Your Transportation in plants images are ready. Transportation in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Transportation in plants files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for transportation in plants images information connected with to the transportation in plants keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
Transportation In Plants. These tissues are made up of elongated dead cells and arranged as continuous vessels. Sieve tubes, companion cells, and vascular parenchyma. After that, they release oxygen and water vapor. • in rooted plants, transport in xylem is unidirectional, from roots to stems.
 Transport System Flowering Plants From sites.google.com
Surface tension holding the water molecules together as they are transported through the plant. In rooted plants, transport in xylem (of water and minerals) is essentially unidirectional, from roots to the stems. • organic compound synthesized in leaves and are exported to other parts of the plant including storage organs. Adhesion allows water to stick to the organic tissues of a plant. The uptake and release of water and solute by individual cells. Plant transport various substances like gases, minerals, water, hormone and organic solutes to short distance (one cell to another) or long distance as water from roots to tips of stem.
Transportation is the process of movement of water and minerals to all parts of the plant body.
Phloem is responsible for the movement of food from leaves to other parts of the plant phloem. The following points highlight the three methods of transport in plants. Plants absorb water and minerals from soil by roots and transport to the leaves. Plants use slow transport system but large as required in tall plants to transport energy from leaves and raw materials form roots. An important aspect that needs to be considered is the direction of transport. Arial ms pgothic garamond wingdings calibri times new roman chalkboard bold verdana bordure 1_bordure transport in plants xylem phloem transport in the xylem movement of minerals to.
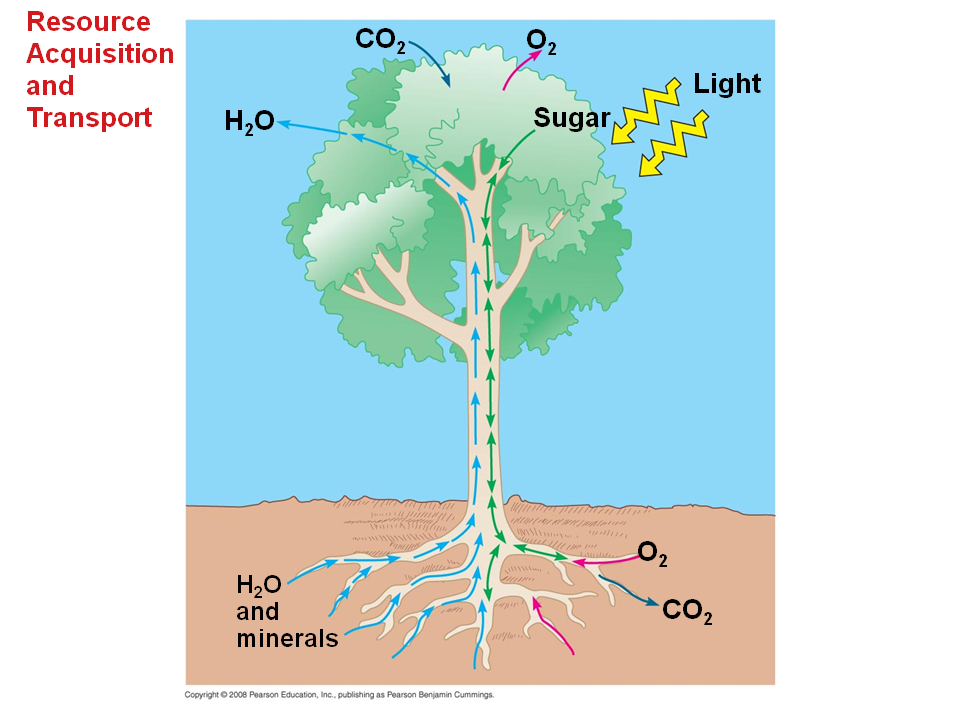
The arrangement of cells in a tissue depends on the function to be performed by the tissue. Transportation is the process of transporting water, minerals and food to all parts of the plant body. It occurs along the concentration gradient, i.e., from region of higher concentration to region of lower concentration provided. • organic compound synthesized in leaves and are exported to other parts of the plant including storage organs. What about transport in plants, how does a redwood, one of the tallest trees in the world, move water from the soil to the needles on its tallest branches over 300 ft in the air?
 Source: sites.google.com
There are three forces involved in this process of transporting water in plants. Surface tension holding the water molecules together as they are transported through the plant. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while. The uptake and release of water and solute by individual cells. It takes place with the help of a conducting tissue called phloem.
