Your What is the role of phloem in a vascular plant images are available in this site. What is the role of phloem in a vascular plant are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the What is the role of phloem in a vascular plant files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for what is the role of phloem in a vascular plant images information connected with to the what is the role of phloem in a vascular plant keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
What Is The Role Of Phloem In A Vascular Plant. What is the role of phloem in plants? Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. Other molecules along with carbohydrates are also transported with the help of phloem. One xylem and one phloem are known as a ‘vascular bundle’ and most plants have multiple vascular bundles running the length of their leaves, stems, and roots.
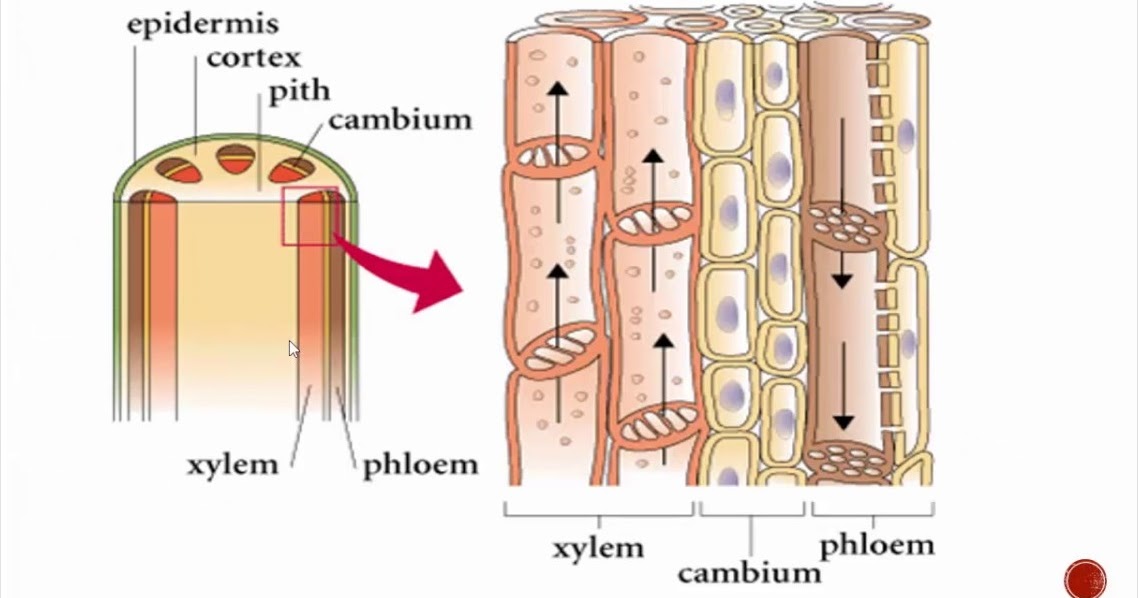 Role of Xylem Phloem, Sclerenchyma, Collenchyma Your From yourlearningpoint.com
Role of Xylem Phloem, Sclerenchyma, Collenchyma Your From yourlearningpoint.com
Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots. These vascular tissues are named as xylem and phloem. In vascular plants the phloem acts as vascular elements that transport the organic substance or photosynthate which are produced as a result of photosynthesis. The term phloem is taken from the greek word ‘phloios’ which means bark, as the phloem makes up most of the bulk of the bark of the plants. Plants such as flowers are not vascular plants because they do not make their own food.
Phloem translocates water and products of photosynthesis from source tissues to the sink regions where they are utilized or stored.
Other molecules such as proteins and mrnas are. Since phloem is the innermost layer of bark, the name comes from the ancient greek word o (phloiós), meaning bark. Xylem absorbs water from the soil with the help of roots and root hairs. Phloem and xylem are closely associated and are usually found right next to one another. Phloem (/ ˈ f l oʊ. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water.
Source: dowta.blogspot.com
The primary vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem, which are specialized, complex tissues in plants. Xylem tissue is used mostly for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves but also transports other. Since phloem is the innermost layer of bark, the name comes from the ancient greek word o (phloiós), meaning bark. Other molecules along with carbohydrates are also transported with the help of phloem. The term phloem is taken from the greek word ‘phloios’ which means bark, as the phloem makes up most of the bulk of the bark of the plants.
