most plants, especially xerophytes, adopt various modes both morphologically and anatomically to reduce excessive transpiration.
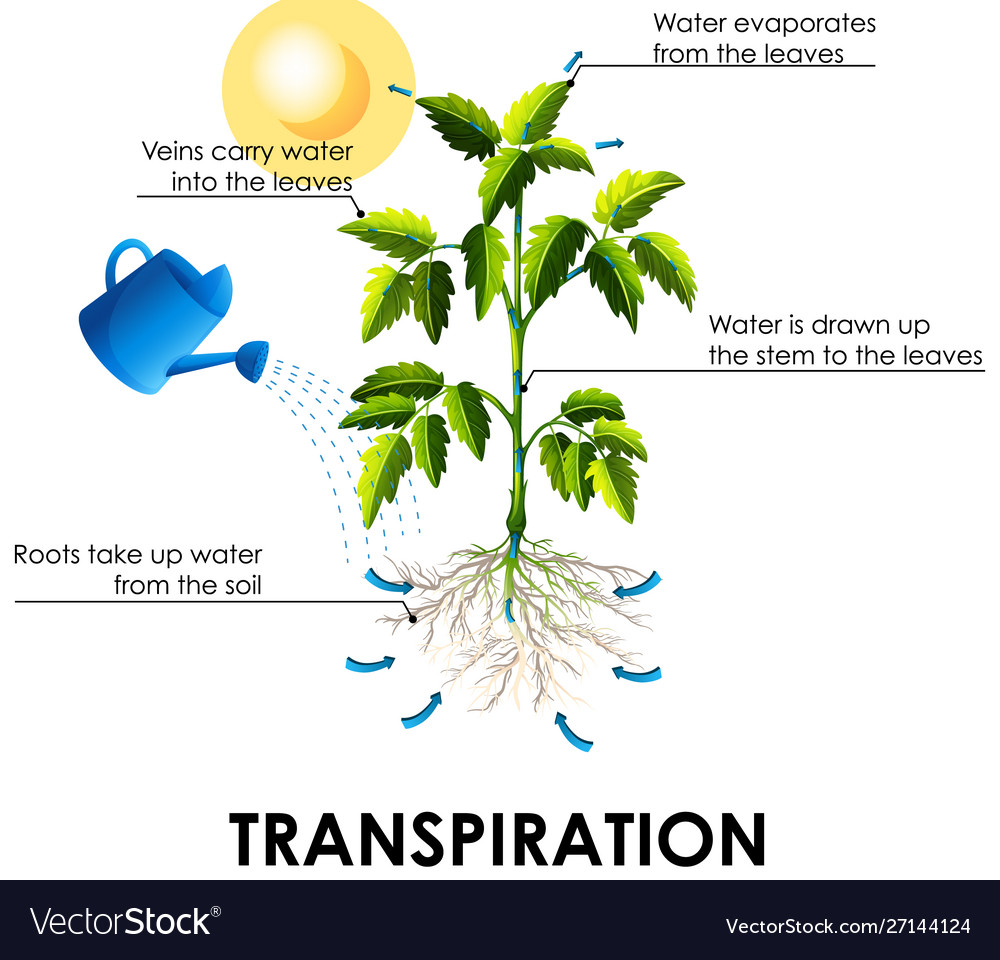 Diagram showing transpiration with plant and water From vectorstock.com
Diagram showing transpiration with plant and water From vectorstock.com
Transpiration occurs because plants take in more water than they actually need at a given. When the plant opens its stomata to let in carbon dioxide, water on the surface of the cells of the spongy mesophyll. The extra water is excreted out to the atmosphere by the leaves in the form of water vapours through stomatal openings. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from a plant�s leaves, stem , or flowers. The loss of water in the form of vapor from the living tissues of aerial parts of plant such as leaf, stem, leaves etc. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples
This water thus transported from roots to leaves helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Transpiration is an important process for the plant, but it is harmful to them also. Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Transpiration is an important process for the plant, but it is harmful to them also. Transpiration is really essential for keeping moisture conditions in the environment. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from a plant�s leaves, stem , or flowers.