The leaves are the food production centres. The transport of food in plants is called translocation. Transportation in plants matthew gibson joliet west high school 401 n. Phloem tissue is inclusive of 3 different types of cells: A tissue is a group of similar cells which work together to perform a particular function.
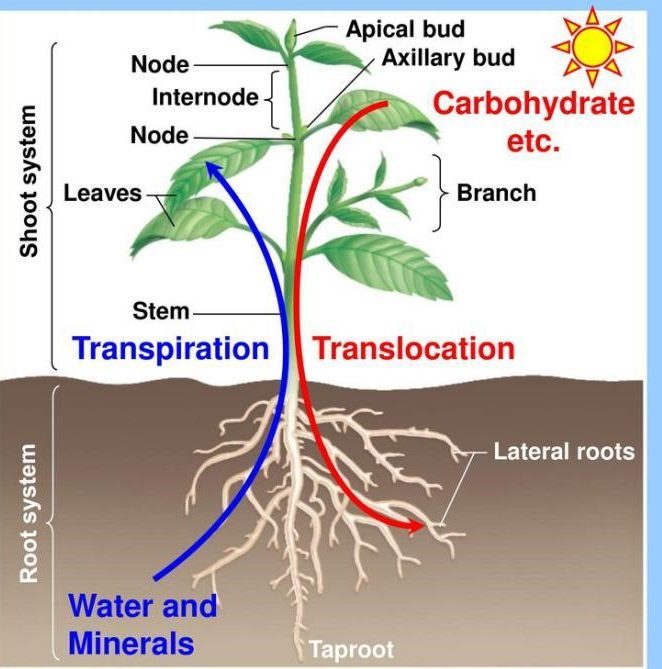 Source: biologyease.com
Source: biologyease.com
An important aspect that needs to be considered is the direction of transport. In rooted plants, transport in xylem (of water and minerals) is essentially unidirectional, from roots to the stems. After that, they release oxygen and water vapor. They use several processes such as translocation, absorption, storage. The transport of food in plants is called translocation.
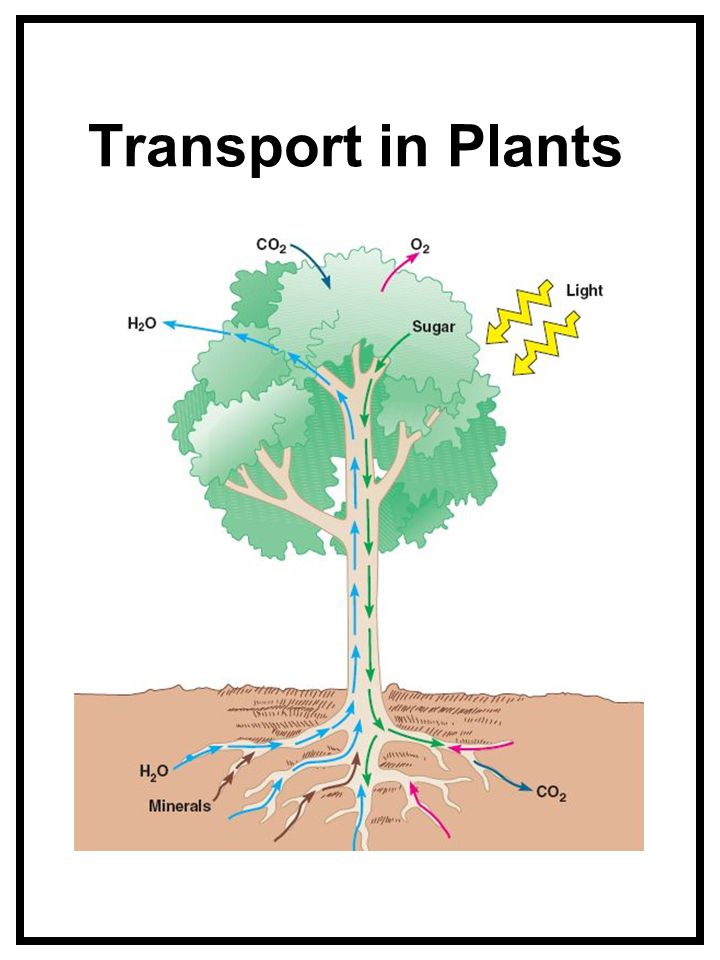
An important aspect that needs to be considered is the direction of transport. Phloem transports glucose, amino acids and other substances from leaves to root, shoot, fruits and seeds. The uptake and release of water and solute by individual cells. • the mineral nutrients are transported upwards • if any plant part goes under senescence, nutrients will be withdrawn from that part and moved to growing parts. Aerial parts) of the plant is known as transpiration.
