Your Vascular tissue in plants images are available. Vascular tissue in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Vascular tissue in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for vascular tissue in plants images information linked to the vascular tissue in plants keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our website always gives you hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Vascular Tissue In Plants. Vascular tissue develops in all organs — root, stem, and leaf — of the plant body. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. The function of the vascular system in plants is conducting dissolved food. Vascular tissue transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant.
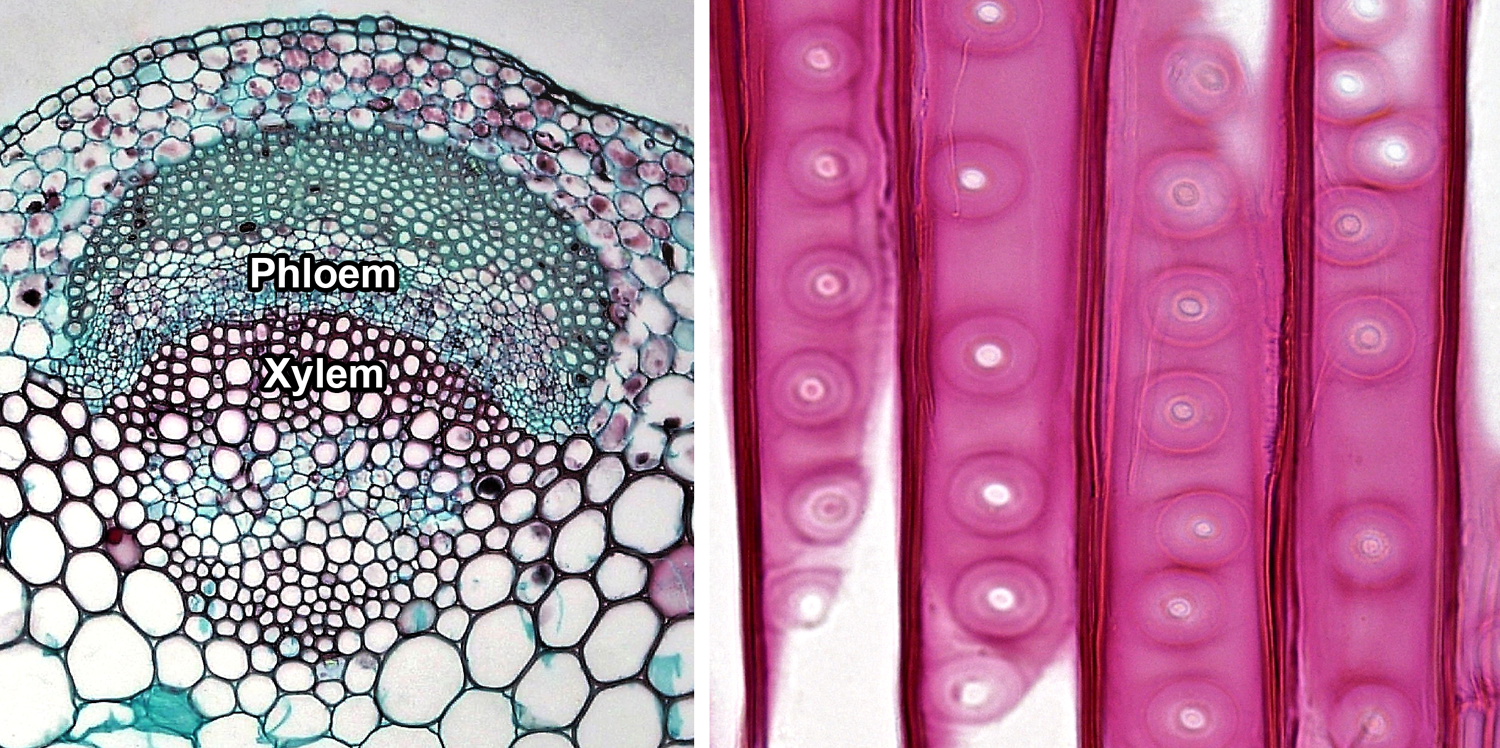 Introduction to Vascular Plant Structure Digital Atlas From digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Introduction to Vascular Plant Structure Digital Atlas From digitalatlasofancientlife.org
One could imagine that life would have developed differently without wood as. Vascular tissue used to transport water and vascular tissue nutrients to great heights, able to feed the tops of trees hundreds of feet high and products of definition photosynthesis to be transported throughout the plant. In stems and roots, the xylem typically lies closer to the interior of the stem with phloem towards the exterior of the stem. There are also two meristems associated with vascular tissue: The vascular tissues include xylem, which conducts water and minerals from the roots upward and throughout the plant, and phloem, which transports dissolved nutrients in all directions within the plant. The vascular system consists of two conducting tissues, xylem and phloem;
Transport water and mineral salts from roots to shoots phloem tissue:
Vascular tissue is made up of xylem and phloem, which transport water and food, respectively, throughout a plant. One could imagine that life would have developed differently without wood as. The vascular tissues are xylem and phloem, and the combination of one xylem and one phloem adjacent to each other is called a vascular bundle. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water. Lower plants, like mosses and algae, don�t have a vascular system and, therefore.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Vascular plants, also called tracheophytes or collectively tracheophyta, form a large group of land plants that have lignified tissues for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. The vascular tissues include xylem, which conducts water and minerals from the roots upward and throughout the plant, and phloem, which transports dissolved nutrients in all directions within the plant. In stems and roots, the xylem typically lies closer to the interior of the stem with phloem towards the exterior of the stem. Vascular tissue is an arrangement of multiple cell types in vascular plants which allows for the transport of water, minerals, and products of photosynthesis to be transported throughout the plant. …primary plant body is the vascular tissue, a continuous system of conducting and supporting tissues that extends throughout the plant body.
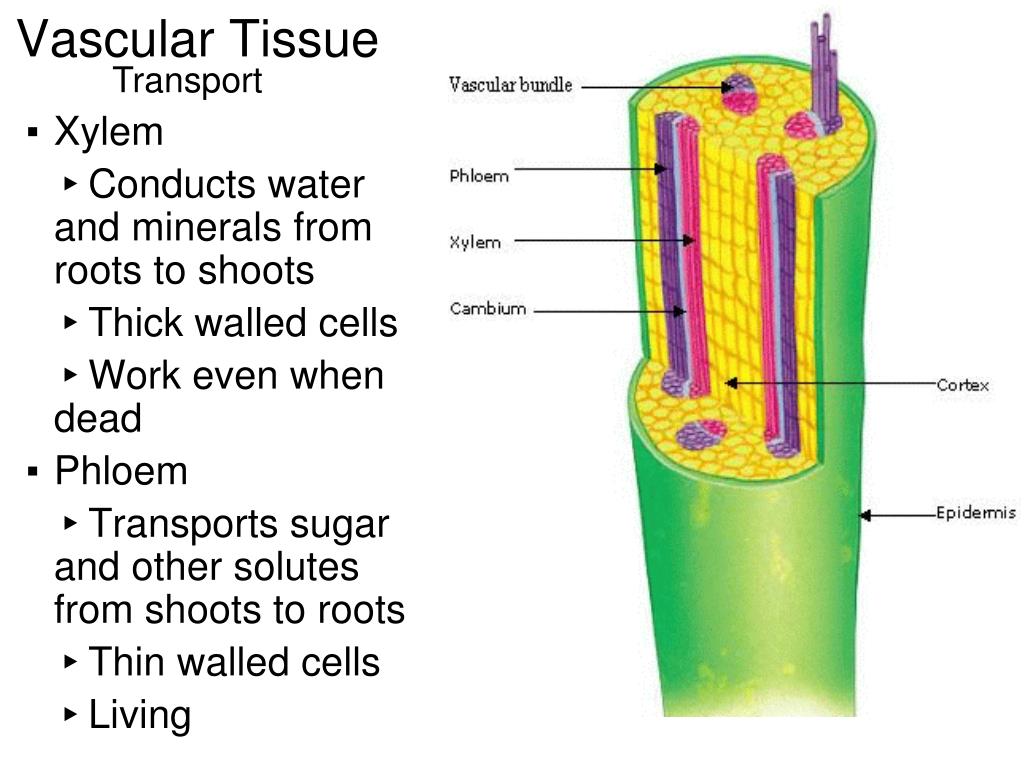 Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. A vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by random house, inc. One could imagine that life would have developed differently without wood as. Vascular tissue is made up of xylem and phloem, which transport water and food, respectively, throughout a plant.