 Source: whadoq.blogspot.com
Source: whadoq.blogspot.com
Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant. Phloem translocates water and products of photosynthesis from source tissues to the sink regions where they are utilized or stored. Photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. Phloem is the vascular tissue in charge of transport and distribution of the organic nutrients. These tissues transport minerals, water and products to the plant which are necessary for photosynthesis.
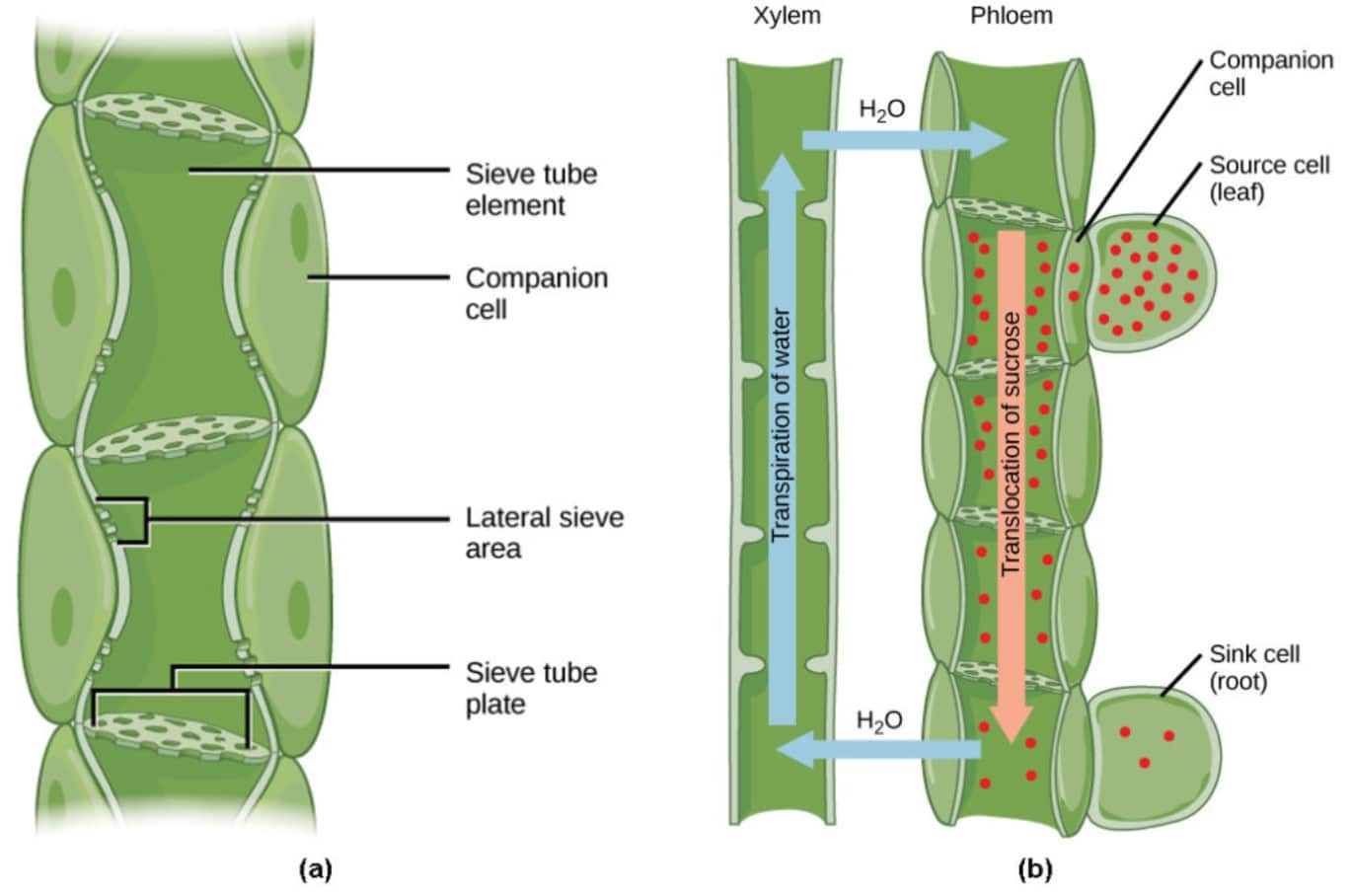 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Phloem is a vascular tissue which helps in the transportation of sugars from the source tissue( where it is formed). The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; Phloem translocates water and products of photosynthesis from source tissues to the sink regions where they are utilized or stored. These tissues transport minerals, water and products to the plant which are necessary for photosynthesis. Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Translocation is the name of this type of transport. Photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; The primary vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem, which are specialized, complex tissues in plants. Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Phloem is the biological tissue of vascular plants that transports photosynthesis, a soluble organic compound produced during photosynthesis, to various regions of the plant. These tissues transport minerals, water and products to the plant which are necessary for photosynthesis. The phloem is the organic tissue tubing that transports glucose, sucrose, and other complex food molecules from the leaves of the plants to the rest of the plant. Translocation is the name of this type of transport. Phloem translocates water and products of photosynthesis from source tissues to the sink regions where they are utilized or stored.
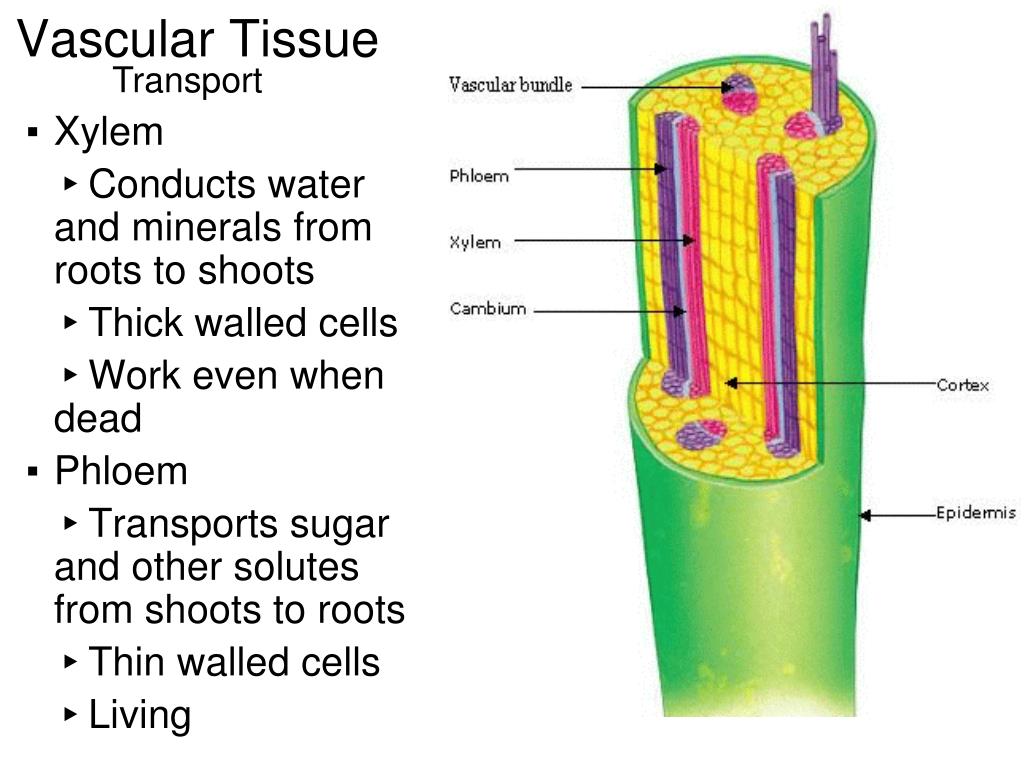 Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
Phloem is a vascular tissue which helps in the transportation of sugars from the source tissue( where it is formed). The leaves of vascular plants have stomata. Other molecules such as proteins and mrnas are. Translocation is the name of this type of transport. Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant.
