Your Xylem plant cell images are available. Xylem plant cell are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Xylem plant cell files here. Get all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for xylem plant cell pictures information related to the xylem plant cell keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
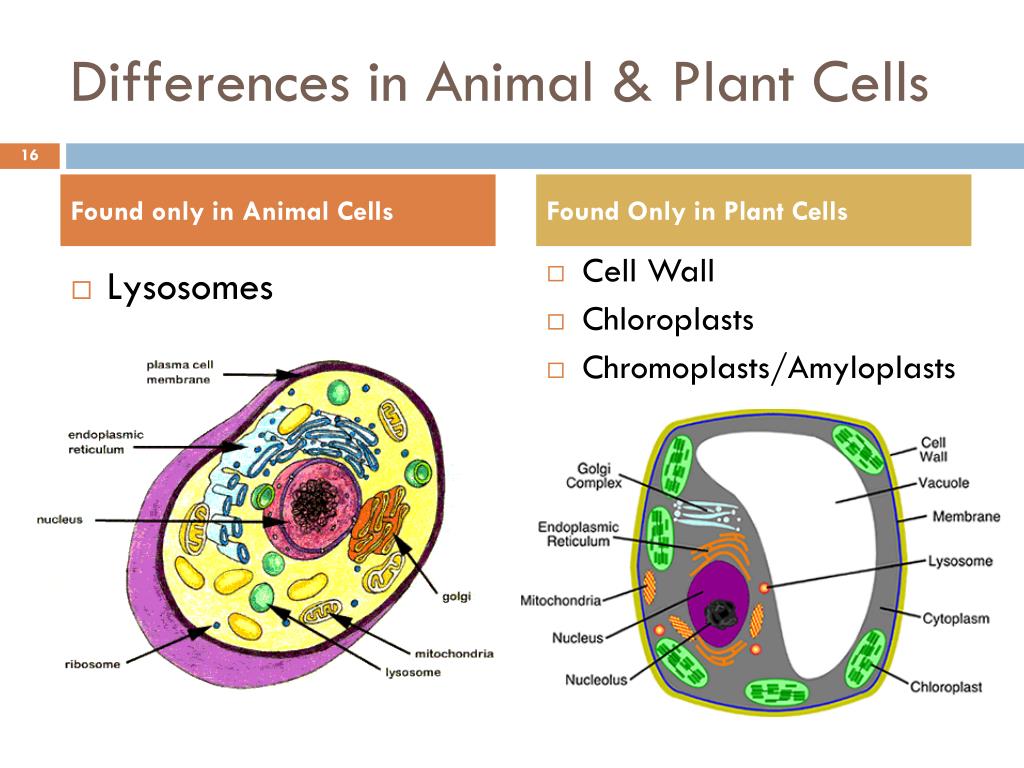
Xylem Plant Cell. The thickenings of tracheary elements of xylem are different. The separation between plants that have veins and plants that do not is one of the great divides within the plant kingdom. David furness, i chose to interpret in thread a colored scanning electron micrograph image (sem) taken by him. Phloem and xylem constitute the complex tissue in plants phloem:
