Your Water transport in plants images are available. Water transport in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Water transport in plants files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for water transport in plants images information linked to the water transport in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
Water Transport In Plants. In order to maintain the balance of necessary elements in the plants’ bodies, they need a transportation system. Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. Both approaches (1) and (2) are used in this investigation. Large variations in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels are recorded in leaf stomatal densities, and may have had profound impacts on the water conservation strategies of.
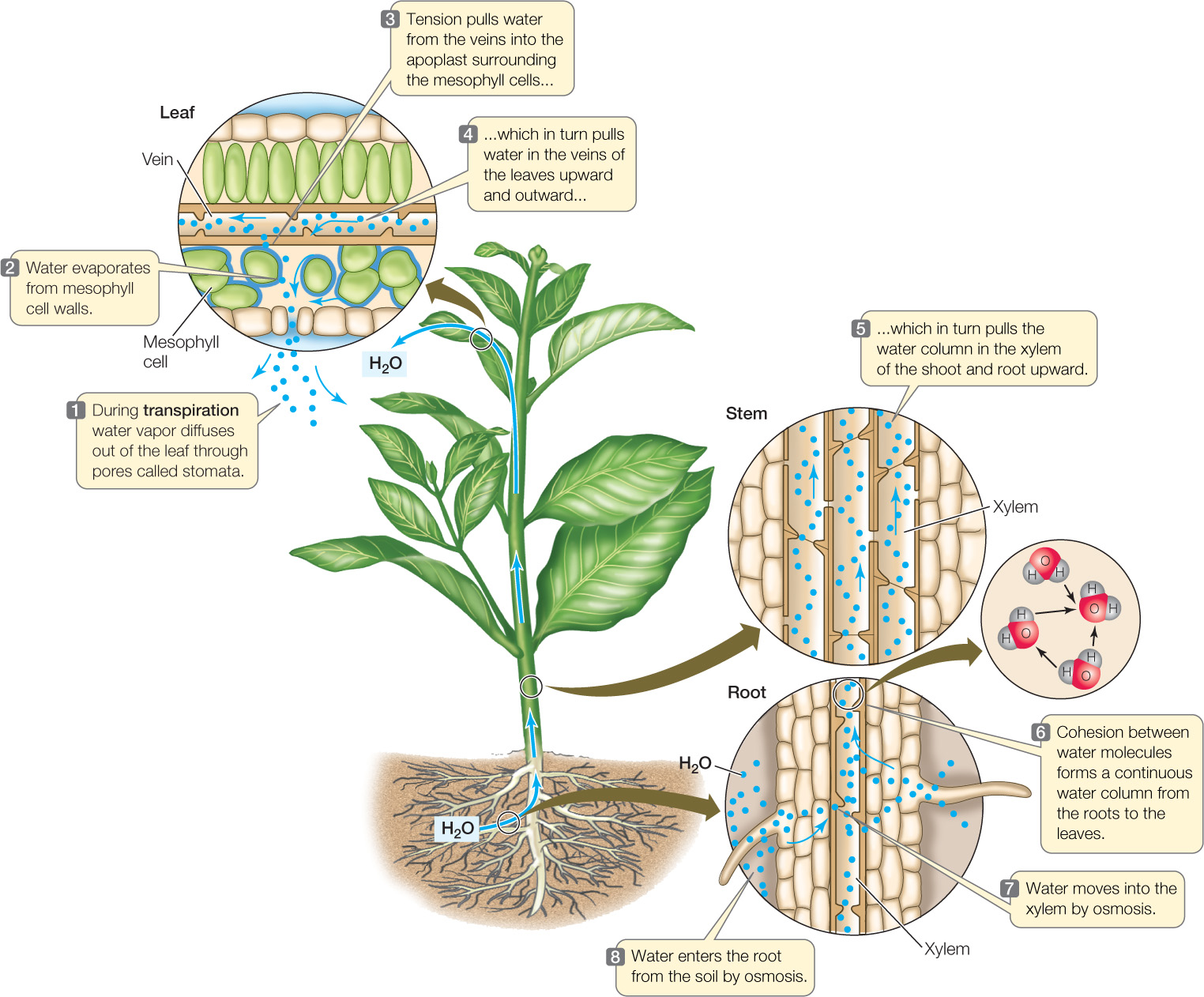 hillis2e_ch25 From macmillanhighered.com
hillis2e_ch25 From macmillanhighered.com
During imbibitions, the water molecules get. Materials need to be transported between the root system and the shoot system transport within plants water and minerals absorbed by roots are drawn upward in the xylem to the shoots sugar produced by photosynthesis is exported from leaves to other organs via the. Plants have a specific mechanism for distributing water and nutrients throughout their bodies. Plants have different tissues that carry water, nutrients and minerals from one part to another. Plants and animals have a system of transporting substances throughout their body. Transport of water and minerals in plants water is good for plants:
Water moves into the root from the soil and then steady it moves into the root xylem, creating a column of water, which is progressively pushed upwards.