 Source: soulmateszz.blogspot.com
Source: soulmateszz.blogspot.com
Plants are cooled down by the loss of their water vapor when the temperature rises above 90f, and water from stems and roots is pushed upward or is pulled into the leaves as well. Definition of fruit • transpiration or water cycle: Roots consume some amount of water from the soil and the rest evaporates in the atmosphere. The passage of watery vapor from a living body (as of a plant) through a membrane or pores. It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration.
 Source: flexiprep.com
Source: flexiprep.com
Transpiration is an important process for the plant, but it is harmful to them also. Parts of plants such as stems, small pores on leaves, and flowers evaporate the water to the atmosphere. It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. Transpiration is of three types, based on the mode of water loss. Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Due to the continuous elimination of water from the plant body, there is a balance of water maintained within the plant. Let us do a quick revision of this topic. Transpiration is the process by which plants absorb water from the soil, circulate it to all the branches and leaves to eventually release water vapor in the atmosphere through the pores of the leaves. A plant does not use most of the water that it absorbs. Plant translocation refers to the transfer of substances within different parts of a plant.
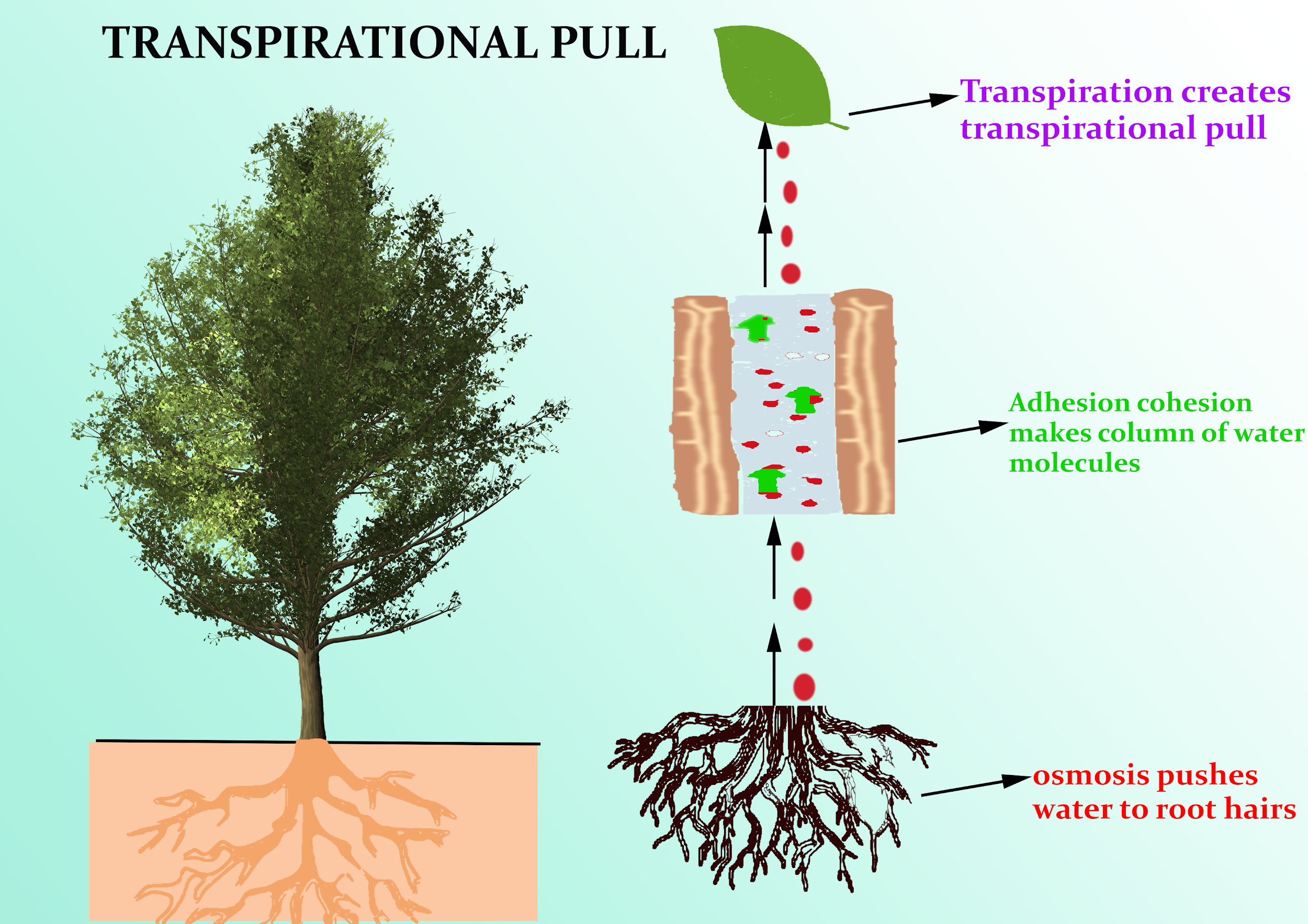 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Evapotranspiration can be defined as the sum of all forms of evaporation plus transpiration, but here at the water science school, we�ll be defining it as the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. The amount of water lost by a plant depends on its size, the light intensity, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and soil water supply. It maintains osmosis and keeps. A plant does not use most of the water that it absorbs.
 Source: vectorstock.com
Source: vectorstock.com
Evapotranspiration can be defined as the sum of all forms of evaporation plus transpiration, but here at the water science school, we�ll be defining it as the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants. Is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts especially from leaves but also from stems and flowers. Transpiration is an important process for the plant, but it is harmful to them also. A human releases its excessive water through sweating, whereas transpiration is the term used in the case of plants. Transpiration is the process in which plants release the water inside it in the form of moisture or water vapor.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
| meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Plants’ stomata undergo transpiration in order to lose water vapor. Transpiration occurs because plants take in more water than they actually need at a given. Let us do a quick revision of this topic. Transpiration can be described as the loss of water from the living tissues of aerial parts of the plant in the form of water vapour.
 Source: vectorstock.com
Source: vectorstock.com
Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular. Transpiration is really essential for keeping moisture conditions in the environment. Definition of transpiration in plants. This loss of water in the form of vapours from the aerial parts of. A water plant, for example, uses water at a much higher rate than a plant that grows in a more arid climate.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The extra water is excreted out to the atmosphere by the leaves in the form of water vapours through stomatal openings. | meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Transpiration in plants refers to the natural process in which a plant releases excessive water into the atmosphere as water vapours like a human body does. In general, the rate of transpiration is proportional to the gradient in water vapor concentration between sources of water within the plant and the bulk atmosphere and the total. A human releases its excessive water through sweating, whereas transpiration is the term used in the case of plants.
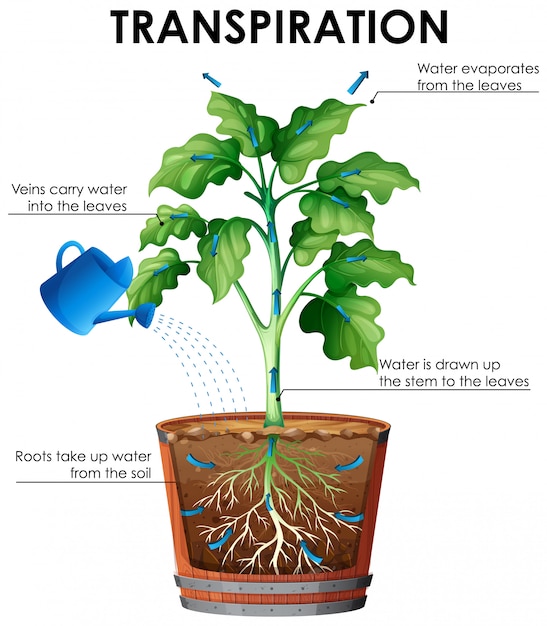 Source: freepik.com
Source: freepik.com
Types, mechanism, affecting factors and significance define transpiration and its significance?. It maintains osmosis and keeps. Evapotranspiration can be defined as the sum of all forms of evaporation plus transpiration, but here at the water science school, we�ll be defining it as the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants. The loss of water in the form of vapor from the living tissues of aerial parts of plant such as leaf, stem, leaves etc. Transpiration is the process that enables plants to take in and use water.