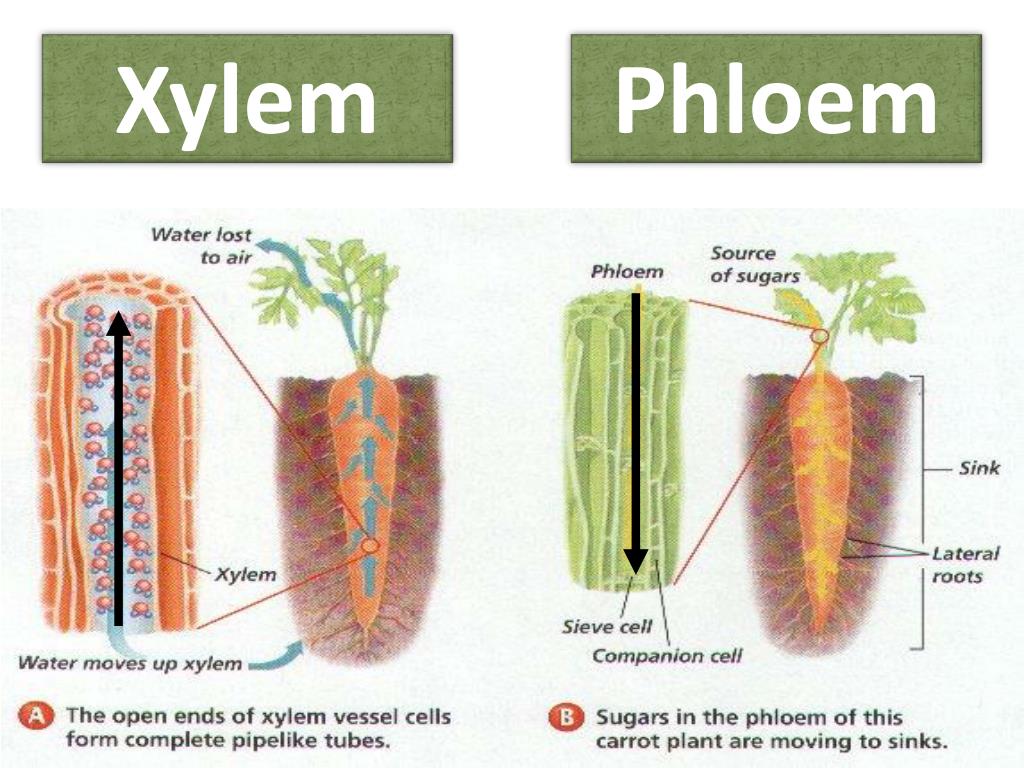 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The phloem is made up of living tissue, which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of atp to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits, flowers, buds and roots; The xylem in a plant is what goes up into the leaves and has minerals, nutrients, and water for the leaves of the plant. The phloem helps the plant to transport food to all parts of the plant. Xylem absorbs water from the soil with the help of roots and root hairs. The function of the vascular system in plants is conducting dissolved food.
 Source: yourlearningpoint.com
Source: yourlearningpoint.com
The xylem and the phloem. What is the role of phloem in plants? The carbohydrates or sugars are transported from the chloroplast of the plant to the other parts of the plant. Its main function is the transport of organic food material from leaves to stem and roots in a downward direction. One defining characteristic of the vascular plant is root, stem, and leaves.
 Source: yaclass.in
Source: yaclass.in
What is the role of phloem and the vascular plant? Phloem (/ ˈ f l oʊ. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. Other molecules such as proteins and mrnas are. Phloem is the biological tissue of vascular plants that transports photosynthesis, a soluble organic compound produced during photosynthesis, to various regions of the plant.