 Xylem Plant Cells, Sem Photograph by Dr David Furness From fineartamerica.com
Xylem Plant Cells, Sem Photograph by Dr David Furness From fineartamerica.com
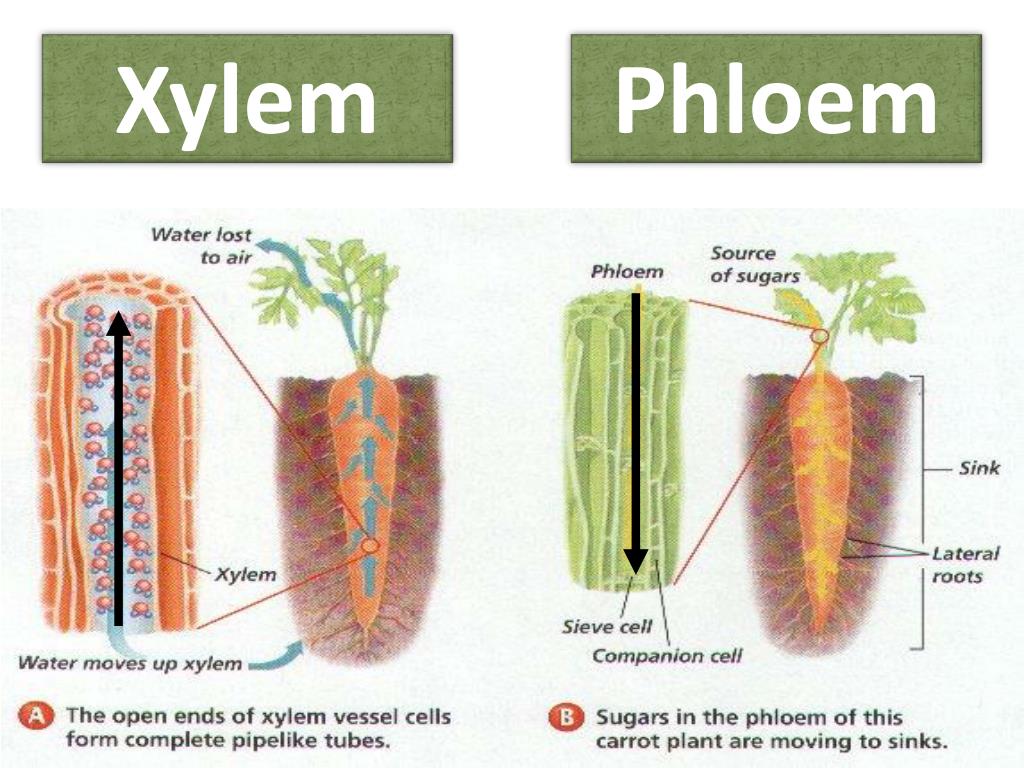
When this happens, the primary. The xylem is used for support in many plants and transporting water and nutrients to all areas of the plant. Two files of phloem strands run at the ridge of the. This allows them to form long tubes to carry water upwards for photosynthesis. Most plants have xylem and phloem and are. X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide.
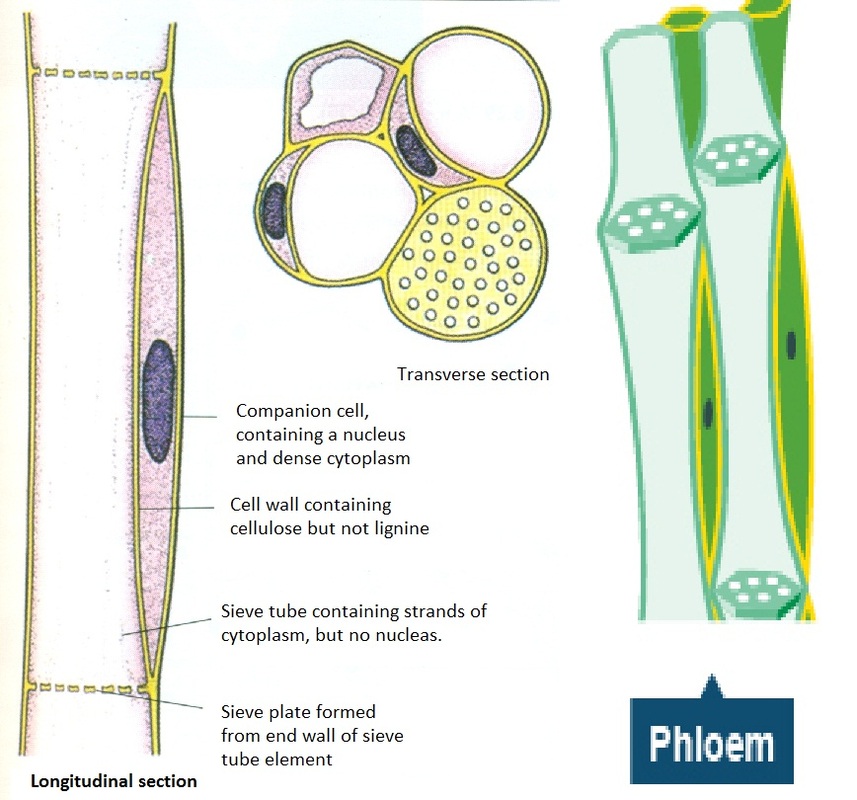
(rays are described under parenchyma cells).