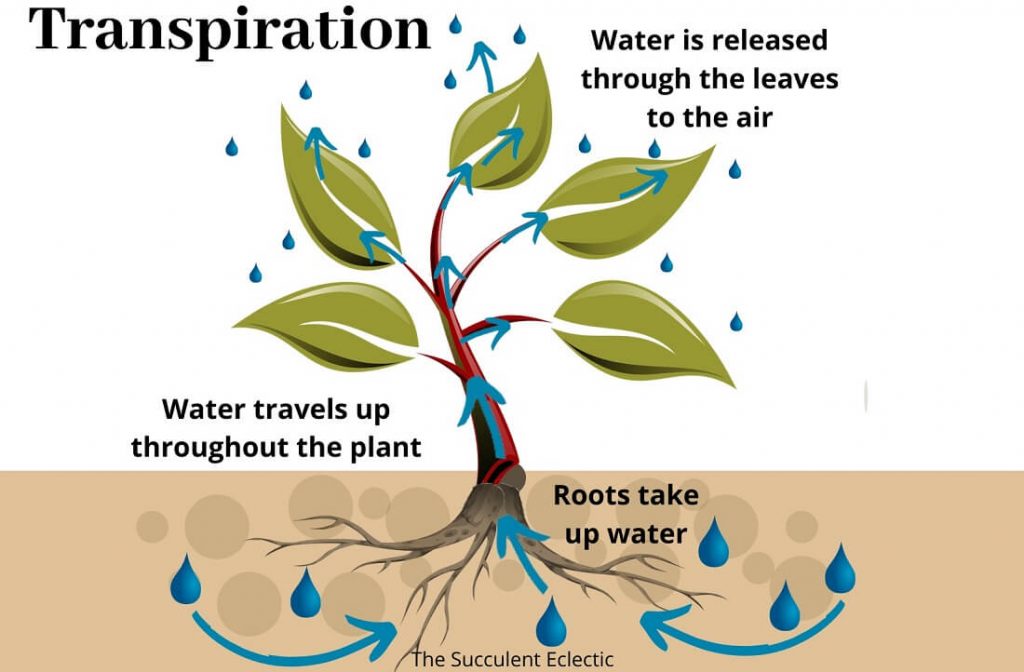 Source: thesucculenteclectic.com
Source: thesucculenteclectic.com
The meaning of transpiration is the act or process or an instance of transpiring; The amount of water lost by a plant depends on its size, the light intensity, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and soil water supply. The loss of water in the form of vapor from the living tissues of aerial parts of plant such as leaf, stem, leaves etc. In general, the rate of transpiration is proportional to the gradient in water vapor concentration between sources of water within the plant and the bulk atmosphere and the total. In simple terms, it is the removal of water vapour from the surface of the plant, mostly leaves.
 Source: vectorstock.com
Source: vectorstock.com
Is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts especially from leaves but also from stems and flowers. Definition of fruit • transpiration or water cycle: Transpiration is defined as the physiological loss of water in the form of water vapor, mainly from the stomata in leaves, but also through evaporation from the surfaces of leaves, flowers, and stems. In simple terms, it is the removal of water vapour from the surface of the plant, mostly leaves. Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Plant translocation refers to the transfer of substances within different parts of a plant. This section of the water science school discusses the earth�s natural water cycle without human interference. Transpiration is really essential for keeping moisture conditions in the environment. It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. Transpiration in plants | definition, types, stomatal movements, factors affecting, advantages.
