Your Water movement in plants images are available in this site. Water movement in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Water movement in plants files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for water movement in plants images information related to the water movement in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Water Movement In Plants. Turgor pressure helps to keep the plant erect and is accomplished when the plasma membrane pushes against the cell wall. The root system takes up water and minerals from the soil, while the shoot system, consisting of leaves and. Osmosis plays a central role in the movement of water between cells and various compartments within plants. The mineral ions from the soil are pushed into the root vascular tissues by diffusion and as a result, the pressure inside the xylem increases.
 Diagram illustrating the movement of water through a plant From flickr.com
Diagram illustrating the movement of water through a plant From flickr.com
This will be considered throughout this chapter. Plants can also use hydraulics to generate enough force to split rocks and buckle sidewalks. These cells form long thin tubes that run from the roots up the stems to the leaves. Root pressure and transpirational pull enables the upward movement of water and minerals in plants. Similarly the movement takes place from warmer soil regions to cooler soil region (fig. Plants can use the water potential to passively move water, reducing energy demands on the plant.
Similarly the movement takes place from warmer soil regions to cooler soil region (fig.
These columns of water continue to flow upward because. In the absence of transpiration, osmotic forces dominate the movement of. Turgor pressure helps to keep the plant erect and is accomplished when the plasma membrane pushes against the cell wall. Plant stems have some very special cells called xylem. These take the form of two types of vascular tissue. Plants can also use hydraulics to generate enough force to split rocks and buckle sidewalks.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Root pressure and transpirational pull enables the upward movement of water and minerals in plants. These columns of water continue to flow upward because. In dry soils some water movement takes place in the vapour form and such vapour movement has some practical implications in supplying water to drought resistant plants. Pressure potential also known as turgor pressure is the water in plant cells. The second, the phloem, moves dissolved.

Turgor pressure helps to keep the plant erect and is accomplished when the plasma membrane pushes against the cell wall. The maximum speeds of purely hydraulic movements were estimated based on a mathematical analysis of water movement through a porous elastic material (skotheim and mahadevan 2005 ). Hygroscopic movements can best be observed in the elaters in bryophytes, peristome teeth in moss capsules, elaters of equisetum spores etc. Similarly the movement takes place from warmer soil regions to cooler soil region (fig. Plants have the amazing ability to move water and transport nutrients through stems, roots, and the environment around them [3].
 Source: brainly.com
Source: brainly.com
Turgor pressure helps to keep the plant erect and is accomplished when the plasma membrane pushes against the cell wall. Water is transported through a plant, from its point of absorption (the root hairs of the roots) up the xylem tissue in the stem, to the leaves of the plant, where water vapour evaporates through a process called transpiration (evaporation of water vapour from the stem and leaves) this is a passive process, as the movement. Further into the roots once inside the root hair, the water needs to be transferred to the xylem, the vascular tissue, (also known as the vascular bundles) involved in water transport through the plant. Water movement at the plant cell level a plant cell bathed in an isotonic solution. These movements are found only in dead parts of the plants which are hygroscopic in nature and result either due to loss or gain of water by them from the atmosphere.
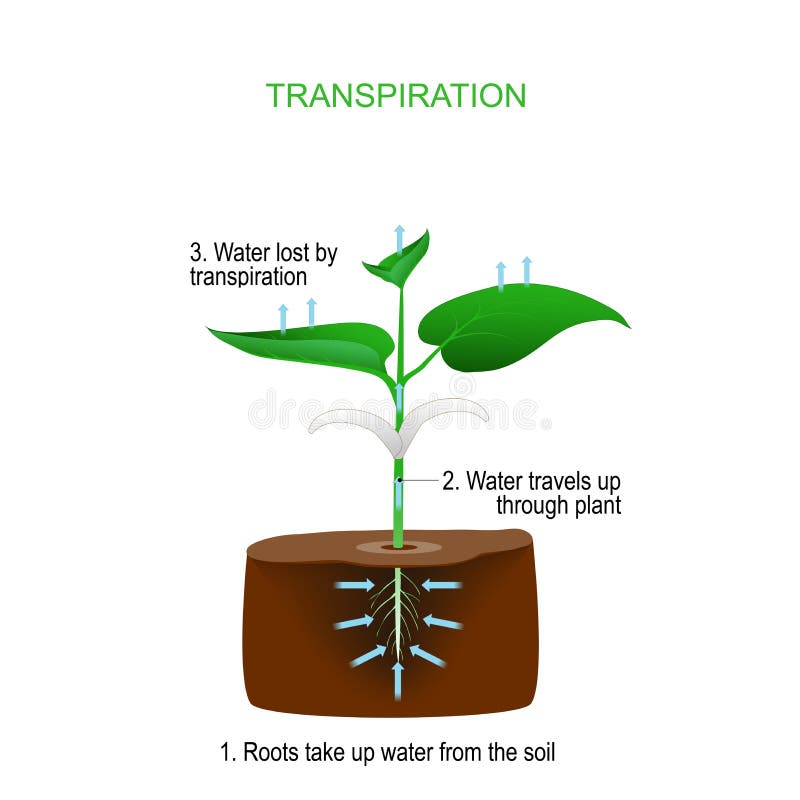 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Plants have the amazing ability to move water and transport nutrients through stems, roots, and the environment around them [3]. Upward water movement in a plant. Water will always move toward a site with lower water potential, which is a measure of the chemical free energy of water. The importance of this stress to the growth and physiology of the plant is indicated. In the absence of transpiration, osmotic forces dominate the movement of.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
These movements are found only in dead parts of the plants which are hygroscopic in nature and result either due to loss or gain of water by them from the atmosphere. Pressure potential also known as turgor pressure is the water in plant cells. The first is to produce and carry the leaves and “hold’ the leaves up to the sunlight and produce and carry buds and flowers. Similarly the movement takes place from warmer soil regions to cooler soil region (fig. The mineral ions from the soil are pushed into the root vascular tissues by diffusion and as a result, the pressure inside the xylem increases.