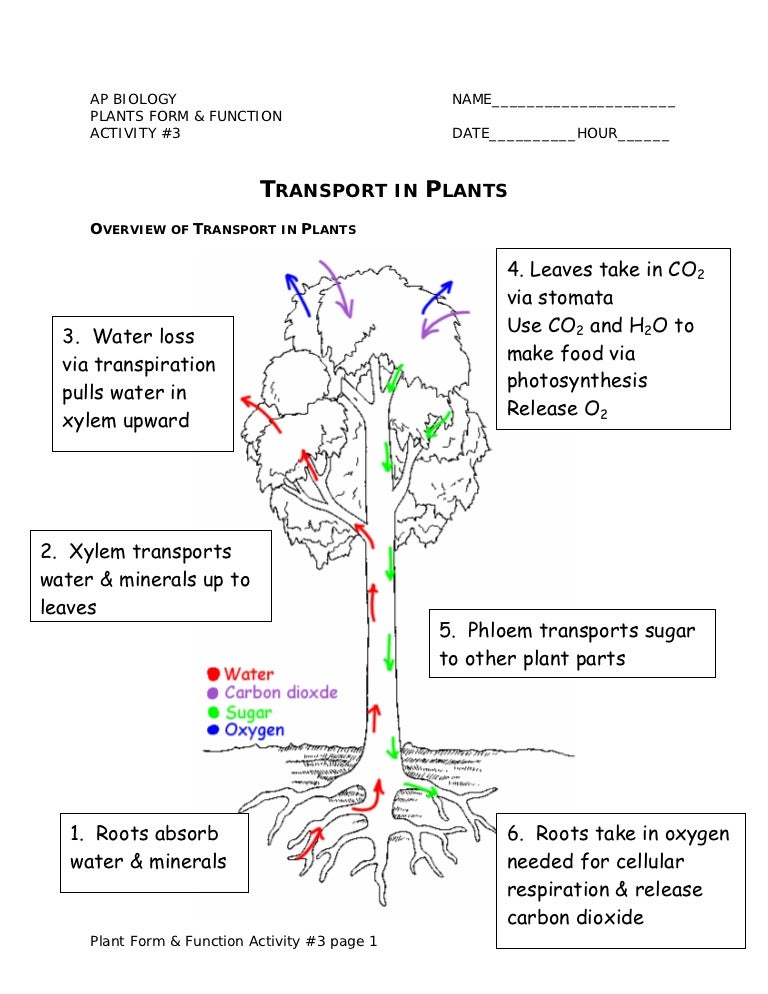 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Long distance transport occurs through vascular system, xylem and phloem called translocation through mass flow. Means of transportation in plants. By this process, plants synthesize their food in the leaves. Desert plant (xerophytes) and plants that grow on other plants (epiphytes) have limited access to water. Transportation in plants matthew gibson joliet west high school 401 n.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
4/6/2007 12:51:07 pm document presentation format: • in rooted plants, transport in xylem is unidirectional, from roots to stems. • transportation is very important in plants.as leaves systhesis their food by photosynthesis and roots absorb water and minerals the food need to be transported to every part of the cell for proper functioning of the plant • plants transport system will move energy stores from leaves. The plant body is generally divided into roots, stem, and leaves. It takes place with the help of a conducting tissue called phloem.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while. As the distance between roots and leaves is large, diffusion is not sufficient to provide raw materials to leaves and energy to roots. • the mineral nutrients are transported upwards • if any plant part goes under senescence, nutrients will be withdrawn from that part and moved to growing parts. Cohesion keeps the water molecules together. Transport system is less elaborate in plants because they are comparatively less active and require less supply of materials either from outside or synthesised by plants themselves.