X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide. Buy now >> with permission from dr. These two processes are regulated by a signalling pathway composed of a peptide ligand and its receptor; The xylem transports water and mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant. The first type is called tracheophytes, which are found in the xylem and are long and tubular. Most plants have xylem and phloem and are.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Xylem formation begins when the actively dividing cells of growing root and shoot tips (apical meristems) give rise to primary xylem. What is commonly referred to as ‘sap’ is indeed the substances that are being transported around a plant by its xylem and phloem. X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide. Phloem fibres, sieve tubes, phloem parenchyma, and companion cells are some components of phloem. Xylem can be defined as a complex tissue that is composed of four basic types of cell (tracheids, trachea, and xylem fibre and xylem parenchyma), remains in close association with phloem and has specialized functions like conduction of water and solutes, and mechanical strength.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
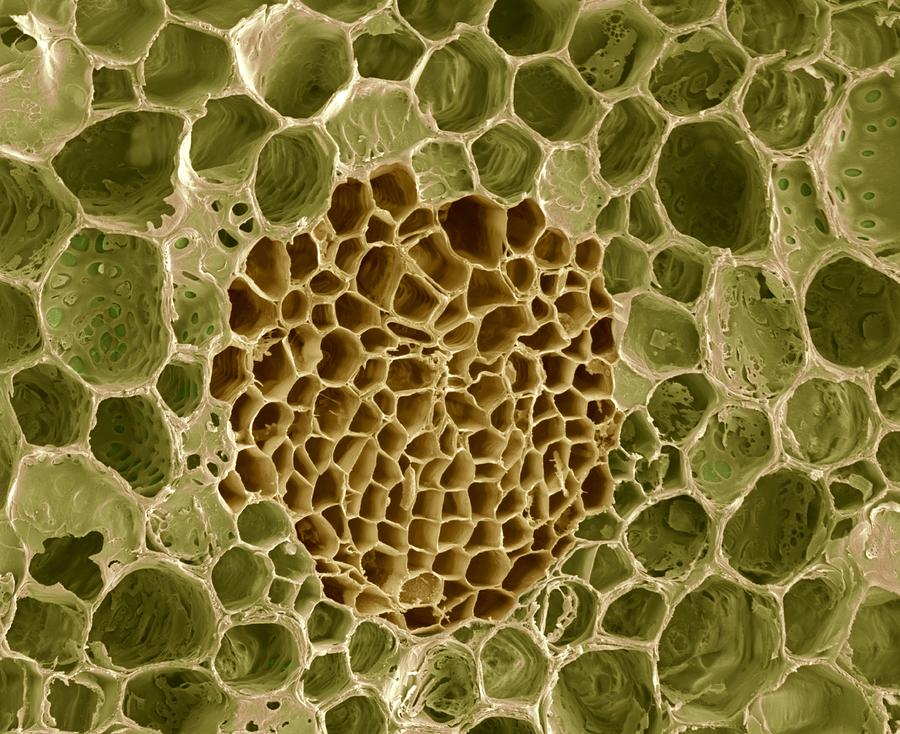
The walls of the xylem vessels are strengthened with lignin (orange), a woody substance that helps to support the plant. X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide. Xylem cells run inside stems of plants from their roots to their leaves. Xylem cells are dead, elongated, and hollow. Two files of phloem strands run at the ridge of the.