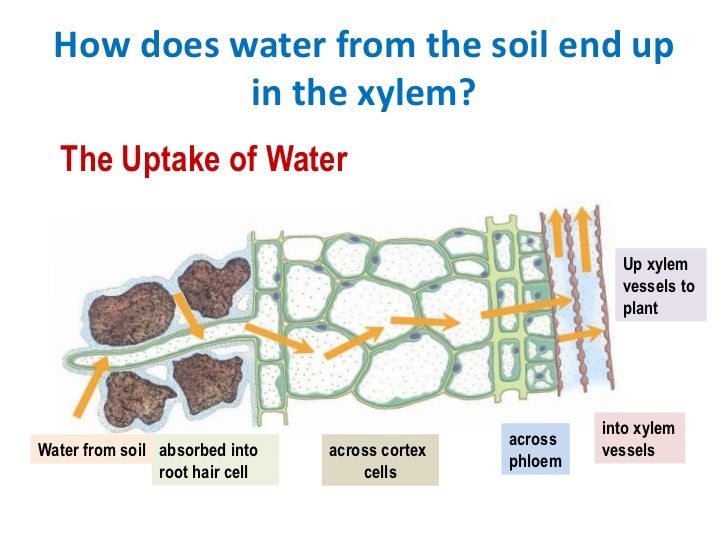 Source: mind42.com
Source: mind42.com
Plant stems have some very special cells called xylem. The soil is the source of water and minerals to be used for a variety of functions, while the atmosphere provides carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The transport path in a plant, water moves via osmosis across the selectively permeable barrier formed by the plasma membrane of the cells. The movement takes place from moist soil having high vapour pressure to a dry soil (low vapour pressure). Will experience a net loss of water.
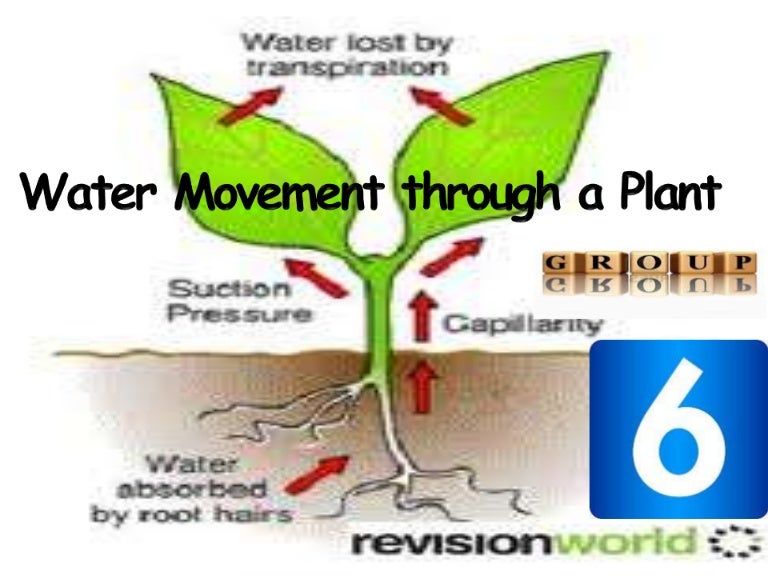 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
There are three key processes involved when water is transported in plants: This positive pressure is known as root. Click here to view a video that explains the movement of water up the stem and across the leaf. Plants can also use hydraulics to generate enough force to split rocks and buckle sidewalks. Turgor pressure helps to keep the plant erect and is accomplished when the plasma membrane pushes against the cell wall.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Why do plants need water? Plants can use the water potential to passively move water, reducing energy demands on the plant. The transport path in a plant, water moves via osmosis across the selectively permeable barrier formed by the plasma membrane of the cells. The root system takes up water and minerals from the soil, while the shoot system, consisting of leaves and. This positive pressure is known as root.
