Your Wetland plants adaptations images are ready in this website. Wetland plants adaptations are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Wetland plants adaptations files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for wetland plants adaptations pictures information connected with to the wetland plants adaptations keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Wetland Plants Adaptations. Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. Some adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems , shallow roots, aerenchyma (which are special air pockets inside their stems), and adventitious roots (which are special roots that sprout off their underwater stems to help the plants take in water, oxygen, and. A wetland is a harsh environment physiologically. Plant anatomy is key to understanding the evolution of plant adaptations.
 PPT Wetland Plant Adaptations PowerPoint Presentation From slideserve.com
PPT Wetland Plant Adaptations PowerPoint Presentation From slideserve.com
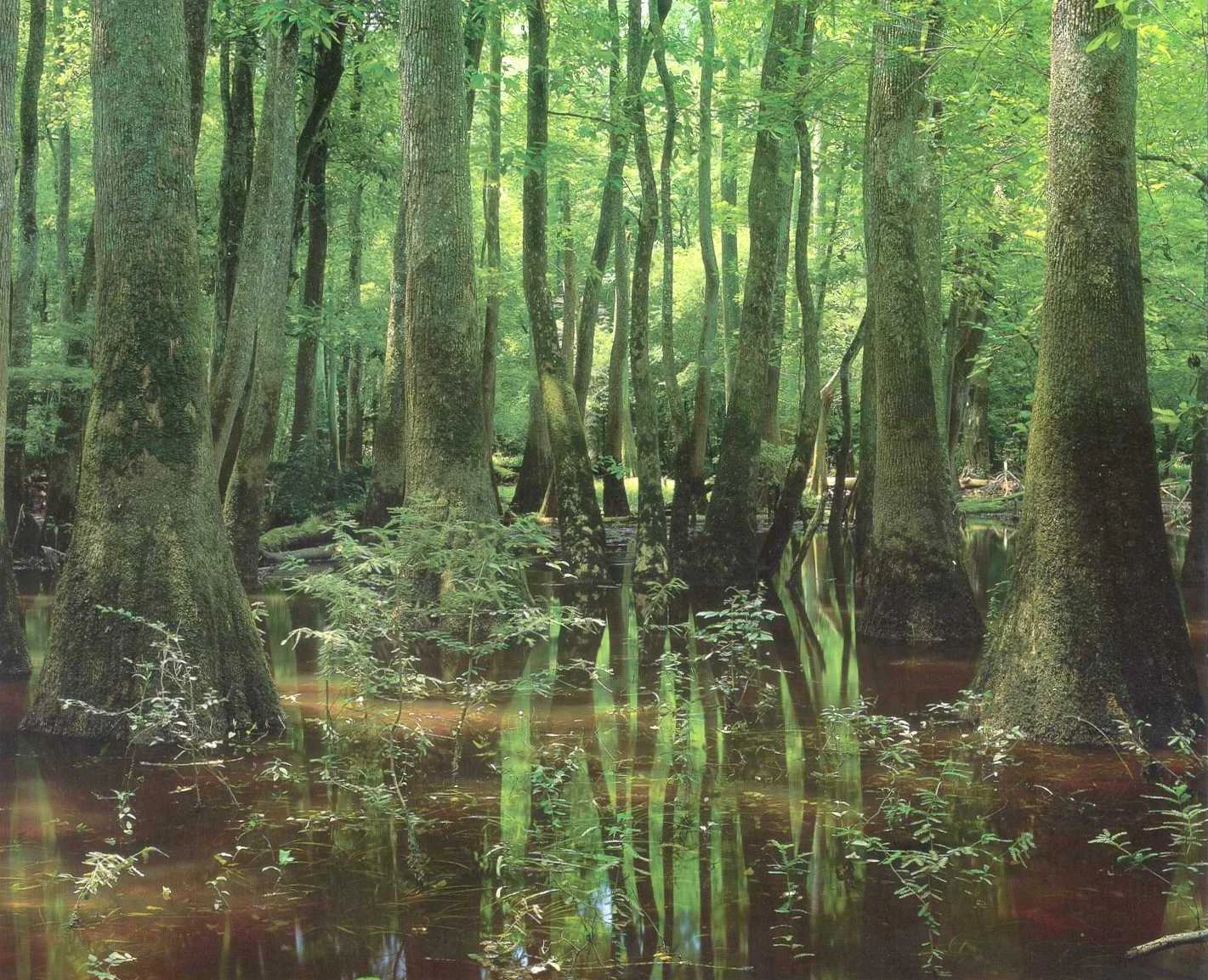
(1) hydric soils (saturated soils), (2) hydrophytic plants (plants adapted to grow in wet/hydric soils, and (3) hydrologic regime (the presence of water over a period of time. Wetland plants are adapted to take advantage of every ray of sunlight yet live a life in water. Why are cattails important to wetlands? To accommodate this, many swamp plants have hollowed stems that transport oxygen down to the roots where they are needed. They also help keep cattails upright in water because they keep the leaves fairly stiff. Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species.