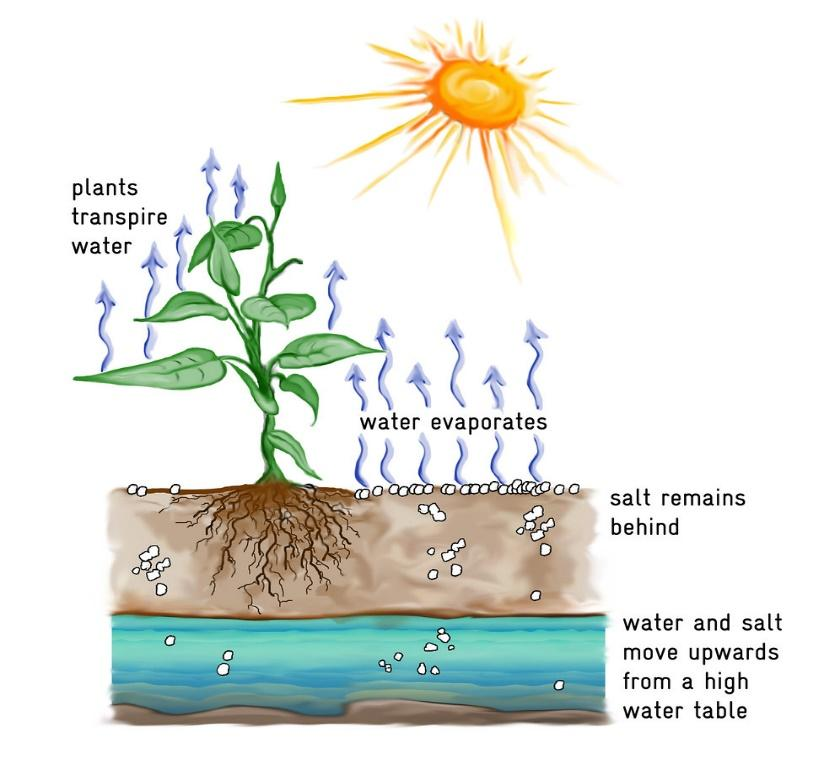 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Transpiration is of three types, based on the mode of water loss. Transpiration, in botany, a plant’s loss of water, mainly through the stomates of leaves. A plant does not use most of the water that it absorbs. Transpiration is an important process for the plant, but it is harmful to them also. Explore the definition and mechanism of plant translocation and discover material movement and transport.
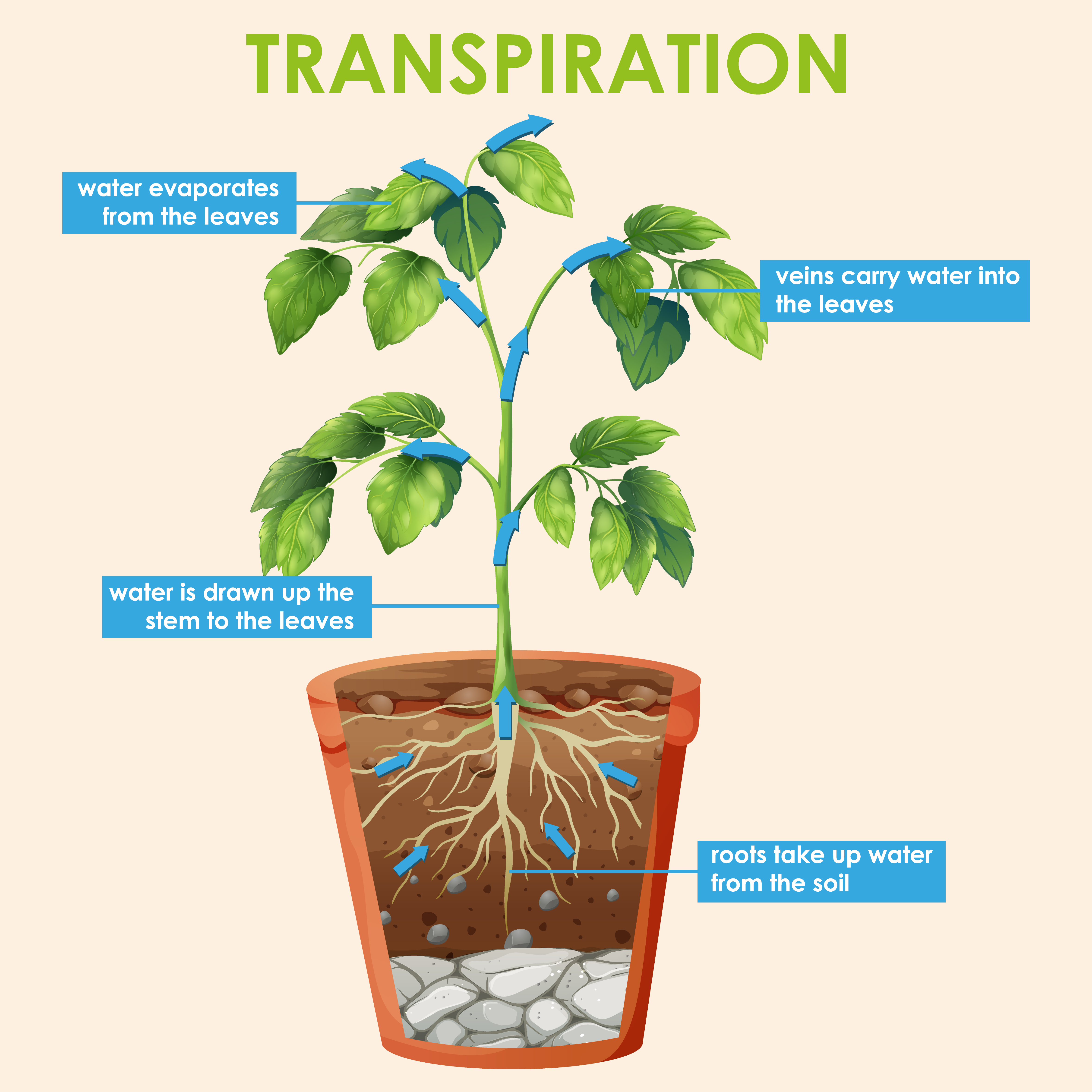 Source: vecteezy.com
Source: vecteezy.com
Plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil. Definition of fruit • transpiration or water cycle: When the plant opens its stomata to let in carbon dioxide, water on the surface of the cells of the spongy mesophyll. The extra water is excreted out to the atmosphere by the leaves in the form of water vapours through stomatal openings. Leaf surfaces are dotted with pores called stomata (singular.
 Source: freepik.com
Source: freepik.com
Transpiration is defined as the physiological loss of water in the form of water vapor, mainly from the stomata in leaves, but also through evaporation from the surfaces of leaves, flowers, and stems. Transpiration in plants refers to the natural process in which a plant releases excessive water into the atmosphere as water vapours like a human body does. Due to the continuous elimination of water from the plant body, there is a balance of water maintained within the plant. Hence, most plants, especially xerophytes, adopt various modes both morphologically and anatomically to reduce excessive transpiration. Transpiration is of three types, based on the mode of water loss.
 Source: brainly.in
Source: brainly.in
This is known as transpiration. Transpiration is of three types, based on the mode of water loss. Plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil. Parts of plants such as stems, small pores on leaves, and flowers evaporate the water to the atmosphere. Evapotranspiration can be defined as the sum of all forms of evaporation plus transpiration, but here at the water science school, we�ll be defining it as the sum of evaporation from the land surface plus transpiration from plants.
 Source: eschool.iaspaper.net
Source: eschool.iaspaper.net
It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. The passage of watery vapor from a living body (as of a plant) through a membrane or pores. Transpiration is defined as the physiological loss of water in the form of water vapor, mainly from the stomata in leaves, but also through evaporation from the surfaces of leaves, flowers, and stems. When the plant opens its stomata to let in carbon dioxide, water on the surface of the cells of the spongy mesophyll. Transpiration occurs because plants take in more water than they actually need at a given.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
Hence, most plants, especially xerophytes, adopt various modes both morphologically and anatomically to reduce excessive transpiration. Plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil. In simple terms, it is the removal of water vapour from the surface of the plant, mostly leaves. Stomatal transpiration is the evaporation of water from a plant’s stomata. The amount of water lost by a plant depends on its size, the light intensity, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and soil water supply.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title transpiration in plants definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