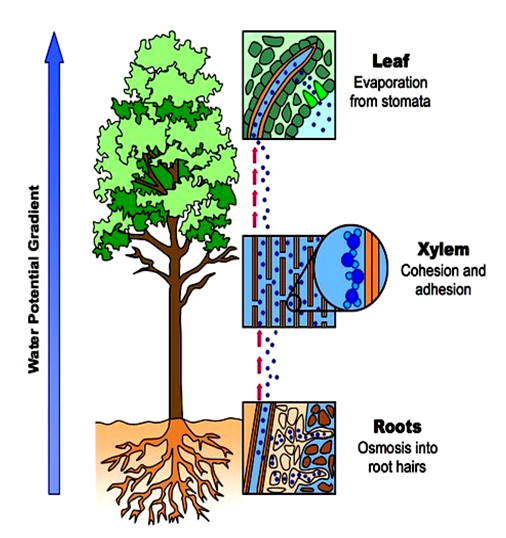 Source: ombiology4u.blogspot.com
Source: ombiology4u.blogspot.com
This lesson is designed for middle school and high school. What about transport in plants, how does a redwood, one of the tallest trees in the world, move water from the soil to the needles on its tallest branches over 300 ft in the air? Desert plant (xerophytes) and plants that grow on other plants (epiphytes) have limited access to water. Transportation is the process of transporting water, minerals and food to all parts of the plant body. Phloem tissue is inclusive of 3 different types of cells:
 Source: scholarzhub.com
Source: scholarzhub.com
Movement by diffusion is passive and slow. Plants have primarily two types of tissues that help transport water, minerals, and nutrients. As the distance between roots and leaves is large, diffusion is not sufficient to provide raw materials to leaves and energy to roots. The following points highlight the three methods of transport in plants. Transportation is the process of transporting water, minerals and food to all parts of the plant body.
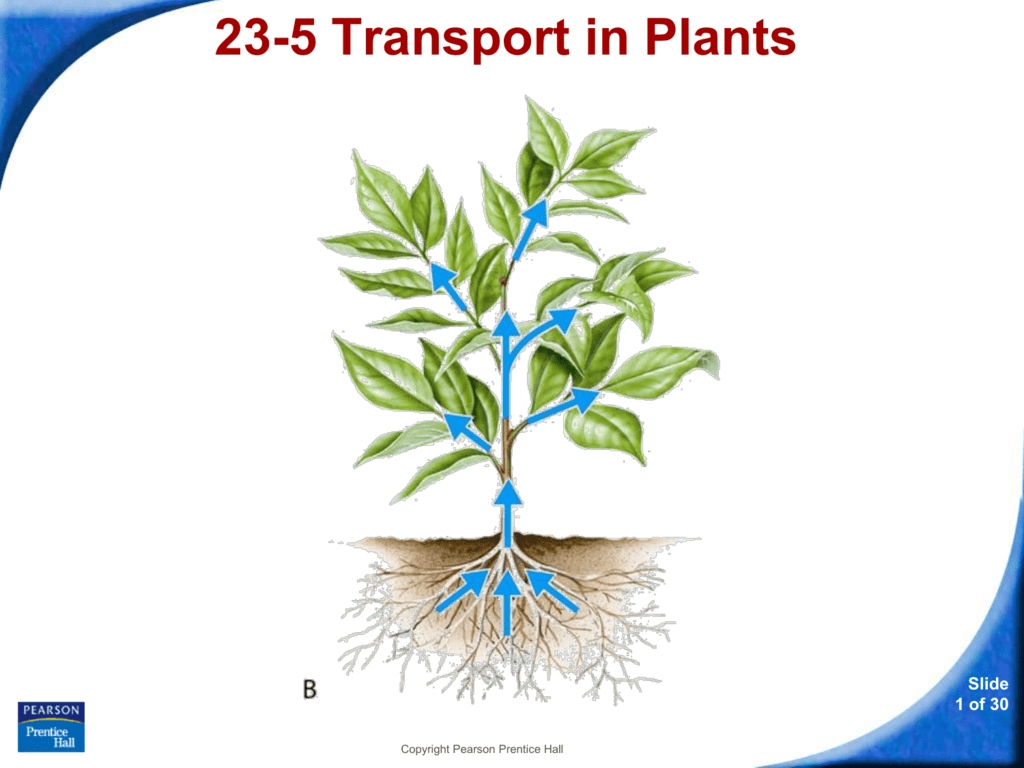 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
All organisms require food and water for their survival. It is responsible for the transportation of water and mineral salts from the roots to different parts of a plant. (that’s over 30 stories high!) or how does a carrot transport the sugars made in its green, leafy tops below the surface of the soil to grow a. The uptake and release of water and solute by individual cells. Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
By this process, plants synthesize their food in the leaves. Transport in plants refers to the process of carrying water, minerals, and nutrients across various parts of the plant body. The transport of food in plants is called translocation. There are three forces involved in this process of transporting water in plants. Phloem transports glucose, amino acids and other substances from leaves to root, shoot, fruits and seeds.
