Your Turgor in plants images are available in this site. Turgor in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Turgor in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for turgor in plants pictures information connected with to the turgor in plants keyword, you have visit the ideal site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Turgor In Plants. Turgor pressure is the force exerted by stored water against a cell wall. However, the membrane does not allow salts or nutrients to pass out of the cell. This pressure is created by the vacuole. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid.
 Turgor Pressure On Plant Cells Stock Illustration From dreamstime.com
Turgor Pressure On Plant Cells Stock Illustration From dreamstime.com
Plant cell turgor is generated by water influx due to the osmolyte concentration gradient through the cell wall and the plasma membrane behaving as an osmotic barrier. Mean leaf water potentials and turgor pressures, and standard deviations for each cultivar and for all three temperature regimes, are listed in supplemental table s1. The commonality of traits in halophytes and glycophytes is emphasised by flowers et al. Osmotic adjustment is of course essential for adapting plants to soils of low water potential, but may. Turgor is caused by the osmotic flow of water from a region of low solute concentration outside the cell vacuole cell that has a higher concentration of solute. Plant cells have both a cell membrane and a cell membrane, but animal cells only have one.
Abstract several reactive oxygen species (ros) are continuously produced in plants as byproducts of aerobic metabolism.
Abstract several reactive oxygen species (ros) are continuously produced in plants as byproducts of aerobic metabolism. In plants, turgor is also known as hydrostatic pressure or water potential or turgor pressure. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Turgor pressure in plants is the force exerted by stored water on a cell wall. What is turgor pressure in a plant cell?turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Turgor is caused by the osmotic flow of water from a region of low solute concentration outside the cell vacuole cell that has a higher concentration of solute.
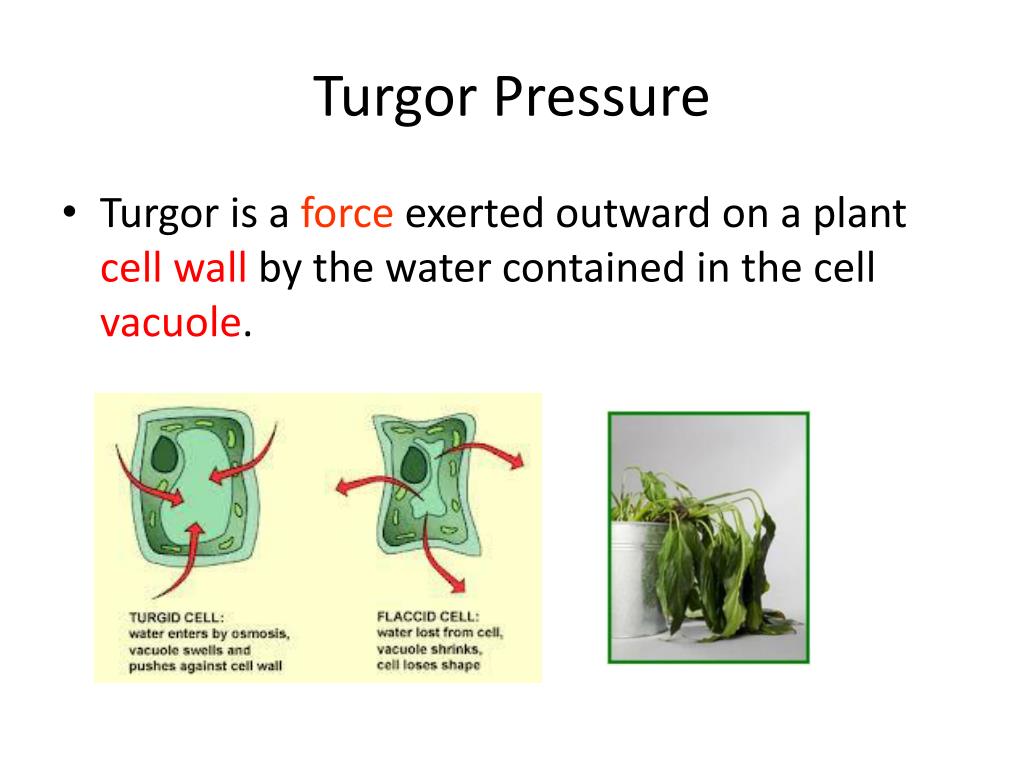 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt. The turgor pressure that is generated by the cell is responsible for providing the motive force for continued cell expansion and shape generation (see chapter 20; Turgor pressures across cultivars averaged 0.45 mpa in the day time, and 0.60 pa at night, with no significant differences among co 2 treatments. The term turgor refers to the water pressure within a plant’s cells. It is also known as hydrostatic pressure and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a specific point within it when it is at equilibrium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Along with size, rigidity of the cell is also caused by turgor pressure ; When the vacuole is full of water is pressed against the cell wall. Turgor definition, the normal distention or rigidity of plant cells, resulting from the pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell walls. By pushing against the cell wall it makes is nice and firm. It occurs only in a plant cell.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. A lower pressure results in a wilted cell or plant structure (i.e. In contrast to a mammal cell, its cell membrane prevents it from bursting despite considerable water inflow. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Turgor pressure occurs when a plant’s cells become turgid due to the pressure exerted by water molecules on the cell wall.
