Your What is capillary action in plants images are ready in this website. What is capillary action in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the What is capillary action in plants files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for what is capillary action in plants pictures information connected with to the what is capillary action in plants interest, you have visit the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
What Is Capillary Action In Plants. In higher plants, the root system includes the root hairs that absorb water from the soil through osmosis. 6 rows capillary action is the movement of liquid along a surface of a solid caused by the attraction of. Where does capillary action occur in plants? Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant.
 Fun Chemistry Experiments! Homeschool Den From homeschoolden.com
Fun Chemistry Experiments! Homeschool Den From homeschoolden.com
Updated on january 09, 2020 capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. In fact, it often acts in opposition to gravity. It is a process through which liquids move up through a solid like a hollow tube. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. It can be defined and more easily understood as the ability of a narrow tube to draw a liquid upwards against the strong force of gravity. Capillary action definition the cohesion and adhesion forces the height water in soil is absorbed by a plant’s roots and propelled upwards to the rest of its organs with absolutely no assistance.
Plants need capillary action to move the water and nutrients they need up into their stalks or trunks.
But capillary action can only “pull” water up a small distance, after which it cannot overcome gravity. Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant. This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur. A plant uses capillary action to draw liquid into it�s system so that it can get the nutrients it needs. Plants grow roots into the moist soil and roots absorb water into the plant. Adhesion is the ability of that liquid to stick to other objects molecularly.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
This attraction is used to help force the water up from the ground and disperse it throughout the plant. The molecules of the water (the liquid) are attracted to the molecules of the inside of the stem (the solid). For plants, cohesion keeps the water molecules together. Plants and trees couldn�t thrive without capillary action. Differences in soil potential ( ) drive capillary action in soil.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
University of florida chemistry outreach program capillary action in plants estimated time: This happens because of the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension. Differences in soil potential ( ) drive capillary action in soil. Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves. For plants, cohesion keeps the water molecules together.
 Source: single-workingmom.blogspot.com
Source: single-workingmom.blogspot.com
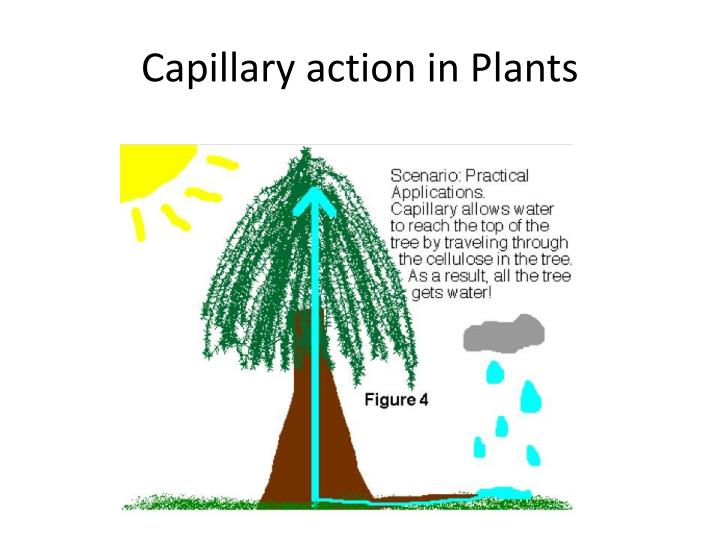
Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant. Cohesion is the ability of a liquid to stick to itself molecularly. Capillary action is a liquid’s (e.g., water) ability to flow through substances in a series of various capillary channels or tubes. In the example of a tree and the water in the ground, the liquid is drawn to the cellulose fibers in the tree trunk, which form small capillaries known as xylem. If playback doesn�t begin shortly, try restarting your device.
 Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
Source: bioscvilla-sya.blogspot.com
Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant. The molecules of the water (the liquid) are attracted to the molecules of the inside of the stem (the solid). Add a comment +6 vote up answer by sallyj (1010) But capillary action can only pull water up a short distance, after which it cannot overcome gravity. In the example of a tree and the water in the ground, the liquid is drawn to the cellulose fibers in the tree trunk, which form small capillaries known as xylem.