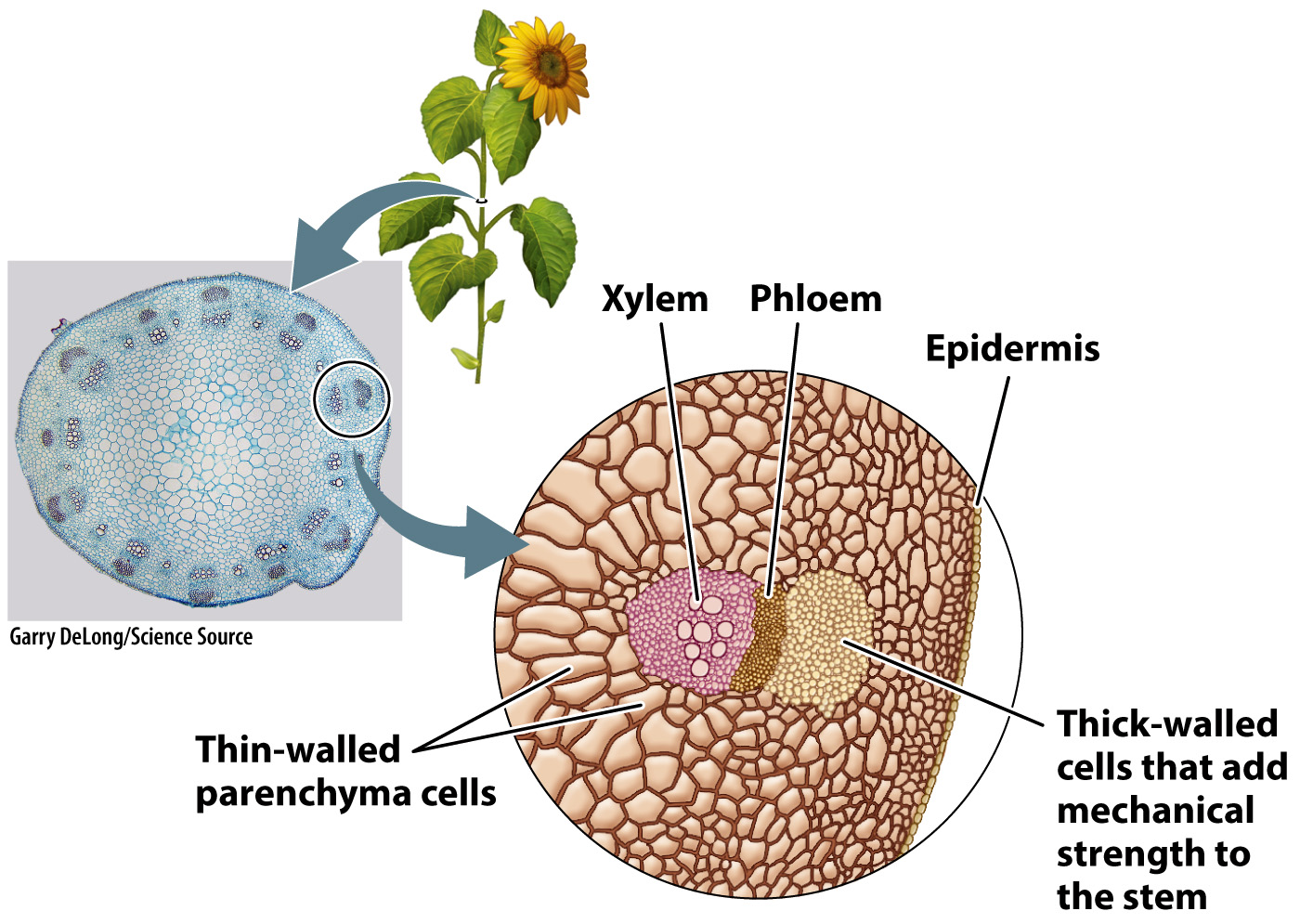 Source: macmillanhighered.com
Source: macmillanhighered.com
Plants such as flowers are not vascular plants because they do not make their own food. Photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. One defining characteristic of the vascular plant is root, stem, and leaves. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water. Their main function is to translocate the food material from one.