 Source: biologychamps.com
Plants are phenomenal hydraulic engineers. All three processes are important for the plant. Upward water movement in a plant. This positive pressure is known as root. The resulting flow of water through the plant gives rise to a water stress in the tissues which is explicable with reference to a simple model.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Pressure potential also known as turgor pressure is the water in plant cells. Plants have the amazing ability to move water and transport nutrients through stems, roots, and the environment around them [3]. Water is transported through a plant, from its point of absorption (the root hairs of the roots) up the xylem tissue in the stem, to the leaves of the plant, where water vapour evaporates through a process called transpiration (evaporation of water vapour from the stem and leaves) this is a passive process, as the movement. Why do plants need water? The water state of a plant is controlled by relative rates of loss and absorption, moreover it depends on the ability to adjust and keep an ad equate water status.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Osmosis plays a central role in the movement of water between cells and various compartments within plants. Cohesion is the attraction of one like molecule to another. Plant stems have two major functions. The movement takes place from moist soil having high vapour pressure to a dry soil (low vapour pressure). The movement of water from the roots to the leaves is a critical function in a plant’s life.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Their job is to carry water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Plants need water to maintain turgor pressure. These columns of water continue to flow upward because. A plant cell bathed in hyperosmotic solution. The movement of water from the roots to the leaves is a critical function in a plant’s life.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The importance of this stress to the growth and physiology of the plant is indicated. Plants are phenomenal hydraulic engineers. In dry soils some water movement takes place in the vapour form and such vapour movement has some practical implications in supplying water to drought resistant plants. This positive pressure is known as root. Water in the soil spaces is taken into the root hairs by the process of osmosis, there being a higher water concentration outside than within the root hair cells.
 Source: wickingbeds.com.au
Source: wickingbeds.com.au
In the absence of transpiration, osmotic forces dominate the movement of. This positive pressure is known as root. The movement takes place from moist soil having high vapour pressure to a dry soil (low vapour pressure). The resulting flow of water through the plant gives rise to a water stress in the tissues which is explicable with reference to a simple model. Structures of the plant tissue like xylem and phloem facilitate this movement.
 Source: biologuy.blogspot.com
Source: biologuy.blogspot.com
The transport path in a plant, water moves via osmosis across the selectively permeable barrier formed by the plasma membrane of the cells. The maximum speeds of purely hydraulic movements were estimated based on a mathematical analysis of water movement through a porous elastic material (skotheim and mahadevan 2005 ). Water in the soil spaces is taken into the root hairs by the process of osmosis, there being a higher water concentration outside than within the root hair cells. This will be considered throughout this chapter. In the absence of transpiration, osmotic forces dominate the movement of.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Water and solute movement in plants. This will be considered throughout this chapter. The root system takes up water and minerals from the soil, while the shoot system, consisting of leaves and. Plant stems have some very special cells called xylem. Hygroscopic movements can best be observed in the elaters in bryophytes, peristome teeth in moss capsules, elaters of equisetum spores etc.
 Source: flickr.com
Source: flickr.com
The root system takes up water and minerals from the soil, while the shoot system, consisting of leaves and. All three processes are important for the plant. These movements are found only in dead parts of the plants which are hygroscopic in nature and result either due to loss or gain of water by them from the atmosphere. The soil is the source of water and minerals to be used for a variety of functions, while the atmosphere provides carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Water will always move toward a site with lower water potential, which is a measure of the chemical free energy of water.
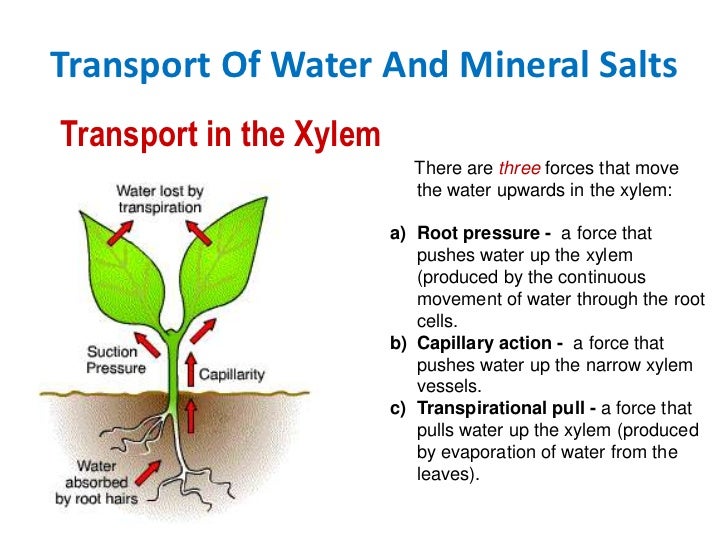 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The importance of this stress to the growth and physiology of the plant is indicated. The movement of water in plants. Plants don’t have a heart to pump liquids around their bodies, so they rely on physical forces to move liquid up to the highest leaf. Similarly the movement takes place from warmer soil regions to cooler soil region (fig. These take the form of two types of vascular tissue.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title water movement in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