 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Vascular tissue is composed of two types of conducting tissues: Xylem is one of the vascular tissues seen in vascular plants. Vascular tissue is composed of two types of conducting tissues: Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The vascular cambium and the cork cambium.

These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. The vascular tissue in plants is arranged in long, discrete strands called vascular bundles. Vascular plants developed stems comprised of vascular tissue and lignin. These functions of the vascular system are realized through fine regulation of the timing and. They also have other cell types like xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma.
 Source: sciencing.com
Source: sciencing.com
In stems and roots, the xylem typically lies closer to the interior of the stem with phloem towards the exterior of the stem. The leaves of vascular plants have stomata. This conduction of water and nutrients enables plants to grow healthily with all parts receiving the necessary resources whenever they need them. There is a meristem associated with vascular tissue: Vascular plants developed stems comprised of vascular tissue and lignin.
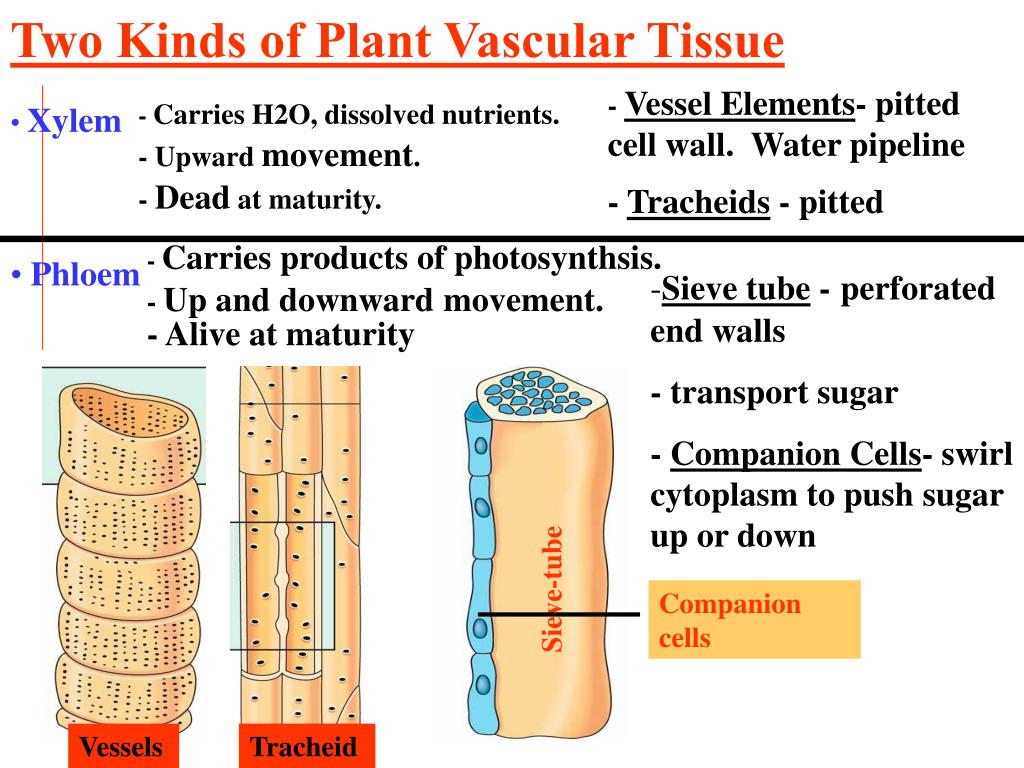 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
(b) a large percentage of cotyledonary nodes appear to have two traces and retain that condition; Vascular tissue, along with several other important plant features, allowed plants to colonize earth�s surface. Vascular tissue used to transport water and vascular tissue nutrients to great heights, able to feed the tops of trees hundreds of feet high and products of definition photosynthesis to be transported throughout the plant. Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. It is composed of two major tissues, xylem and phloem, that are differentiated from the meristemic tissue, procambium.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The plant vascular system is a complicated network of conducting tissues that interconnects all organs and transports water, minerals, nutrients, organic compounds, and various signaling molecules throughout the plant body. This conduction of water and nutrients enables plants to grow healthily with all parts receiving the necessary resources whenever they need them. Its basic function is to transport water from roots to the leaves and stems. …primary plant body is the vascular tissue, a continuous system of conducting and supporting tissues that extends throughout the plant body. The vascular tissues include xylem, which conducts water and minerals from the roots upward and throughout the plant, and phloem, which transports dissolved nutrients in all directions within the plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Transport in plants is carried out by vascular tissues which consist of : All the vascular tissues within a particular plant together constitute the vascular tissue system of that plant. The two types of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, are responsible for moving water, minerals, and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. It also transports nutrients along with water. The vascular cambium and the cork cambium.
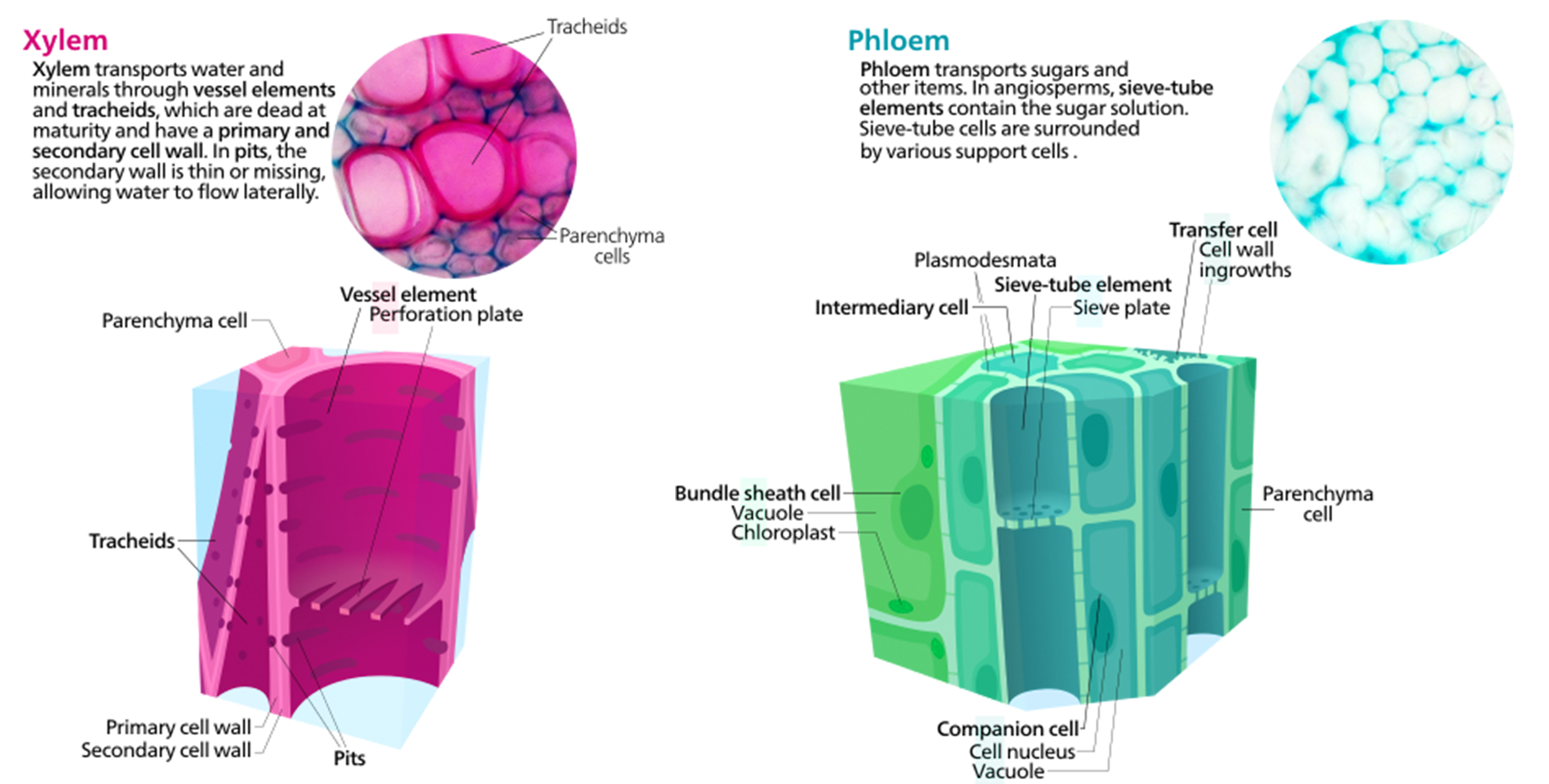 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
A vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. Vascular tissue used to transport water and vascular tissue nutrients to great heights, able to feed the tops of trees hundreds of feet high and products of definition photosynthesis to be transported throughout the plant. Vascular tissue is made up of xylem and phloem, which transport water and food, respectively, throughout a plant. For centuries, humans have grown and used structures based on vascular tissues in plants. The leaves of vascular plants have stomata.
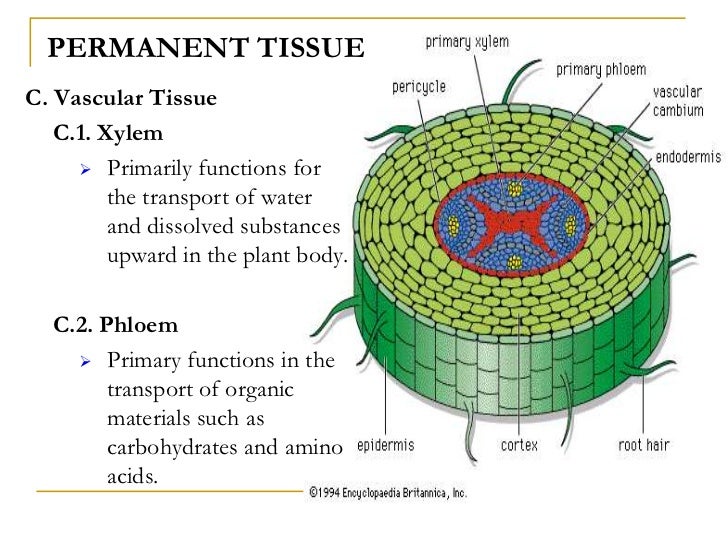 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
…primary plant body is the vascular tissue, a continuous system of conducting and supporting tissues that extends throughout the plant body. It also transports nutrients along with water. …primary plant body is the vascular tissue, a continuous system of conducting and supporting tissues that extends throughout the plant body. Vascular tissue develops in all organs — root, stem, and leaf — of the plant body. Water, nutrients, and carbohydrates are transported through vascular tissue to various areas of the plant.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Phloem tissue acts as a transport system. Today, our planet hosts an enormous diversity of vascular plant life, including such different forms as ferns, redwood trees, oak trees, and orchids. The leaves of vascular plants have stomata. (b) a large percentage of cotyledonary nodes appear to have two traces and retain that condition; Its basic function is to transport water from roots to the leaves and stems.