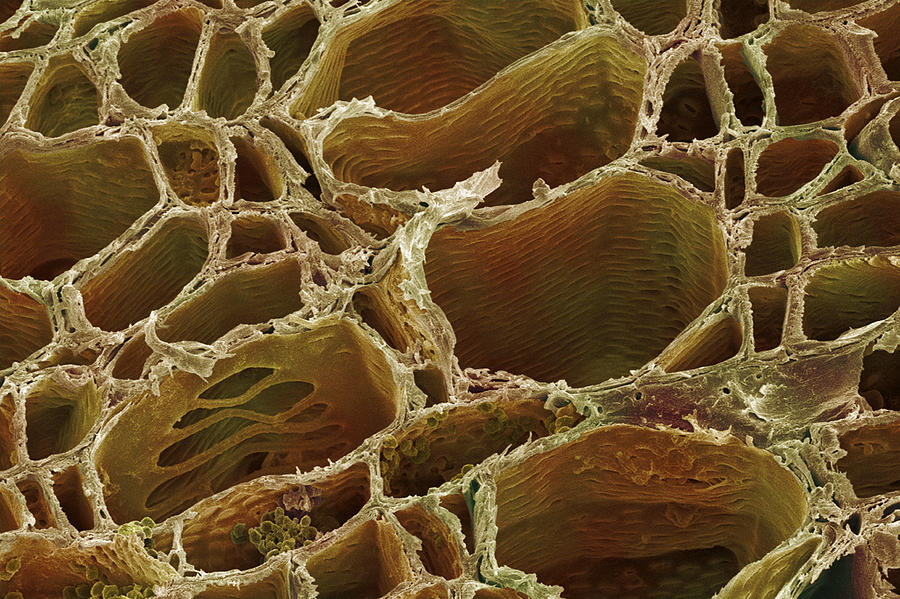 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Thick secondary cell walls on xylem cells give the cells physical strength to help support the. They occur both in primary. Xylem consists of tracheids, xylem fibres, vessels and xylem parenchyma. Complex plant tissue can be further classified as xylem and phloem. They lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous, hollow tube.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
In trees, it is found inside cambium the woody part of the tree extends through the trunk centre or to the pith and is transported to branches, foliage, etc. Xylem consists of xylem fiber cells, xylem parenchyma cells, and treachery elements. The depth and the values were. They occur both in primary. Complex plant tissue can be further classified as xylem and phloem.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Xylem is often a major portion of the plant body. They occur both in primary. Xylem cells are dead, elongated, and hollow. In woody plants, secondary xylem constitutes the major part of a mature stem or root and is formed as the plant expands in girth and builds a ring of new xylem around the original primary xylem tissues. It conducts water to various parts of the plant.
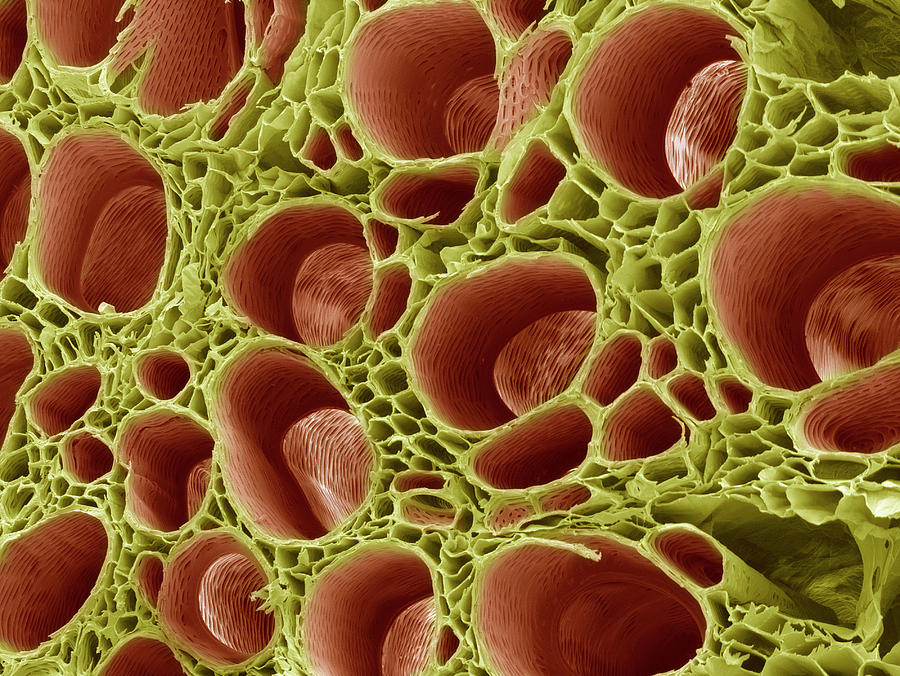 Source: pixels.com
Source: pixels.com
The xylem is a tissue which transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves. (rays are described under parenchyma cells). Plant cells multiply by cell division, a mechanism known as mitosis, which takes place within its nucleus. When this happens, the primary. Xylem consists of xylem fiber cells, xylem parenchyma cells, and treachery elements.