 Source: homeschoolden.com
Source: homeschoolden.com
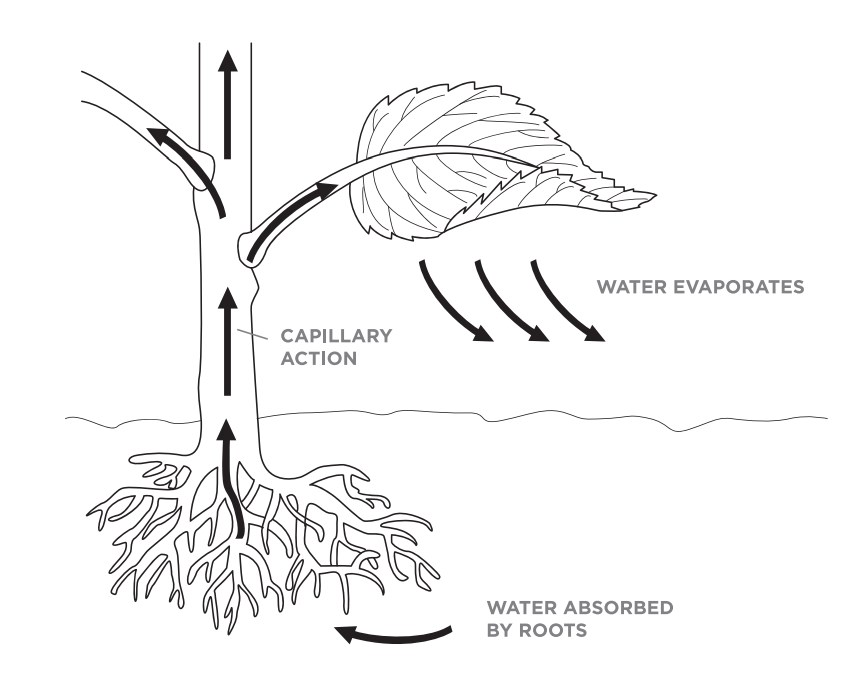
To get water up to all the branches and leaves, the forces of adhesion and cohesion go to work in the plant’s xylem to move water to the furthest leaf. Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves. In hydrology, capillary action describes the attraction of water molecules to soil particles. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. Capillary action helps bring water up into the roots.
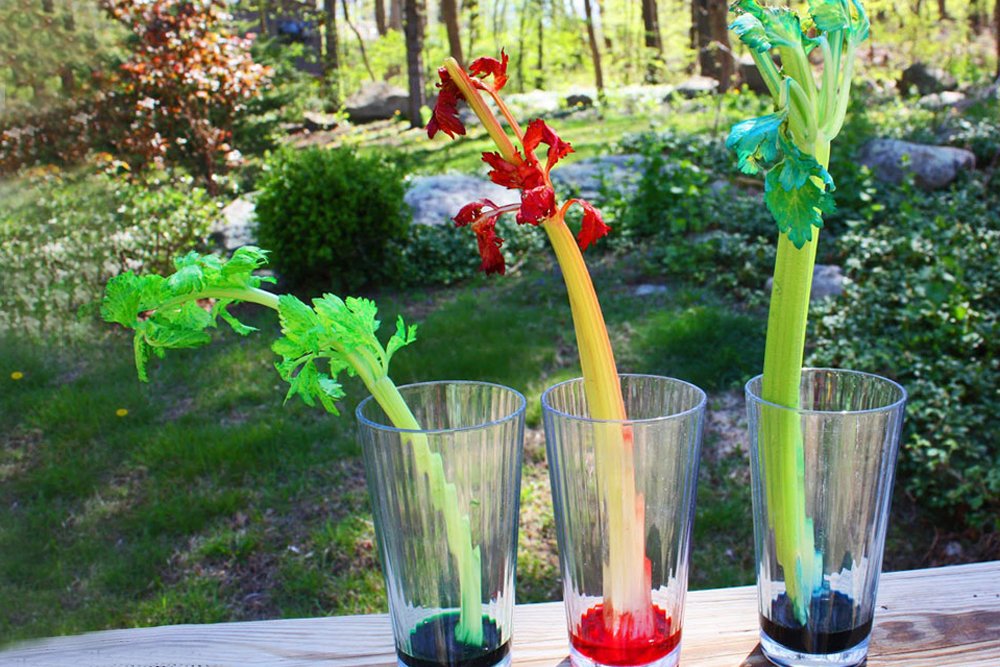 Source: scienceabc.com
Source: scienceabc.com
Capillary action is responsible for moving water through the xylem of a vascular plant. Capillary action is the name of the process when liquids, like water, move up through a solid, like a hollow tube or spongy material. Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves. Capillary action is responsible for moving water through the xylem of a vascular plant. The second factor is adhesion, the tendency of some substances to be drawn to unlike substances.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Updated on january 09, 2020 capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. These three properties are the basis for how capillary action works as a whole and are defined as follows: In hydrology, capillary action describes the attraction of water molecules to soil particles. What is capillary action in plants? The molecules of the water (the liquid) are attracted to the molecules of the inside of the stem (the solid).