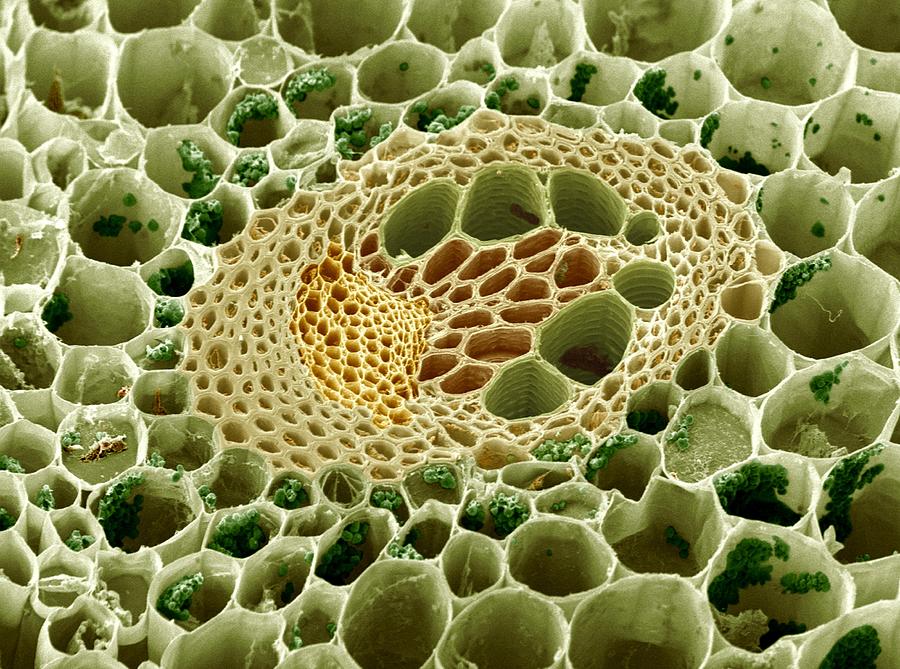 Source: myriverside.sd43.bc.ca
Source: myriverside.sd43.bc.ca
Xylem is one of the vascular tissues seen in vascular plants. These functions of the vascular system are realized through fine regulation of the timing and. Transport photosynthetic product and other organic substances from shoots to other parts (b) a large percentage of cotyledonary nodes appear to have two traces and retain that condition; These bundles include both xylem and phloem, as well as supporting and protective cells.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Vascular tissue is a complex tissue found in vascular plants. A vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. Transport water and mineral salts from roots to shoots phloem tissue: The vascular tissue in plants is arranged in long, discrete strands called vascular bundles. One could imagine that life would have developed differently without wood as.
 Source: csus.edu
Vascular tissue used to transport water and vascular tissue nutrients to great heights, able to feed the tops of trees hundreds of feet high and products of definition photosynthesis to be transported throughout the plant. Due to their vascular tissues, the stems keep tall plants filled with water to prevent them from drying out in the atmosphere. Background the vascular system of plants consists of two main tissue types, xylem and phloem. Transport photosynthetic product and other organic substances from shoots to other parts The vascular tissues of plants, which are composed of specialized conducting tissues, xylem and phloem, form continuous systems through the plant body and provide transport pathways for water, nutrients, and signaling molecules and support a plant body against mechanical stresses.