 Source: homeschoolersresources.blogspot.com
Source: homeschoolersresources.blogspot.com
Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Plant cells need a certain amount of pressure to make sure that the cell wall stays rigid. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. (2010), particularly the ability for osmotic adjustment.
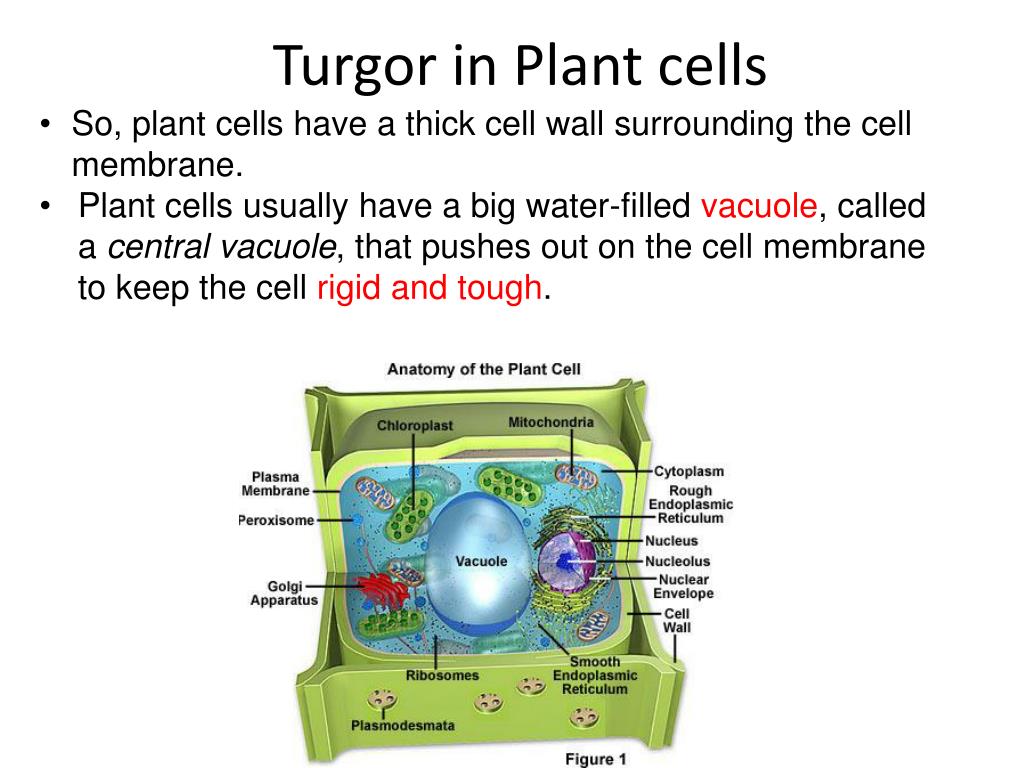 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt. While the cell walls of. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Hence, leaf droops down for a short time. Turgor pressure is the force exerted by stored water against a cell wall.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Hydrostatic pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. Osmotic adjustment is of course essential for adapting plants to soils of low water potential, but may. The commonality of traits in halophytes and glycophytes is emphasised by flowers et al.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Turgor pressure is a chemical process that a plant uses to water its cells, keeping the cells alive. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. The turgor pressure that is generated by the cell is responsible for providing the motive force for continued cell expansion and shape generation (see chapter 20; Turgor pressure is the force exerted by stored water against a cell wall. By pushing against the cell wall it makes is nice and firm.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Examples of turgor movement in plants are: Turgor pressures across cultivars averaged 0.45 mpa in the day time, and 0.60 pa at night, with no significant differences among co 2 treatments. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. This pressure is created by the vacuole. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. It also provides the motive force for leaflet movements, tendril curling, stomatal movements, and. Given the role of turgor in the structural strength of a plant, it is not surprising that dynamic variations in turgor have been implicated in plant movements (sibaoka, 1969; Forterre, 2013), for instance in the circadian movement of leaves. Turgor pressure in plants is the force exerted by stored water on a cell wall.