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Capillary action occurs when the forces binding a liquid together (cohesion and surface tension) and the forces attracting that bound liquid to another surface (adhesion) are greater than the force. It can be defined and more easily understood as the ability of a narrow tube to draw a liquid upwards against the strong force of gravity. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. Capillary action is a liquid’s (e.g., water) ability to flow through substances in a series of various capillary channels or tubes. Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is a process through which liquids move up through a solid like a hollow tube. Capillary action is a liquid’s (e.g., water) ability to flow through substances in a series of various capillary channels or tubes. Capillary action and transpiration pull are biological concepts we discuss under the movement of water through a plant. These three properties are the basis for how capillary action works as a whole and are defined as follows: In plants, capillary action allows water to move from the roots to leaves.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A plant uses capillary action to draw liquid into it�s system so that it can get the nutrients it needs. Capillary action is all around us every day if you dip a paper towel in water, you will see it magically climb up the towel, appearing to ignore gravity. Capillary action is important for moving water (and all things dissolved in it) around. The molecules of the water (the liquid) are attracted to the molecules of the inside of the stem (the solid). This attraction is used to help force the water up from the ground and disperse it throughout the plant.
 Source: awo.aws.org
Source: awo.aws.org
This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur. Capillary action is responsible for moving water through the xylem of a vascular plant. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. It can be defined and more easily understood as the ability of a narrow tube to draw a liquid upwards against the strong force of gravity. Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant.
 Source: scienceworld.ca
Source: scienceworld.ca
Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant. Adhesion is the ability of that liquid to stick to other objects molecularly. Plants grow roots into the moist soil and roots absorb water into the plant. Capillary action is the reason why every plant or tree is still living in the world. Capillary action is also commonly known as capillarity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The key difference between capillary action and transpiration pull is that capillary action occurs due to the effect of adhesive and cohesive forces, whereas transpiration pull occurs due to evaporation. Capillary action is responsible for moving groundwater from wet areas of the soil to dry areas. Cohesion is the ability of a liquid to stick to itself molecularly. In higher plants, the root system includes the root hairs that absorb water from the soil through osmosis. Adhesion is the ability of that liquid to stick to other objects molecularly.
 Source: water.usgs.gov
Source: water.usgs.gov
Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant. Capillary action definition the cohesion and adhesion forces the height water in soil is absorbed by a plant’s roots and propelled upwards to the rest of its organs with absolutely no assistance. In hydrology, capillary action describes the attraction of water molecules to soil particles. In higher plants, the root system includes the root hairs that absorb water from the soil through osmosis.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
But capillary action can only pull water up a short distance, after which it cannot overcome gravity. Differences in soil potential ( ) drive capillary action in soil. Updated on january 09, 2020 capillary action is defined as the spontaneous flow of a liquid into a narrow tube or porous material. Capillary action is all around us every day if you dip a paper towel in water, you will see it magically climb up the towel, appearing to ignore gravity. Plants put down roots into the soil which are capable of.
 Source: emmymade.com
Source: emmymade.com
Both these terms explain the upward movement. Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves. Capillary action is sometimes called capillary motion, capillarity, or wicking. In higher plants, the root system includes the root hairs that absorb water from the soil through osmosis. Capillary action occurs when the forces binding a liquid together (cohesion and surface tension) and the forces attracting that bound liquid to another surface (adhesion) are greater than the force of gravity.
Source: rieson.blogspot.com
Water starts climbing up through the plant through tiny tubes in the stems and leaves. This movement does not require the force of gravity to occur. What is capillary action in plants? Capillary action has fascinated people so deeply, in fact, that einstein’s first paper didn’t explore his esoteric theory of cause and effect or gravity, nor did it demonstrate the particle nature of light. Plants use capillary action to bring water up the roots and stems to the rest of the plant.
 Source: trendssoul.blogspot.com
Source: trendssoul.blogspot.com
Where does capillary action occur in plants? Water can be drawn up through a plant’s vascular tissues (xylem and phloem ) via capillary action, although transpiration also plays a significant role. In the example of a tree and the water in the ground, the liquid is drawn to the cellulose fibers in the tree trunk, which form small capillaries known as xylem. To get water up to all the branches and leaves, the forces of adhesion and cohesion go to work in the plant’s xylem to move water to the furthest leaf. The molecules of the water (the liquid) are attracted to the molecules of the inside of the stem (the solid).
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what is capillary action in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