Source: igcse-biology-notes.blogspot.com
Tracheary element differentiation inhibitory factor (tdif) and tdif receptor (tdr). The main function of xylem is to transport water, and some soluble nutrients including minerals and inorganic ions, upwards from the roots to the rest of the plant. These cells can be both alive and dead, and there are several different types of xylem cell which can be found within the parts of a plant known collectively as xylem. Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting liquid materials throughout the plant. They become strengthened by a substance called lignin.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
This picture presents the various types of plant cells including xylem phloem sclerenchyma and collenchyma plant cell ground tissue plant cell picture diagram showing internal stem structure free vector freepik freevector education nature cartoon science stem structure stem plant tissue Wood is made of mature xylem with full secondary wall thickening. In woody plants, secondary xylem constitutes the major part of a mature stem or root and is formed as the plant expands in girth and builds a ring of new xylem around the original primary xylem tissues. Companion cells, sieve tubes, bast fibres, phloem fibres, intermediary cells and the phloem parenchyma. Coloured scanning electron micrograph (sem) of xylem cells from a plant leaf.
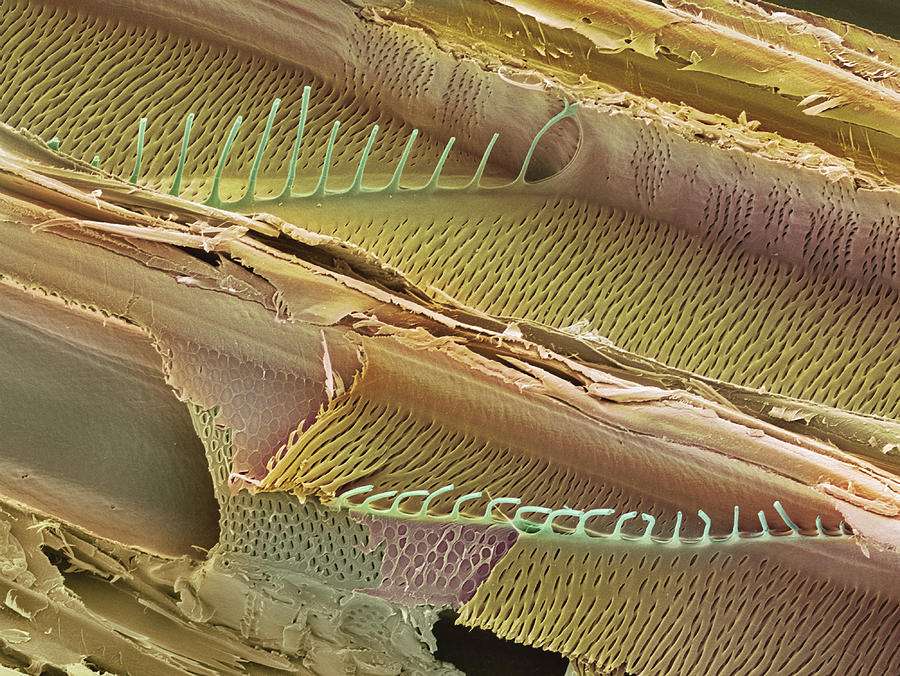 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
The xylem is mainly composed of tracheids (purple, centre). The walls of the xylem vessels are strengthened with lignin (orange), a woody substance that helps to support the plant. Xylem and phloem together constitute the conducting tissues in plants. X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide. Most plants have xylem and phloem and are.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Plant cells multiply by cell division, a mechanism known as mitosis, which takes place within its nucleus. In addition, the xylem is required for supporting the plant body vertically on land. Phloem fibres, sieve tubes, phloem parenchyma, and companion cells are some components of phloem. Phloem and xylem constitute the complex tissue in plants phloem: The depth and the values were.