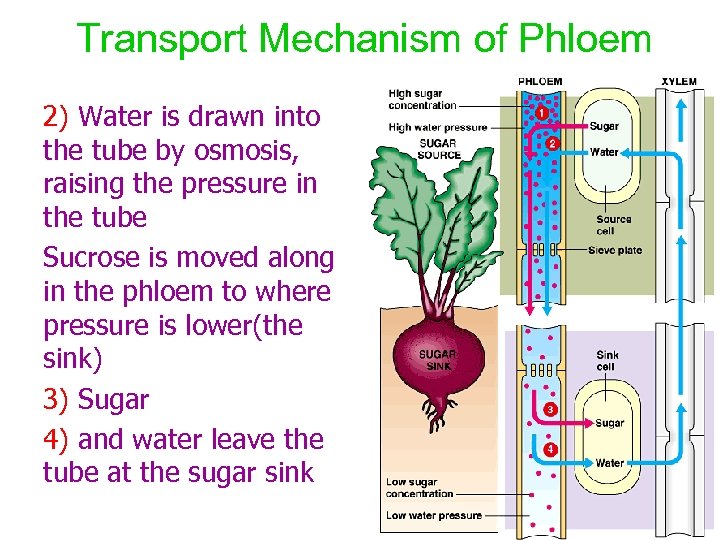 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
Phloem is the biological tissue of vascular plants that transports photosynthesis, a soluble organic compound produced during photosynthesis, to various regions of the plant. The phloem is the organic tissue tubing that transports glucose, sucrose, and other complex food molecules from the leaves of the plants to the rest of the plant. Xylem tissue is used mostly for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves but also transports other. Phloem and xylem are closely associated and are usually found right next to one another. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,.
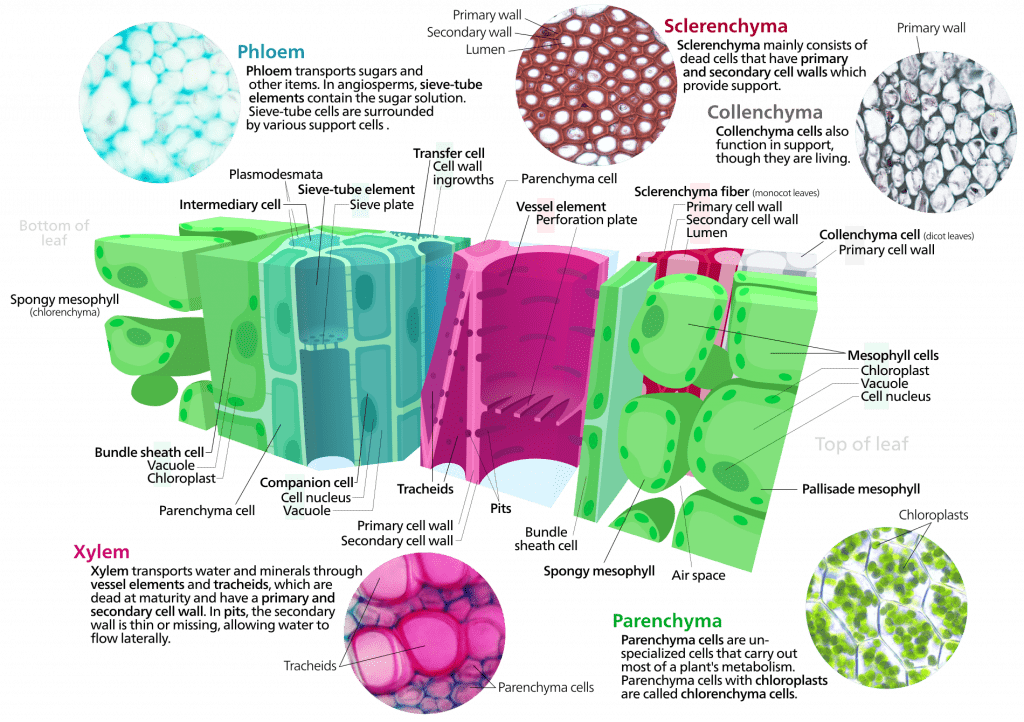 Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
The other material that makes up the vascular plant. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water. Since phloem is the innermost layer of bark, the name comes from the ancient greek word o (phloiós), meaning bark. Other molecules along with carbohydrates are also transported with the help of phloem. Phloem is a vascular tissue which helps in the transportation of sugars from the source tissue( where it is formed).