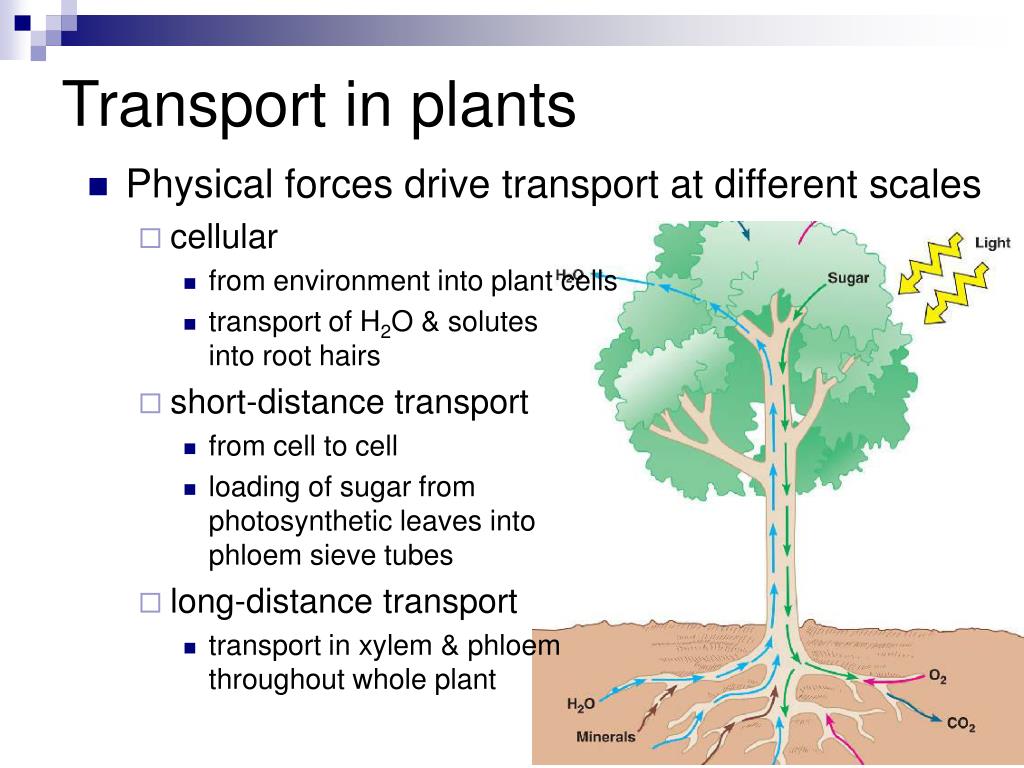 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
These tissues are made up of elongated dead cells and arranged as continuous vessels. Long distance transport occurs through vascular system, xylem and phloem called translocation through mass flow. 1) students will understand how the forces of adhesion and cohesion and the process of transpiration aid in the. The following points highlight the three methods of transport in plants. Phloem transports glucose, amino acids and other substances from leaves to root, shoot, fruits and seeds.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Short distance transport of substances from one cell to another. • in rooted plants, transport in xylem is unidirectional, from roots to stems. This pressure moves the material in the phloem to tissues which have less pressure. Plants use a slow transport system but large as required in tall plants to transport energy from leaves and raw materials from roots. 4/6/2007 12:51:07 pm document presentation format:
 Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
Long distance transport occurs through vascular system, xylem and phloem called translocation through mass flow. Definition of transportation in plants. Means of transportation in plants. Transport in plants refers to the process of carrying water, minerals, and nutrients across various parts of the plant body. Transport of food compared to the xylem and its movement of water and minerals, the transportation of food in plants is a bit more complex.
 Source: yaclass.in
Source: yaclass.in
Transport system is less elaborate in plants because they are comparatively less active and require less supply of materials either from outside or synthesised by plants themselves. The plant body is generally divided into roots, stem, and leaves. Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. 4/6/2007 12:51:07 pm document presentation format: Transport in plants refers to the process of carrying water, minerals, and nutrients across various parts of the plant body.
 Source: mrexham.com
Source: mrexham.com
Aerial parts) of the plant is known as transpiration. Transportation is the process of transporting water, minerals and food to all parts of the plant body. Transport of food compared to the xylem and its movement of water and minerals, the transportation of food in plants is a bit more complex. A tissue is a group of similar cells which work together to perform a particular function. Plant transport various substances like gases, minerals, water, hormone and organic solutes to short distance (one cell to another) or long distance as water from roots to tips of stem.

Sieve tubes, companion cells, and vascular parenchyma. These tissues are made up of elongated dead cells and arranged as continuous vessels. As the distance between roots and leaves is large, diffusion is not sufficient to provide raw materials to leaves and energy to roots. By taking in carbon dioxide from the air, minerals, and water from the soil, plants make their own food. What about transport in plants, how does a redwood, one of the tallest trees in the world, move water from the soil to the needles on its tallest branches over 300 ft in the air?
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title transportation in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