 Source: pinterest.pt
Source: pinterest.pt
David furness, i chose to interpret in thread a colored scanning electron micrograph image (sem) taken by him. Xylem tissue is responsible for transporting liquid materials throughout the plant. Transports soluble mineral nutrients and water molecules from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant. Xylem cells die and their ends break down. Secondary xylem equals wood formation.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
When this happens, the primary. Xylem is often a major portion of the plant body. Xylem cells are dead, elongated, and hollow. Microscape (saqa global exhibition) price. X400 when printed 10 centimetres wide.
 Source: liberary-online.blogspot.com
Source: liberary-online.blogspot.com
Xylem is made of mainly cellulose, and it is composed of three different types of plant cells. Xylem formation begins when the actively dividing cells of growing root and shoot tips (apical meristems) give rise to primary xylem. The xylem is used for support in many plants and transporting water and nutrients to all areas of the plant. Xylem consists of tracheids, xylem fibres, vessels and xylem parenchyma. The cells that make up the xylem are adapted to their function:
 Source: diagram.oyajino.com
Source: diagram.oyajino.com
The phloem carries important sugars, organic compounds, and minerals around a plant (both directions). Xylem cells run inside stems of plants from their roots to their leaves. A xylem cell is a cell which is responsible for providing support to a plant. What is commonly referred to as ‘sap’ is indeed the substances that are being transported around a plant by its xylem and phloem. Xylem can be defined as a complex tissue that is composed of four basic types of cell (tracheids, trachea, and xylem fibre and xylem parenchyma), remains in close association with phloem and has specialized functions like conduction of water and solutes, and mechanical strength.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
They lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous, hollow tube. They are the vascular tissues that transport substances throughout the plant. Companion cells, sieve tubes, bast fibres, phloem fibres, intermediary cells and the phloem parenchyma. The xylem is responsible for keeping a plant hydrated by transporting water upward from the roots. In woody plants, secondary xylem constitutes the major part of a mature stem or root and is formed as the plant expands in girth and builds a ring of new xylem around the original primary xylem tissues.
 Source: pixels.com
Source: pixels.com
This allows them to form long tubes to carry water upwards for photosynthesis. Xylem and phloem give vascular plants their classification; In woody plants, secondary xylem constitutes the major part of a mature stem or root and is formed as the plant expands in girth and builds a ring of new xylem around the original primary xylem tissues. Xylem consists of xylem fiber cells, xylem parenchyma cells, and treachery elements. Tracheids are long tubular cells that have walls strengthened with lignin, a woody fibre that helps to support the structure of the plant.
 Source: wisegeek.com
Source: wisegeek.com
This allows them to form long tubes to carry water upwards for photosynthesis. The plant vasculature mediates transport of photosynthates from source to sink, and water and nutrients from the root to aerial tissues. Xylem consists of xylem fiber cells, xylem parenchyma cells, and treachery elements. The xylem consists of tracheary elements, xylem parenchyma cells, and xylem fiber cells. They occur both in primary.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
These cells can be both alive and dead, and there are several different types of xylem cell which can be found within the parts of a plant known collectively as xylem. The main function of xylem is to conduct water and minerals from roots to leaves. The thickenings of tracheary elements of xylem are different. This allows the xylem to withstand pressure changes as. Phloem tissue aids in the movement of food throughout the plant.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title xylem plant cell by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.