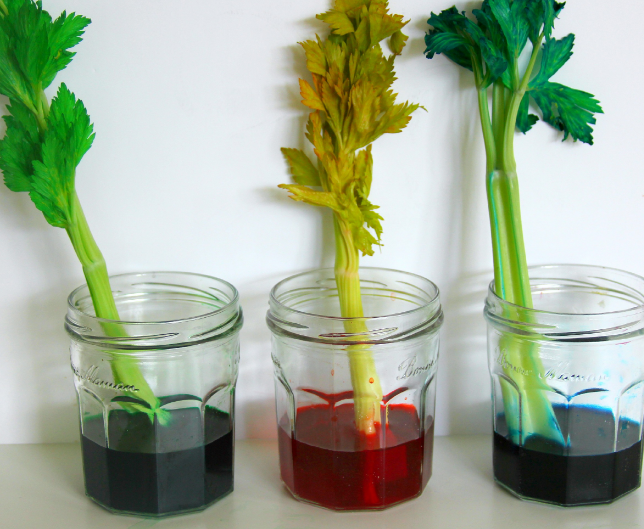
In higher plants (vascular plants) xylem conducts the water whereas the phloem conducts the. In order to maintain the balance of necessary elements in the plants’ bodies, they need a transportation system. Plants have 3 ways of transport: In higher plants (vascular plants) xylem conducts the water whereas the phloem conducts the. Plants use capillary suction to transport water from the roots to the leaves without using metabolic energy, and the xylem conduits themselves are cheap to. A thin cross section of the stem, viewed under a compound microscope, will reveal dye attached to the walls of certain cells thus marking the path taken by the solution.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Water transport, perception, and response in plants. Accepted in revised form 5 april 1996 key words: The xylem tissue looks like open tubes similar to a garden hose, through which the water can move easily over longer distances. These processes help the plants keep the balance of water and nutrients equal so that the photosynthesis process happens smoothly. A thin cross section of the stem, viewed under a compound microscope, will reveal dye attached to the walls of certain cells thus marking the path taken by the solution.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Water taken up by the roots of a plant is transported through a plant to the leaves where some of it passes into the air. Plants have a specific mechanism for distributing water and nutrients throughout their bodies. Accepted in revised form 5 april 1996 key words: Transportation refers to the conduction of water and minerals throughout the plant�s body. Transpiration is the movement of water through a plant and evaporation from leaves, stems and flowers.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
The xylem tubes are similar to your blood vessels. © 2016 paul billiet odws phloem made of living cells (sieve tubes and their companion cells) uses active transport to load the phloem. #long distance transport of water#how do plants absorb water#water movement up a plant#biology class 11#ch 11#l 3# Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. The solid particles which imbibe water or any other liquid are called imbibate.
 Source: pinterest.co.uk
Source: pinterest.co.uk
Several types of f g and f Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis. The xylem tissue looks like open tubes similar to a garden hose, through which the water can move easily over longer distances. Large variations in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels are recorded in leaf stomatal densities, and may have had profound impacts on the water conservation strategies of. In higher plants (vascular plants) xylem conducts the water whereas the phloem conducts the.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Water transport, perception, and response in plants. Transpiration is the movement of water through a plant and evaporation from leaves, stems and flowers. In plants, water is the medium of transport. Transport in plants xylem moves water from roots to the leaves, and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. © 2016 paul billiet odws phloem made of living cells (sieve tubes and their companion cells) uses active transport to load the phloem.