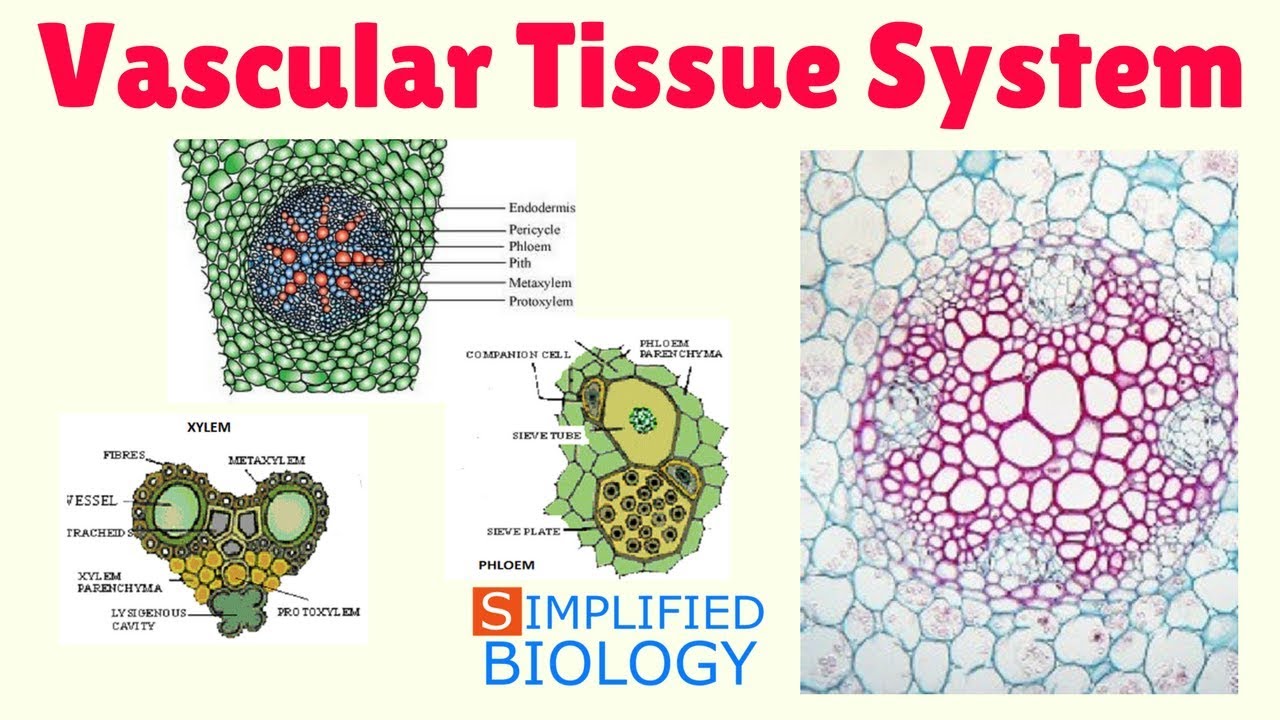 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
They also have other cell types like xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma. The vascular tissues are xylem and phloem, and the combination of one xylem and one phloem adjacent to each other is called a vascular bundle. Transport photosynthetic product and other organic substances from shoots to other parts One defining characteristic of the vascular plant is root, stem, and leaves. The leaves of vascular plants have stomata.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The vascular tissue within provides a means of. Today, our planet hosts an enormous diversity of vascular plant life, including such different forms as ferns, redwood trees, oak trees, and orchids. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water. The vascular system consists of two conducting tissues, xylem and phloem; The primary vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem, which are specialized, complex tissues in plants.