 Source: oercommons.org
Source: oercommons.org
The function of the vascular system in plants is conducting dissolved food. Phloem is the complex tissue, which acts as a transport system for soluble organic compounds within vascular plants. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. One xylem and one phloem are known as a ‘vascular bundle’ and most plants have multiple vascular bundles running the length of their leaves, stems, and roots. The xylem and the phloem.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The function of the vascular system in plants is conducting dissolved food. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. Their main function is to translocate the food material from one. The phloem helps the plant to transport food to all parts of the plant. One defining characteristic of the vascular plant is root, stem, and leaves.
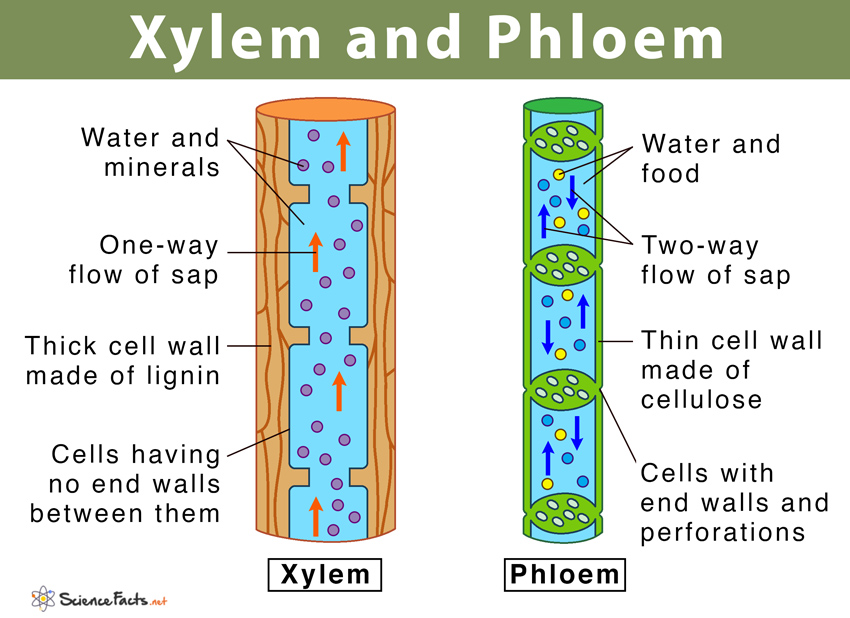 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
The phloem helps the plant to transport food to all parts of the plant. Its main function is the transport of organic food material from leaves to stem and roots in a downward direction. The vascular plants are covered with a cuticle or waxy layer that holds in water. Other molecules along with carbohydrates are also transported with the help of phloem. Xylem absorbs water from the soil with the help of roots and root hairs.
 Source: kwhatdo.blogspot.com
Source: kwhatdo.blogspot.com
The xylem and the phloem. Wang, in encyclopedia of applied plant sciences (second edition), 2017 abstract. The xylem transports water and minerals through the stem and the phloem transports the food. Combined, these studies provide evidence that the vascular phloem plays a significant role in the mediation and control of host responses during infection and as such is a site of considerable modulation by the infecting virus. In vascular plants the phloem acts as vascular elements that transport the organic substance or photosynthate which are produced as a result of photosynthesis.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
These vascular tissues are named as xylem and phloem. Since phloem is the innermost layer of bark, the name comes from the ancient greek word o (phloiós), meaning bark. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant,. The other material that makes up the vascular plant. Their main function is to translocate the food material from one.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Plants such as flowers are not vascular plants because they do not make their own food. The phloem is the organic tissue tubing that transports glucose, sucrose, and other complex food molecules from the leaves of the plants to the rest of the plant. The phloem helps the plant to transport food to all parts of the plant. The vascular tissues are xylem and phloem, and the combination of one xylem and one phloem adjacent to each other is called a vascular bundle. The primary vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem, which are specialized, complex tissues in plants.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what is the role of phloem in a vascular plant by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