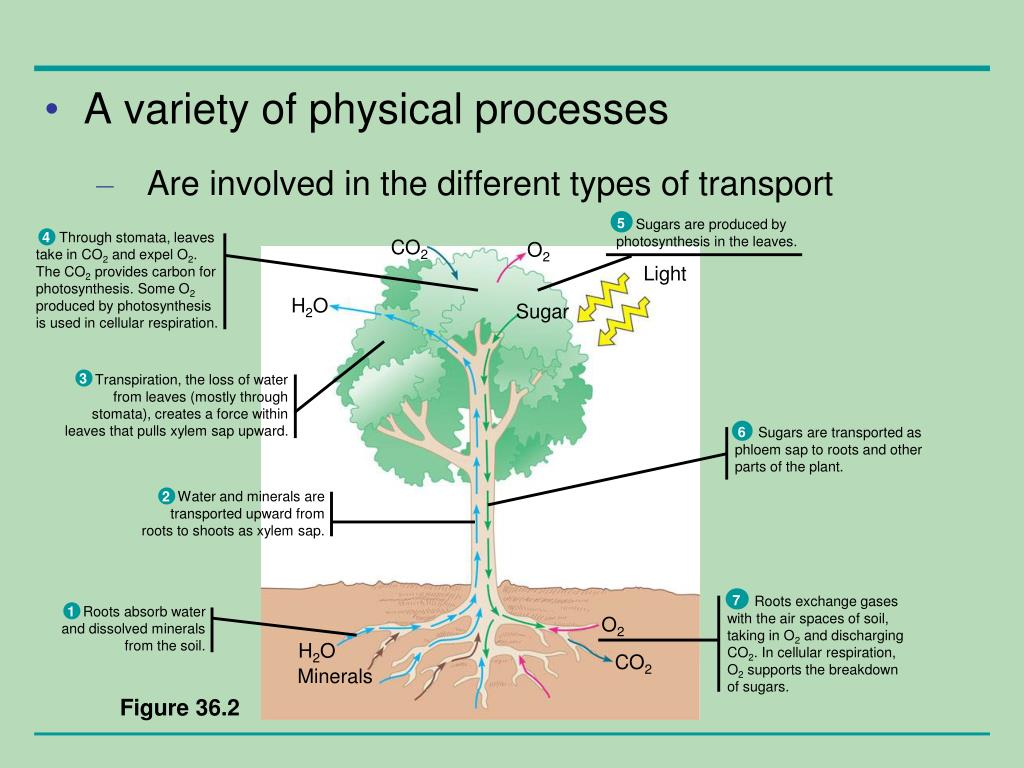 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Water through their roots is continuously absorbed by the plants. Water and inorganic nutrient uptake are covered in sections 2 and 3. The xylem tubes are similar to your blood vessels. Water through their roots is continuously absorbed by the plants. A thin cross section of the stem, viewed under a compound microscope, will reveal dye attached to the walls of certain cells thus marking the path taken by the solution.
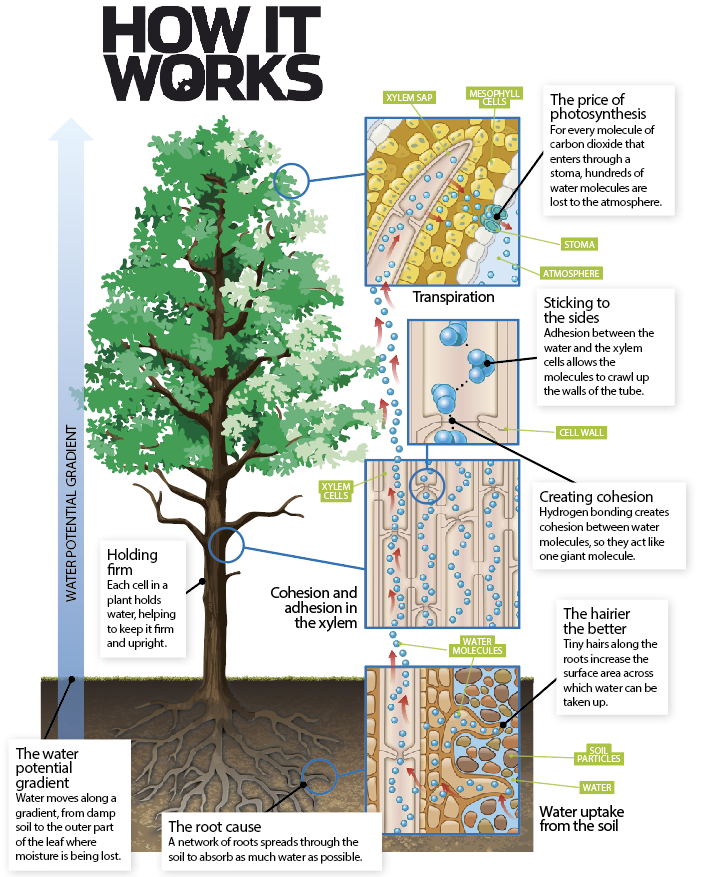 Source: howitworksdaily.com
Source: howitworksdaily.com
In higher plants (vascular plants) xylem conducts the water whereas the phloem conducts the. Without sufficient water, plants cells become flaccid, and the plant as a whole goes limp and wilts. During imbibitions, the water molecules get. Both approaches (1) and (2) are used in this investigation. From the roots, the water moves through various cell layers into the part of the plant, called xylem, that is specialized for water transport.