 Source: vectormine.com
Source: vectormine.com
It is a kind of pressure which is produced due to water. Turgor refers to the fact that plant cells can build up pressure inside their cells. Therefore, plants depend on turgor to maintain their gravity. Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt.what is the It occurs only in a plant cell.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Turgor pressures across cultivars averaged 0.45 mpa in the day time, and 0.60 pa at night, with no significant differences among co 2 treatments. Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt. Examples of turgor movement in plants are: This pressure is created by the vacuole. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Osmotic adjustment is of course essential for adapting plants to soils of low water potential, but may. Osmosis helps maintain a plant’s cellular turgor, and the membrane of the plant’s cells controls the turgor. Depending on the stimuli, turgor and growth movements are common nasties seen in some plants. Plant cells need a certain amount of pressure to make sure that the cell wall stays rigid. The commonality of traits in halophytes and glycophytes is emphasised by flowers et al.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Turgor is involved in cell metabolism, and is often the regulation of turgor pressure, the key to the plant�s response to changes in the environment. Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt. Turgor movement is due to the difference of turgidity of the cells in the lower half and upper half of pulvinus (petiole of leaf). Water passes through the membrane into the middle of the cell and then back out. Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall.
 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Depending on the nature of the ros species, some are highly toxic and rapidly detoxified by various cellular enzymatic. Fungi, protists, bacteria, and plants all secrete various extracellular molecules form together to create a solid wall on the outside of their cells.as water fills the cells, it pushes against the cell membrane and cell wall, producing turgor pressure. Given the role of turgor in the structural strength of a plant, it is not surprising that dynamic variations in turgor have been implicated in plant movements (sibaoka, 1969; Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. Turgor definition, the normal distention or rigidity of plant cells, resulting from the pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell walls.
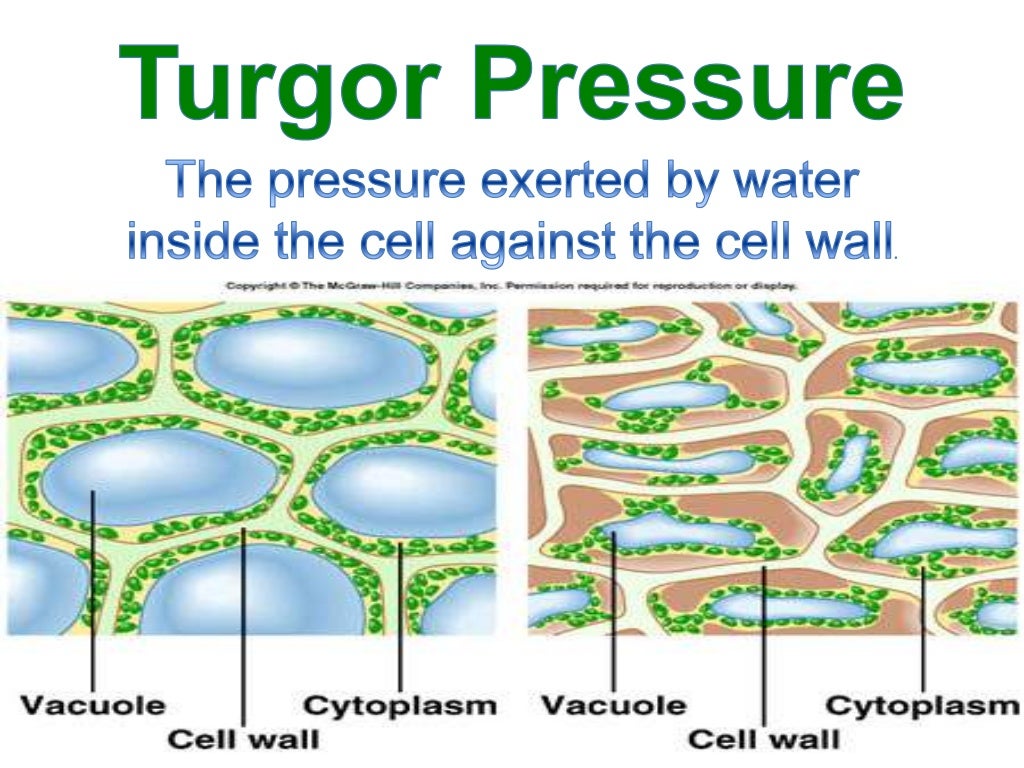 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
The turgor pressure that is generated by the cell is responsible for providing the motive force for continued cell expansion and shape generation (see chapter 20; Examples of turgor movement in plants are: Turgor movement is due to the difference of turgidity of the cells in the lower half and upper half of pulvinus (petiole of leaf). Turgor, pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Forterre, 2013), for instance in the circadian movement of leaves.