Adaptations of hydrophytes may allow plants to establish and effectively eliminate competition from plants less adapted to wet conditions.
Compilation of a wetland plant indicator list a list of hydrophytes has been assembled to supplement the queensland wetland definition and help identify wetlands. 1) it has no branches. Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. S ome adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma (which are special air pockets inside their stems), and adventitious roots (which are special roots that sprout off their underwater stems to help the plants take in water, oxygen,. Compilation of a wetland plant indicator list a list of hydrophytes has been assembled to supplement the queensland wetland definition and help identify wetlands. They have ways to expose their leaves to the sun and avoid being shaded by other plants.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Plant anatomy is key to understanding the evolution of plant adaptations. Animal adaptations to wetland life (mostly assumes adaptations to aquatic life) 1.respiration 2.osmoregulation 3.feeding 4.movement 5.reproduction & life history invertebrates fish amphibians reptiles birds mammals S ome adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma (which are special air pockets inside their stems), and adventitious roots (which are special roots that sprout off their underwater stems to help the plants take in water, oxygen,. In order to do so, they have adaptations that. Some adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma and adventitious roots.
 Source: cardiffbikeshop.com
Source: cardiffbikeshop.com
Their tall stiff stems extend high above the water and other nearby plants, which helps them take in more sunlight. Some adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma and adventitious roots. (1) hydric soils (saturated soils), (2) hydrophytic plants (plants adapted to grow in wet/hydric soils, and (3) hydrologic regime (the presence of water over a period of time. Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species. These plants and the birds, mammals, fish, and insects that flourish in wetlands develop adaptations —distinct features that allow them to survive in moist conditions.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A wetland is an ecosystem that arises when inundation by water produces soils dominated by anaerobic and aerobic processes, which, in turn, forces the biota, particularly rooted plants, to adapt to flooding.: Known as aerenchyma, these channels move oxygen. What are some plant adaptations in the wetlands? If you cut a cattail leaf open, you can actually see the aerenchyma in the leaves! Aquatic plants can�t deal with periodic drying and temperatures tend to be more extreme because the water�s shallow terrestrial plants can�t deal with long floods.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The prolonged presence of water creates conditions that favor the growth of specially adapted plants (hydrophytes) and promote the development of characteristic wetland (hydric) soils. Aquatic plants can�t deal with periodic drying and temperatures tend to be more extreme because the water�s shallow terrestrial plants can�t deal with long floods. Some adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma and adventitious roots. • extended parenchyma and limited lignification ensure resilience to biomass loss. Their tall stiff stems extend high above the water and other nearby plants, which helps them take in more sunlight.