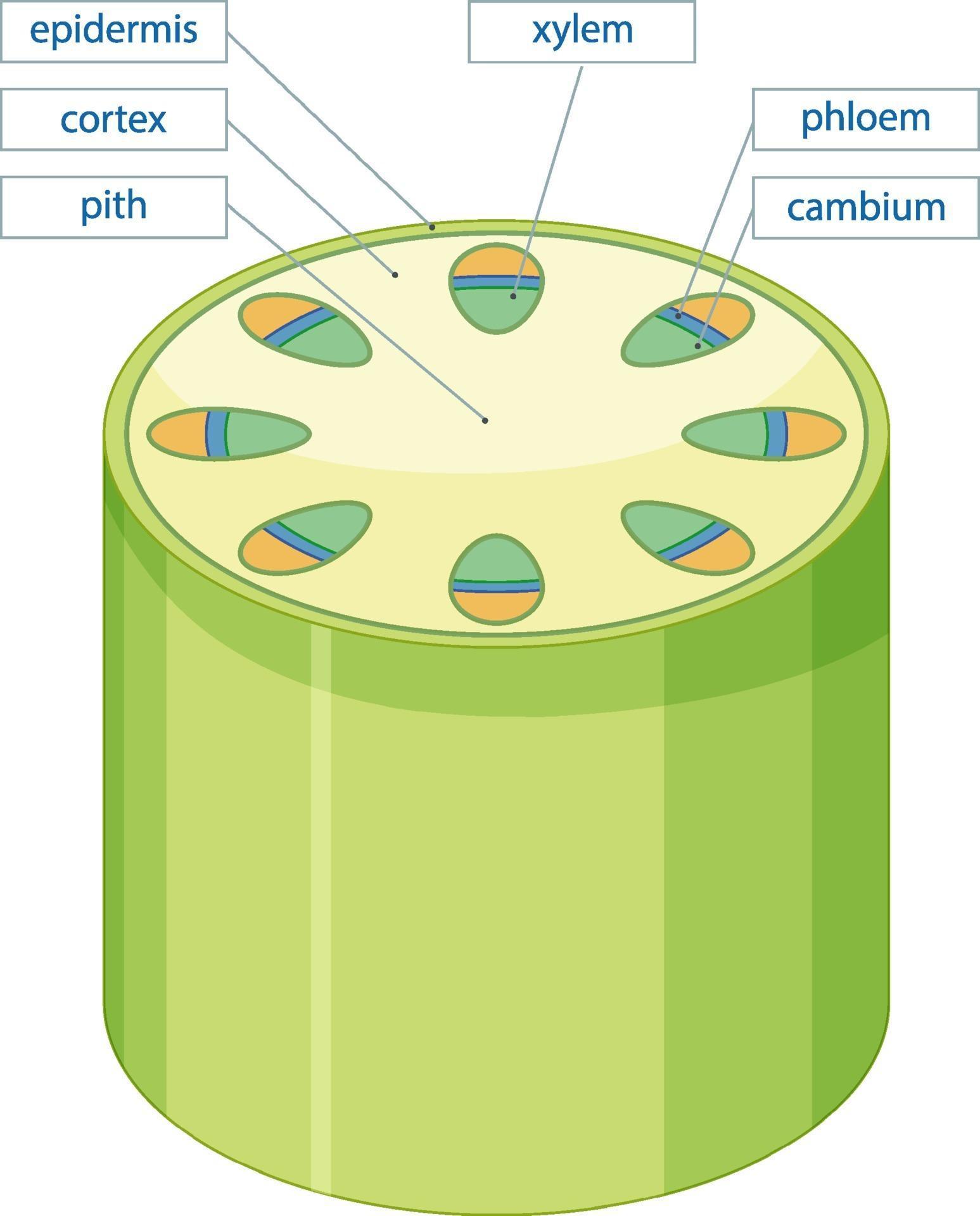 Source: vecteezy.com
Source: vecteezy.com
Vascular tissue transports water, minerals, and sugars to different parts of the plant. The vascular tissues of plants, which are composed of specialized conducting tissues, xylem and phloem, form continuous systems through the plant body and provide transport pathways for water, nutrients, and signaling molecules and support a plant body against mechanical stresses. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. Xylem tissue transports water and nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant, and also plays a role in structural support in the stem. The function of the vascular system in plants is conducting dissolved food.
 Source: siyavula.com
Source: siyavula.com
The leaves of vascular plants have stomata. Transport in plants is carried out by vascular tissues which consist of : The vascular tissue in plants is arranged in long, discrete strands called vascular bundles. Vascular tissue is composed of two types of conducting tissues: One could imagine that life would have developed differently without wood as.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title vascular tissue in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