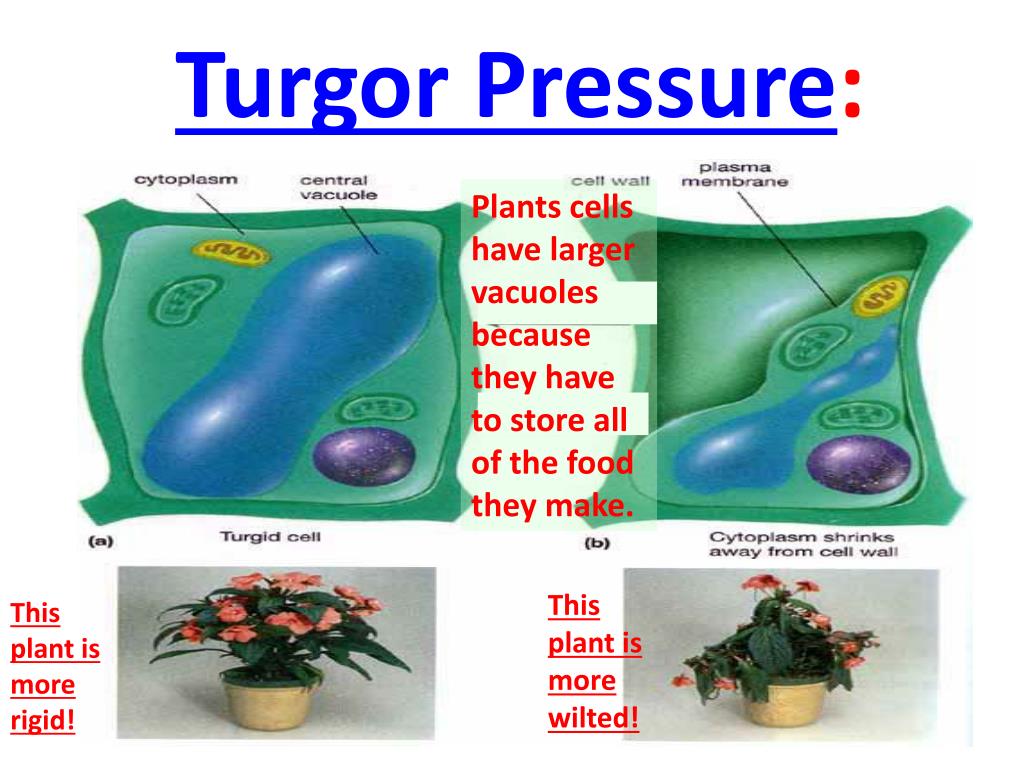 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
If there is too little or too much water. Pressure from fluid within the cell pushing against the cell wall is called turgor pressure. Turgor pressures across cultivars averaged 0.45 mpa in the day time, and 0.60 pa at night, with no significant differences among co 2 treatments. In contrast to a mammal cell, its cell membrane prevents it from bursting despite considerable water inflow. Examples of turgor movement in plants are:

Osmotic adjustment is of course essential for adapting plants to soils of low water potential, but may. If there is too little or too much water. Turgor plays a key role in the opening and closing of stomata (see stoma) in leaves. Turgor is involved in cell metabolism, and is often the regulation of turgor pressure, the key to the plant�s response to changes in the environment. Turgor refers to the fact that plant cells can build up pressure inside their cells.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt. Plant cells have both a cell membrane and a cell membrane, but animal cells only have one. Mean leaf water potentials and turgor pressures, and standard deviations for each cultivar and for all three temperature regimes, are listed in supplemental table s1. Abstract several reactive oxygen species (ros) are continuously produced in plants as byproducts of aerobic metabolism. The turgor pressure of plant cells is typically between 10 5 and 10 6 pa, although higher and lower values exist.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title turgor in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