![vangilst [licensed for use only] / Wetlands vangilst [licensed for use only] / Wetlands](http://vangilst.pbworks.com/f/adaps.jpg) Source: vangilst.pbworks.com
Source: vangilst.pbworks.com
However, when plants break down the sugars produced by photosynthesis to create energy, they use oxygen. If you cut a cattail leaf open, you can actually see the aerenchyma in the leaves! Many times they live in the middle between the land, and have to deal with changing water levels and a lack of oxygen. Yes, plants do produce oxygen during photosynthesis. How do plants adapt in wetlands?
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Rushes like wīwī, raupō and sedges like kuta have spongy tissues that form air channels inside of their stems. 2 under the ramsar international wetland conservation treaty, wetlands are defined as follows: 1) it has no branches. Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. Plant anatomy is key to understanding the evolution of plant adaptations.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Plants and animals living in wetland areas have adaptations suited to the moist conditions of their surroundings. 2) leaves are reduced to spines. They also have roots that can pull in water and still get air.(fig 10.4) plants that grow in shallow water often have roots that tightly hold onto the soil so. They also help keep cattails upright in water because they keep the leaves fairly stiff. The different vegetation types in a wetland can be divided up into emergents, floating, and submerged plants.
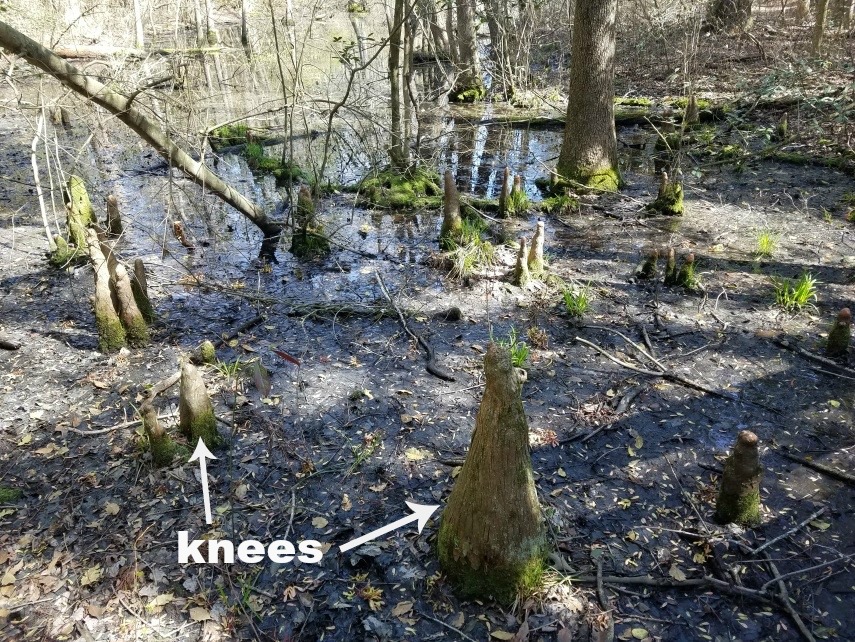 Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
Additional adaptations, like special gills, reduced activity levels, breathable skin, and modified kidneys (which filter their blood and make urine) help. This keeps the parts of the plant that are submerged happy! Discover the amazing adaptations wetland birds have developed to survive in their habitat.home learning session plans and accompanying resources, written with parents in mind, containing indoor and outdoor activities for children. Many times they live in the middle between the land, and have to deal with changing water levels and a lack of oxygen. If you cut a cattail leaf open, you can actually see the aerenchyma in the leaves!
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Wetland plants are adapted to take advantage of every ray of sunlight yet live a life in water. They also have roots that can pull in water and still get air.(fig 10.4) plants that grow in shallow water often have roots that tightly hold onto the soil so. Wetland plants have very interesting adaptations too! Cattails ( typha latifolia) grow in the muddy water at the edges of ponds and lakes. Many times they live in the middle between the land, and have to deal with changing water levels and a lack of oxygen.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
This keeps the parts of the plant that are submerged happy! Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. Additional adaptations, like special gills, reduced activity levels, breathable skin, and modified kidneys (which filter their blood and make urine) help. They also help keep cattails upright in water because they keep the leaves fairly stiff. Many other herbaceous wetland plants share this same adaptation to survive in wetland environments.
 Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
They also help keep cattails upright in water because they keep the leaves fairly stiff. Many wetland plants have one or more morphological and anatomical adaptations that allow them to tolerate soil saturation and anoxia for short to long time periods, primarily by allowing more oxygen to reach the plant root system. Wetland plants are adapted to take advantage of every ray of sunlight yet live a life in water. Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. I thought plants produced oxygen.” these were my first thoughts when learning about wetland plant adaptations as i read wading right in by catherine owen koning and sharon m.
 Source: powerlisting.wikia.com
Source: powerlisting.wikia.com
Wetland habitats present challenging conditions, so some plants have adaptations that help them survive. Plants in a wetland these include cattails, water lilies, bulltongue, sedges, tamarisk, and many kinds of rush. Compilation of a wetland plant indicator list a list of hydrophytes has been assembled to supplement the queensland wetland definition and help identify wetlands. (1) hydric soils (saturated soils), (2) hydrophytic plants (plants adapted to grow in wet/hydric soils, and (3) hydrologic regime (the presence of water over a period of time. Many wetland plants have one or more morphological and anatomical adaptations that allow them to tolerate soil saturation and anoxia for short to long time periods, primarily by allowing more oxygen to reach the plant root system.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Many times they live in the middle between the land, and have to deal with changing water levels and a lack of oxygen. Wetlands are considered highly productive environments because the. Many other herbaceous wetland plants share this same adaptation to survive in wetland environments. To accommodate this, many swamp plants have hollowed stems that transport oxygen down to the roots where they are needed. Why are cattails important to wetlands?
 Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
• extended parenchyma and limited lignification ensure resilience to biomass loss. The different vegetation types in a wetland can be divided up into emergents, floating, and submerged plants. Wetland habitats present challenging conditions, so some plants have adaptations that help them survive. Yes, plants do produce oxygen during photosynthesis. These plants and the birds, mammals, fish, and insects that flourish in wetlands develop adaptations —distinct features that allow them to survive in moist conditions.
 Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
Source: wmap.blogs.delaware.gov
These plants and the birds, mammals, fish, and insects that flourish in wetlands develop adaptations —distinct features that allow them to survive in moist conditions. Plants that live in wetlands are uniquely adapted to their watery soil. Wetland plants have very interesting adaptations too! In order to do so, they have adaptations that. Plants and animals living in wetland areas have adaptations suited to the moist conditions of their surroundings.
 Source: nybg.org
Source: nybg.org
Rushes like wīwī, raupō and sedges like kuta have spongy tissues that form air channels inside of their stems. Why are cattails important to wetlands? They have ways to expose their leaves to the sun and avoid being shaded by other plants. Plants in a wetland these include cattails, water lilies, bulltongue, sedges, tamarisk, and many kinds of rush. In order to do so, they have adaptations that.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Plants in a wetland these include cattails, water lilies, bulltongue, sedges, tamarisk, and many kinds of rush. I thought plants produced oxygen.” these were my first thoughts when learning about wetland plant adaptations as i read wading right in by catherine owen koning and sharon m. They also help keep cattails upright in water because they keep the leaves fairly stiff. They also have roots that can pull in water and still get air.(fig 10.4) plants that grow in shallow water often have roots that tightly hold onto the soil so. Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Some adaptations that help the plants deal with low oxygen and changing water levels are elongated stems, shallow roots, aerenchyma and adventitious roots. • smaller conduits and scalariform perforation evolved to reduce embolism risk. Wetland plants are called hydrophytes. Wetland plants are plants that have developed special adaptations that allow them to live in the water. In hydric soils, there is no oxygen so plants must thrive in anaerobic conditions.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title wetland plants adaptations by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