 Source: peregene.com
Source: peregene.com
Large variations in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels are recorded in leaf stomatal densities, and may have had profound impacts on the water conservation strategies of. Water from the soil enters the root hairs by moving along a water potential gradient and into the xylem through either the. These are the examples in plant systems are adsorption of after by cell wall, swelling and rupture of seed coats during germination, etc. Several types of f g and f In both, water and some nutrients are transported around the organism’s body.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Plants use capillary suction to transport water from the roots to the leaves without using metabolic energy, and the xylem conduits themselves are cheap to. Plants have different tissues that carry water, nutrients and minerals from one part to another. Accepted in revised form 5 april 1996 key words: Water from the soil enters the root hairs by moving along a water potential gradient and into the xylem through either the. Plants don’t have a heart to pump liquids around their bodies, so they rely on physical forces to move liquid up to the highest leaf.
 Source: oercommons.org
Source: oercommons.org
Sufficient water availability in the environment is critical for plant survival. Plant physiology and soil science research have contributed greatly to our understanding of how water. Two of the most important forces are cohesion and adhesion. A thin cross section of the stem, viewed under a compound microscope, will reveal dye attached to the walls of certain cells thus marking the path taken by the solution. Turgidity is developed by the process of endosmosis which helps to maintain a definite shape of leaves, stems and flowers.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Water through their roots is continuously absorbed by the plants. Plants have a specific mechanism for distributing water and nutrients throughout their bodies. Two of the most important forces are cohesion and adhesion. In order to maintain the balance of necessary elements in the plants’ bodies, they need a transportation system. A thin cross section of the stem, viewed under a compound microscope, will reveal dye attached to the walls of certain cells thus marking the path taken by the solution.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Water absorption as a result of transpiration or root pressure represents a form of passive transport, as energy is not required to transport water through the plant. Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis. Transportation refers to the conduction of water and minerals throughout the plant�s body. Transpiration is the movement of water through a plant and evaporation from leaves, stems and flowers. In plants, water is the medium of transport.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
These processes help the plants keep the balance of water and nutrients equal so that the photosynthesis process happens smoothly. Transport in plants xylem moves water from roots to the leaves, and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. In plants, water is the medium of transport. These processes help the plants keep the balance of water and nutrients equal so that the photosynthesis process happens smoothly.
![Water Transport in a Plant [PPT Powerpoint] Water Transport in a Plant [PPT Powerpoint]](https://reader011.documents.pub/reader011/slide/20190125/568137e3550346895d9f8f49/document-10.png?t=1606852641) Source: documents.pub
Source: documents.pub
This water is sent up through the stem to all parts of the plant, including the leaves. These processes help the plants keep the balance of water and nutrients equal so that the photosynthesis process happens smoothly. Water moves through the xylem vessels of a plant in a continuous transpiration stream. The phloem (tissue) transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves (where they are synthesized) to other parts of the plant. In order to maintain the balance of necessary elements in the plants’ bodies, they need a transportation system.
 Source: efcl.postech.ac.kr
Source: efcl.postech.ac.kr
The stages of the process are: Transportation refers to the conduction of water and minerals throughout the plant�s body. Θ, ratio of these functions). Water transport in plants 165 horizontally to neighboring tissue. Plants and animals have a system of transporting substances throughout their body.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The xylem tissue looks like open tubes similar to a garden hose, through which the water can move easily over longer distances. Water taken up by the roots of a plant is transported through a plant to the leaves where some of it passes into the air. Movement of water in plants. Xylem made of dead cells (xylem vessels) uses physical mechanisms to transport the fluid (the transpiration flow) transports water and mineral salts only from the root to the leaves www.skidmore.edu/academics/biology/plant_bio/. In plants, water is the medium of transport.
 Source: macmillanhighered.com
Source: macmillanhighered.com
Transpiration is the movement of water through a plant and evaporation from leaves, stems and flowers. Two of the most important forces are cohesion and adhesion. In both, water and some nutrients are transported around the organism’s body. The phloem (tissue) transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves (where they are synthesized) to other parts of the plant. Sufficient water availability in the environment is critical for plant survival.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Accepted in revised form 5 april 1996 key words: Movement of water in plants. Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis. This water is sent up through the stem to all parts of the plant, including the leaves. Both approaches (1) and (2) are used in this investigation.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title water transport in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







